No products in the cart.
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group:B vitamins + other drugs
ATX code: A11DB/N07X
Pharmacological properties
.Pharmacodynamics
A combined multivitamin drug. The action of the drug is determined by the properties of the vitamins in its composition. Neurotropic B vitamins have a favorable effect on inflammatory and degenerative diseases of the nervous system and the musculoskeletal system.
Tiamine (vitamin B 1) – plays a key role in the processes of carbohydrate metabolism, which is critical in the metabolic processes of nervous tissue (involved in the conduct of the nerve impulse) and the Krebs cycle with subsequent participation in the synthesis of thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Pyridoxine (vitamin B6) – has a vital effect on the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates and fats, is essential for normal hematopoiesis and the functioning of the central and peripheral nervous system. It provides synaptic transmission, the processes of inhibition in the central nervous system (CNS), participates in the transport of sphingosine, which is part of the nerve sheath, participates in the synthesis of catecholamines.
The physiological function of both vitamins (B1 and B6) is to potentiate each other’s action, manifesting as a positive effect on the nervous, neuromuscular and cardiovascular systems.
Cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12) – is involved in the synthesis of nucleotides, is an important factor for normal growth, hematopoiesis and development of epithelial cells; it is necessary for the metabolism of folic acid and the synthesis of myelin.
Lidocaine has anesthetic effect at the injection site, dilates blood vessels and promotes the absorption of vitamins. The local anesthetic effect of lidocaine is due to the blockade of potential-dependent sodium channels, which prevents generation of impulses in the endings of sensitive nerves and conduct of pain impulses along the nerve fibers.
Pharmacokinetics
Thiamine
.After intramuscular administration, thiamine is rapidly absorbed from the injection site and enters the blood (484 ng/mL after 15 minutes on the first day of a 50 mg dose) and is unevenly distributed in the body with a leukocyte content of 15%, erythrocyte content of 75%, and plasma content of 10%. Because of the lack of significant stores of the vitamin in the body, it must be supplied daily. Thiamine penetrates through the blood-brain barrier and placental barrier and is found in breast milk. Thiamine is excreted by the kidneys in the alpha phase after 0.15 hours, in the beta phase – after 1 hour, in the final (terminal) phase – within 2 days. The main metabolites are: thiaminicarboxylic acid, pyramine and some unknown metabolites. Of all vitamins, thiamine is retained in the body in the smallest amounts. The adult body contains about 30 mg of thiamine: 80% as thiamine pyrophosphate, 10% as thiamine triphosphate and the rest as thiamine monophosphate.
Pyridoxine
.After intramuscular injection, pyridoxine is rapidly absorbed from the injection site and distributed in the body, acting as a coenzyme after phosphorylation of the CH2OH group in the 5th position. About 80% of the vitamin is bound to plasma proteins. Pyridoxine is distributed throughout the body, passes through the placenta, is found in breast milk. It accumulates in the liver and is oxidized to 4-pyridoxic acid, which is excreted by the kidneys a maximum of 2-5 hours after absorption.
The human body contains 40-150 mg of vitamin B6 and its daily elimination rate is about 1.7-3.6 mg with a 2.2-2.4% supplementation rate.
Cyanocobalamin
Cyanocobalamin binds to transcobalamin I and II after intramuscular administration and is transported to various body tissues. Maximum concentration after intramuscular administration is reached after 1 hour. Binding with blood plasma proteins is 90%. It penetrates through the placental barrier and is detected in breast milk. It is metabolized mainly in the liver to form adenosylcobalamin, which is the active form of cyanocobalamin. It is deposited in the liver, passes into the intestine with the bile and is absorbed back into the blood (enterohepatic recirculation phenomenon). The half-life is long, it is excreted mainly by the kidneys (7-10%) and through the intestines (50%). With decreased renal function, excretion by the kidneys is 0-7 % and through the intestine 70-100 %.
Lidocaine
In intramuscular administration, the maximum plasma concentration of lidocaine is observed 5-15 minutes after injection. Depending on the dose, about 60-80% of lidocaine is bound to plasma proteins. It is rapidly distributed (within 6-9 minutes) in organs and tissues with good perfusion, including heart, lung, liver, kidney and then in muscle and fat tissue. It penetrates through the blood-brain barrier and the placental barrier, is found in breast milk (up to 40% of the concentration in maternal plasma). It is metabolized in the liver with the participation of microsomal enzymes to form active metabolites – monoethylglycinxylide and glycinxylide, which have half-life of 2 and 10 hours, respectively. The intensity of metabolism is reduced in liver disease. It is excreted mainly as metabolites by kidneys and up to 10% unchanged.
Form of release
Form of release
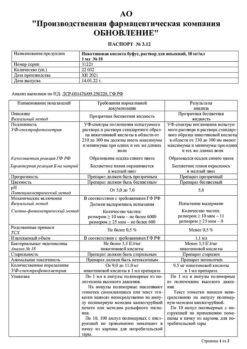
Solution for intramuscular administration.
2 ml in light-protective glass ampoules.
5 ampoules are placed in a blister pack made of polyvinyl chloride film.
1 or 2 blister packs along with instructions for use are placed in a cardboard pack.
Additional information
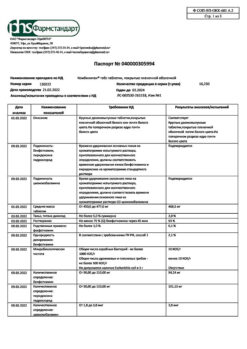
| Shelf life | 2 years. Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In the dark place at the temperature from 2 to 8 oC. Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Pharmstandard-UfaVITA, Russia |
| Medication form | solution |
| Brand | Pharmstandard-UfaVITA |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Combilipen, 2 ml 5 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.