No products in the cart.
Tranexam, 250 mg 10 pcs
€8.00 €6.67
Description
Tranexamic has a hemostatic, anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic effect.
Tranexamic acid is an antifibrinolytic agent specifically inhibiting the activation of profibrinolysin (plasminogen) and its conversion into fibrinolysin (plasmin).
It has local and systemic hemostatic action in bleeding associated with increased fibrinolysis as well as anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, anti-infective and
anti-tumor action due to suppression of formation of kinins and other active peptides involved in allergic and inflammatory reactions.
The intrinsic analgesic activity of tranexamic acid was confirmed in the experiment, as well as the supersumptive andotensive effect with respect to the analgesic activity of opiates.
Pharmacokinetics
The distribution in tissues is relatively uniform (exception is cerebrospinal fluid, where the concentration is 1/10 of the plasma concentration); penetrates through the placental and blood-brain barrier, into breast milk (about 1% of the concentration in maternal plasma).
Detected in seminal fluid, where it reduces fibrinolytic activity, but does not affect sperm migration.
The initial volume of distribution is 9-12 liters. Binding with plasma proteins (profibrinolysin) is less than 3%. In the blood about 3% is bound to protein (plasminogen).
The concentration in cerebrospinal fluid is 1/10 of plasma. Total renal clearance is equal to plasma clearance. Antifibrinolytic concentration in various tissues persists for 17 hours, in plasma – up to 7-8 hours.
A small part is metabolized. The concentration-time curve has a three-phase shape with a half-life of -2 hours in the terminal phase. Total renal clearance is equal to plasma clearance (7 l/h).
Extracted by the kidneys (main route – glomerular filtration) – more than 95% unchanged in the first 12 hours.
Two metabolites of tranexamic acid have been identified: N-acetylated and deaminated derivatives. There is a risk of cumulation of tranexamic acid in impaired renal function.
Indications
Indications
Use in short courses for bleeding or risk of bleeding due to increased fibrinolysis or fibrinogenolysis. Local fibrinolysis, which is observed in the following conditions:
Prostatectomy and bladder surgery;
Menorrhagia (heavy and prolonged menstrual bleeding);
Nosebleeds;
Conization of the cervix;
Traumatic hyphema.
Hereditary angioedema.
Bleeding after tooth extraction in patients with hemophilia.
Use in children
Information on the effectiveness, dosage regimen and safety of the drug in children is limited.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Hemostatic agents. Fibrinolysis inhibitors.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Antifibrinolytic agent. Tranexamic acid specifically inhibits the activation of profibrinolysin (plasminogen) and its conversion to fibrinolysin (plasmin). It has a local and systemic hemostatic effect in case of bleeding associated with increased fibrinolysis (platelet pathology, menorrhagia).
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption after oral administration of doses in the range of 0.5-2 g is 30-50%. The time of onset of maximum concentration when taken orally 0.5, 1 and 2 g is 3 hours, the maximum concentration is 5, 8 and 15 mcg/ml, respectively. Connection with plasma proteins (profibrinolysine) – less than 3%.
Distributed relatively evenly in tissues (with the exception of cerebrospinal fluid, where the concentration is 1/10 of the plasma concentration); penetrates the placental barrier into breast milk (about 1% of the concentration in maternal plasma). It is found in seminal fluid, where it reduces fibrinolytic activity, but does not affect sperm migration. The initial volume of distribution is 9-12 liters. Antifibrinolytic concentration in various tissues lasts 17 hours, in plasma – up to 7-8 hours.
A small part is metabolized. The area under the curve curve has a three-phase shape with a half-life in the final phase of 3 hours. The total renal clearance is equal to plasma (7 l/h). Excreted by the kidneys (the main route is glomerular filtration) – more than 95% unchanged during the first 12 hours. 2 metabolites of tranexamic acid have been identified: N-acetylated and deaminated derivatives. If renal function is impaired, there is a risk of accumulation of tranexamic acid.
Special instructions
Special instructions
The ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles or other mechanisms
There are no data on the effect of the drug on the ability to drive vehicles or use other mechanisms.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Tranexamic acid
Composition
Composition
Active substance: Tranexamic acid 250.0 mg.
Excipients (core): microcrystalline cellulose, hydroxypropylcellulose (E-463), sodium starch glycolate (type A), talc, colloidal anhydrous silica, calcium stearate (E-572).
Excipients (shell): hypromellose 2910 (E-464), titanium dioxide (E-171), talc, macrogol 6000.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Tranexamic acid penetrates the placental barrier, its concentration in umbilical cord blood is comparable to the concentration in maternal blood. Adequate and strictly controlled studies have not been conducted in pregnant women, and experience with the clinical use of tranexamic acid in this category of patients is limited. Although no teratogenic effect was found in animal studies, all aspects of reproductive toxicity have not been adequately studied. Therefore, as a precaution, it is not recommended to use tranexamic acid in the first trimester of pregnancy. Use during pregnancy is possible only if clearly necessary, if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the possible risk to the fetus.
Tranexamic acid passes into breast milk (about 1% of the concentration in maternal plasma). An antifibrinolytic effect in a breastfed infant is unlikely. The use of tranexamic acid in breastfeeding women should be done with caution, after a careful assessment of the benefit-risk ratio.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to tranexamic acid or other components of the drug.
Severe renal failure (due to the risk of drug accumulation).
Thrombosis or thromboembolic disorders in the acute phase or in history (such as deep vein thrombosis of the lower extremities, pulmonary embolism, cerebral thrombosis).
Fibrinolytic conditions associated with disseminated intravascular coagulation syndrome.
History of seizures.
Subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Color vision impairment.
Massive bleeding from the upper urinary tract (especially in hemophilia).
Precautions
With upper tract hematuria (especially in patients with hemophilia), there may be a risk of mechanical anuria as a result of clot formation in the urethra.
With a long course of treatment in patients with hereditary angioedema, it is necessary to regularly check the function of the visual organ (visual acuity, color vision, fundus, visual fields, intraocular pressure) and liver (liver function tests). Tranexamic acid should only be prescribed to patients with hereditary angioedema by a physician experienced in treating this condition.
It is not recommended to prescribe tranexamic acid to patients with irregular menstrual bleeding until the reasons for their irregularity are clarified. If, as a result of using the drug, the intensity of menstrual bleeding has not decreased sufficiently, other methods of therapy should be used.
Tranexamic acid should be administered with caution to patients receiving oral contraceptives due to the increased risk of thrombosis.
In patients with a history of thromboembolic disease and in patients with an increased incidence of thromboembolic events in the family history (patients at high risk of thrombophilia), tranexamic acid should be prescribed only when strictly medically indicated. The use of the drug in such patients should be carried out under close medical supervision.
In patients with renal failure, the concentration of tranexamic acid in the blood increases, so in such cases it is recommended to reduce the dose of the drug (see section “Dosage and Administration”).
The use of tranexamic acid in cases of increased fibrinolysis due to disseminated intravascular coagulation is not recommended.
In patients with visual impairment, the use of the drug should be discontinued. Cases of seizures have been reported in association with the use of tranexamic acid. In cardiac surgery (after coronary artery bypass grafting), the majority of cases of seizures have been reported following intravenous administration of high doses of tranexamic acid. When using the recommended lower therapeutic doses, the incidence of postoperative seizures did not exceed that in patients not taking tranexamic acid.
There is no clinical experience with the use of tranexamic acid for menorrhagia in children under 15 years of age.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Classification of the frequency of side effects: very often (>1/10 cases), often (>1/100 and 1/1000 and 1/10000 and <1/1000 cases), very rarely (<1/10000 cases), frequency unknown (cannot be estimated based on available data).
Immune system disorders: very rarely – hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis.
Visual disturbances: rarely – impaired color vision, occlusion of the retinal arteries.
Nervous system disorders: often – headache, dizziness; frequency unknown – convulsions, especially in case of incorrect dosage.
Vascular disorders: rarely – thromboembolic events; very rarely – arterial or venous thrombosis of any location.
Gastrointestinal disorders: very rarely – digestive disorders, such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, which disappear after reducing the dose.
Disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissues: rarely – allergic skin reactions.
Interaction
Interaction
Tranexamic acid prevents the development of the thrombolytic effect of fibrinolytic drugs.
Simultaneous treatment with anticoagulants is possible only under the close supervision of a doctor – a specialist in the field of hemostasis pathology.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: possible nausea, vomiting, dizziness and headache, orthostatic hypotension.
Treatment: induce vomiting, then perform gastric lavage, prescribe activated charcoal, and, if necessary, symptomatic therapy. Drink plenty of fluids and maintain adequate diuresis. Predisposed patients are at risk of thrombosis. In these cases, the need for anticoagulant therapy should be considered.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 30 °C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
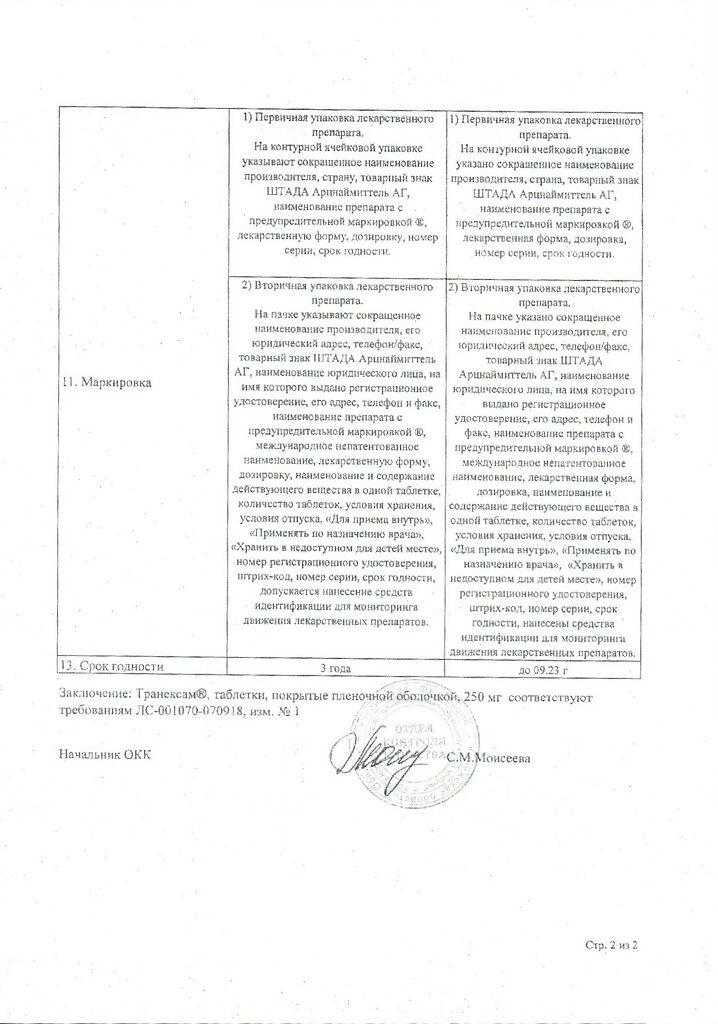
3 years. Do not use after expiration date.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Obninsk HFC, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At the temperature not more than 30 ° C. Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Obninsk HFC, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Obninsk HFC |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Tranexam, 250 mg 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.