No products in the cart.
Lidocaine, 2%, 2 ml, 10 pcs.
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Lidocaine is a local anesthetic and antiarrhythmic drug.
Antiarhythmic activity is due to inhibition of phase 4 (diastolic depolarization) in Purkinje fibers, reduction of automaticity, suppression of ectopic foci of excitation. The rate of rapid depolarization (phase 0) is not affected or slightly reduced.
It increases membrane permeability to potassium ions, accelerates the process of repolarization and shortens the action potential. It does not change the excitability of the sinus-atrial node and has little effect on conduction and myocardial contractility. When administered intravenously it works quickly and shortly (10-20 min).
The mechanism of local anesthetic effect consists in stabilization of neuronal membrane, reduction of its permeability for sodium ions which prevents generation of action potential and impulse conducting.
Possible antagonism with calcium ions. It is rapidly hydrolyzed in a weakly alkaline environment of tissues and after a short latent period is active for 60-90 minutes. In case of inflammation (tissue acidosis) anesthetic activity decreases. It is effective for all types of local anesthesia. It dilates blood vessels. It has no irritating effect on the tissues.
When using the drug in pharyngeal or nasopharyngeal surgery the pharyngeal reflex is suppressed.
The drug is good at slowing the cough reflex, which can lead to bronchopneumonia.
The effects of lidocaine in aerosol form develop within 1 min and last 5-6 min. The achieved desensitization slowly disappears within 15 min.
It is evenly distributed in the body. It penetrates through the placental barrier.
Indications
Indications
It is used for:
Lidocaine hydrochloride is used as an antiarrhythmic agent in the treatment of mono- and polytopic extrasystoles and ventricular tachycardia (including those which occur during general anesthesia, during cardiac surgery, in overdose of cardiac glycosides and others.), to stop ventricular fibrillation in the acute phase of myocardial infarction, as well as in ventricular defibrillation as a component of pharmacotherapy. In addition, it is used for prevention of ventricular extrasystoles and tachycardia of any origin.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient: lidocaine hydrochloride;
Auxiliary substances: sodium chloride, caustic soda 1 M solution to pH 5.0 – 7.0 water for injections;
Injectors.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
For local conduction anesthesia the usual dose is 5 ml to 10 ml of Lidocaine 2% solution. For anesthesia of the brachial and sacral plexus 5-10 ml of 2% solution is administered. For anesthesia of the fingers and toes, 2 ml to 3 ml of 2% solution is administered. The maximum dose of Lidocaine 2% solution is 10 ml, and this dose should not be administered again within 24 hours. In local anesthesia the drug should be injected into highly vascularized tissues with caution to avoid its entry into the bloodstream. Before administering Lidocaine in high doses, administration of barbiturates is recommended.
When used in cardiology, the single dose is administered by IV, the single dose is 1-2 mg/kg of body weight and can be up to 100 mg maximum. This dose may be repeated every 3 to 4 minutes up to a total dose of 300 mg.
Introduce by IV drip at a dose of 20-55 mcg/kg/min, but no more than 2 mg/min in isotonic solution or Ringer’s solution. IV drip infusion is used only after a jet infusion. Duration of the IV drops administration is 24-36 hours.
Injection is carried out in a dose of 2-4 mg/kg of body weight into the gluteal or deltoid muscle at intervals of 4 h to 6 h. The single dose should not exceed 200 mg.
In myocardial infarction, before transporting the patient to the hospital, Lidocaine is administered in a 4 mg/kg dose in m/m as a single preventive dose (200 to 300 mg maximum).
Interaction
Interaction
It is undesirable to combine lidocaine with the following drugs:
With beta-adrenoblockers because of increased toxic properties of lidocaine, with digitoxin because of weakened cardiotonic effect, with curare-like drugs – increased muscle relaxation.
Lidocaine should not be administered together with aymalin, amiodarone, verapamil or quinidine due to increased cardiodepressant effect.
Concomitant use of lidocaine and novocainamide may cause CNS agitation and hallucinations.
In intravenous administration of hexenal or thiopental sodium with lidocaine may cause respiratory depression.
MoA inhibitors may increase the local anesthetic effect of lidocaine. Patients taking MAO inhibitors should not administer lidocaine parenterally.
The simultaneous administration of lidocaine and polymyxin-B may increase inhibitory effects on neuromuscular transmission; therefore, in this case the patient’s respiratory function should be monitored.
The simultaneous use of lidocaine with hypnotics or sedatives may increase their CNS depressant effect. When lidocaine is administered intravenously to patients taking cimetidine, such unwanted effects as stunned state, somnolence, bradycardia, parasthesias, etc. may occur. This is associated with increased plasma levels of lidocaine, which is explained by the release of lidocaine from bonding with blood proteins, as well as a slowdown of its inactivation in the liver. If combination therapy with these drugs is necessary, the dose of lidocaine should be reduced.
Pharmaceutical interactions
When used concomitantly, the following drugs increase serum lidocaine concentrations: aminazin, cimetidine, propranolol, pethidine, bupivacaine, quinidine, disopyramide, amitriptyline, imipramine, nortriptyline.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
With caution use in patients with hepatic impairment, circulatory insufficiency, arterial hypotension, renal failure, epilepsy. In these cases a reduction in the dose of the drug is required.
In case of rapid intravenous administration, there may be a sharp decrease in blood pressure and development of collapse.
In these cases, mesaton, ephedrine and other vasoconstrictors are used. Care should be used when administering lidocaine solutions into highly vascularized tissue to avoid entrapment in the lumen (e.g., neck during thyroid surgery) (Lower doses of lidocaine are indicated in these cases).
Particular caution should be exercised when mucosal trauma is present, when there is mental retardation, and in very old and/or debilitated patients who are already receiving lidocaine-type medications for cardiac problems.
In dentistry and orthopedics, the drug should only be used with elastic blinders.
Ingestion of the aerosol or contact with the eyes should be avoided and it is important to prevent the aerosol from entering the respiratory tract (risk of aspiration). Application of the drug to the back of the throat requires special care. Remember that Lidocaine suppresses the pharyngeal reflex and inhibits the cough reflex, which can lead to aspiration, bronchopneumonia.
Pediatric use
It should be borne in mind that in children the swallowing reflex occurs much more frequently than in adults.
Lidocaine aerosol is not recommended for local anesthesia before tonsillectomy and adenotomy in children under 8 years of age.
Impact on driving and operating machinery
If the side effects after using the drug do not cause discomfort, there are no restrictions to driving and operating machinery.
If the side effects of the drug do not cause discomfort.
Contraindications
Contraindications
The aerosol is contraindicated when plaster is used as an impression material in dentistry because of the risk of aspiration.
Side effects
Side effects
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: CNS symptoms (including seizures) and cardiovascular symptoms are possible.
Treatment: in case of CNS and cardiovascular symptoms it is necessary to ensure that the airway is open, to provide fresh air, oxygen and/or artificial respiration. If convulsions occur, 50-100 mg of ditiline and/or 5-15 mg of diazepam should be administered as soon as possible; barbituric acid derivatives (sodium thiopental) may be used. Dialysis is ineffective in the acute phase of lidocaine overdose.
Atropine 0.5-1 mg IV may be administered for bradycardia, cardiac conduction disorders.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry place protected from light. |
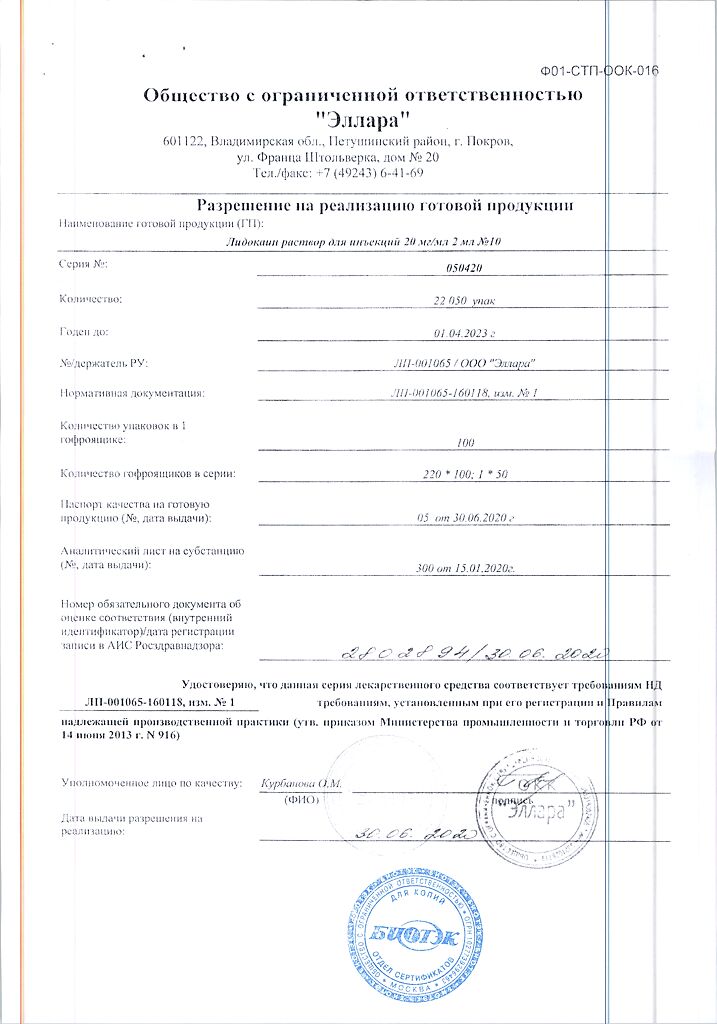
| Manufacturer | Ellara, Russia |
| Medication form | solution for injection |
| Brand | Ellara |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Lidocaine, 2%, 2 ml, 10 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.