No products in the cart.
Folic acid tablets, 1 mg 50 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Pharmacodynamics
Folic acid is a B vitamin (vitamin B9), can be synthesized by the intestinal microflora. In the body, folic acid is reduced to tetrahydrofolic acid, which is a coenzyme involved in various metabolic processes. It is necessary for normal maturation of megaloblasts and formation of normoblasts.
Stimulates erythropoiesis, participates in the synthesis of amino acids (including glycine, methionine), nucleic acids, purines, pyrimidines, choline and histidine metabolism.
Pharmacokinetics
Folic acid, prescribed as a drug, is well and completely absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, mainly in the upper 12 duodenal (even in the presence of malabsorption syndrome against tropical sprue, at the same time food folate is poorly absorbed in malabsorption syndrome). Intensively bound to plasma proteins. It penetrates through the HEB, the placenta and into breast milk. TCmax – 30-60 min.
Deposited and metabolized in liver with formation of tetrahydrofolic acid (in the presence of ascorbic acid under the action of dihydrofolate reductase).
It is excreted by the kidneys mainly as metabolites; if the dose taken significantly exceeds the daily requirement for folic acid, it is excreted unchanged.
Extracted by hemodialysis.
Indications
Indications
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Interaction
Interaction
Decreases the effect of phenytoin (requires increasing its dose).
Analgesics (long-term therapy), anticonvulsants (including phenytoin and carbamazepine), estrogens, oral contraceptives increase the need for folic acid. Antacids (including preparations of Ca2+, Al3+ and Mg2+), cholestyramine, sulfonamines (including sulfasalazine) reduce absorption of folic acid.
In order to prevent megaloblastic anemia in patients taking cytostatics (methotrexate) or antiepileptic drugs, concomitant administration of folic acid is recommended.
Pyrimethamine, triamterene, trimethoprim inhibit dihydrofolate reductase and decrease the effect of folic acid (patients taking these drugs should be given calcium folinate instead).
There is no definitive information about Zn2+ preparations: some studies show that folate inhibits absorption of Zn2+, others refute this data.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
The drug is not intended to prevent hypo- and avitaminosis in children (because of the mismatch between the daily requirement and the dosage of the drug).
For the prevention of hypovitaminosis B9 a balanced diet is most preferable. Foods rich in vitamin B9 are green vegetables (lettuce, spinach, tomatoes, carrots), fresh liver, legumes, beets, eggs, cheese, nuts, cereals.
Folic acid is not used for the treatment of B12-deficiency (pernicious), normocytic and aplastic anemia as well as for anemia refractory to therapy. In pernicious (B12-deficient) anemia folic acid, while improving hematological parameters, masks neurological complications. While pernicious anemia is not excluded, administration of folic acid in doses greater than 0.1 mg/day is not recommended (except for pregnancy and lactation).
Patients on hemodialysis need more folic acid.
During treatment, antacids should be used 2 hours after folic acid; cholestyramine should be used 4 to 6 hours before or 1 hour after folic acid administration.
Please note that antibiotics can distort (deliberately underestimate) the results of microbiological assessment of plasma and erythrocyte folic acid concentration.
When using high doses of folic acid, as well as therapy for a long period may decrease the blood concentration of vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin). Long-term use of folic acid is recommended to be combined with taking vitamin B12.
Impact on the ability to drive and work with moving mechanisms:
No effect.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Overdose
Overdose
Doses of folic acid up to 4 to 5 mg are well tolerated.
Higher doses may cause: disorders of the central nervous system (irritability and insomnia) and the gastrointestinal tract (nausea, abdominal pain, flatulence).
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
The drug is used under indications in pregnancy and during lactation. Daily intake of folic acid in early pregnancy can prevent neural tube defects of the fetus (anencephaly, spina bifida).
If the drug is started after the fourth week of pregnancy, folic acid is not effective in preventing neural tube defects.
Additional information
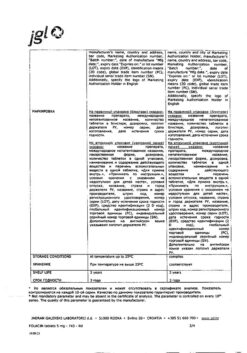
| Conditions of storage | In a place protected from light and moisture, at a temperature not exceeding 25ºC. |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Borisov Medical Preparations Plant, Belarus |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Borisov Medical Preparations Plant |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Folic acid tablets, 1 mg 50 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.