No products in the cart.
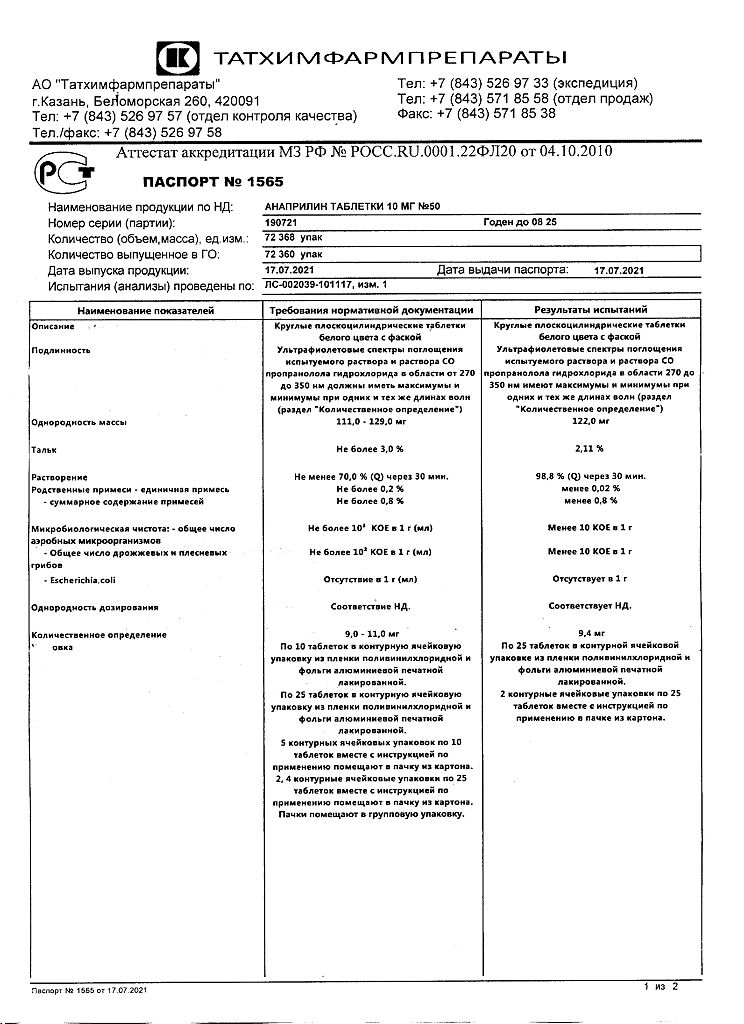
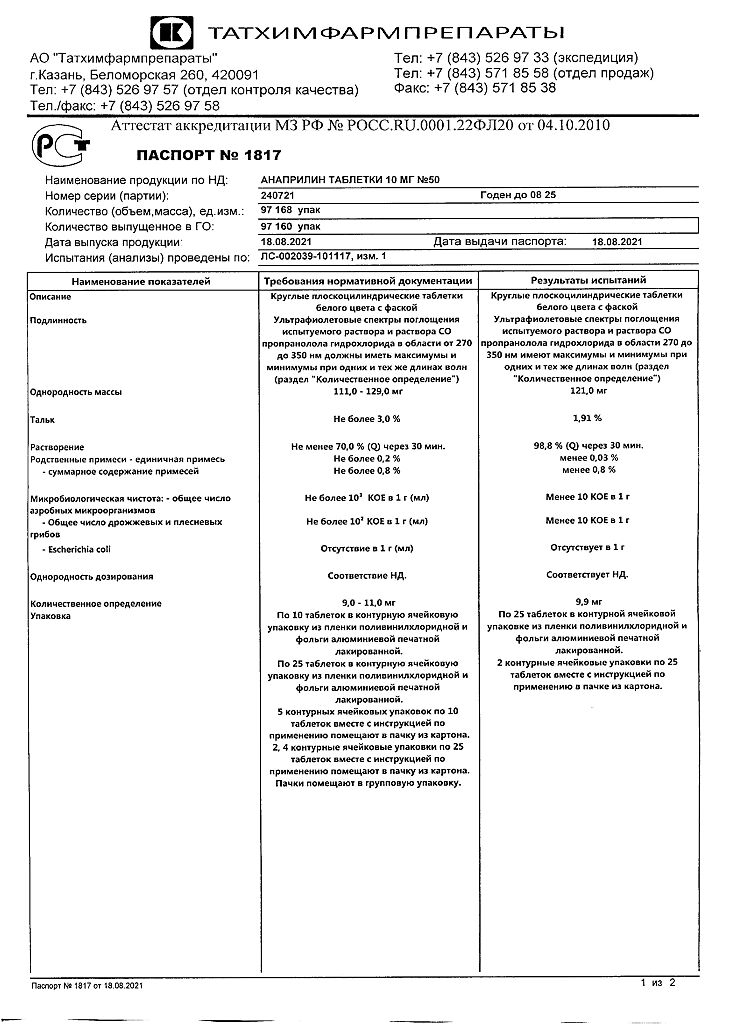
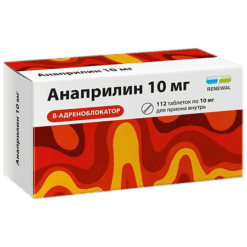
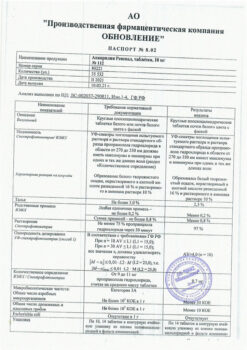
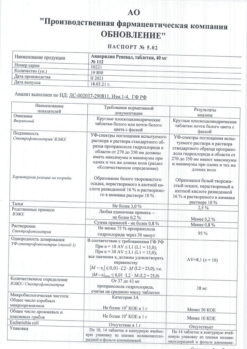
Anaprilin, tablets 10 mg 50 pcs
€1.68 €1.27
Description
Anapriline is antiarrhythmic, hypotensive, antianginal.
Pharmacodynamics
Decreases automatism of the sinus node, myocardial excitability, the occurrence of ectopic foci of excitation; Has membrane stabilizing effect, decreases HR, slows AV conduction, reduces myocardial contractility and myocardial oxygen demand.
It has a hypotensive effect, which stabilizes by the end of the 2nd week of treatment. Reduces the activity of the renin-angiotensin system. Increases the atherogenic properties of the blood.
Enhances uterine contractions (spontaneous and caused by means stimulating the myometrium), which helps to reduce bleeding during labor and in the postoperative period.
Enhances bronchial tone, in high doses causes a sedative effect.
Limits intraocular pressure by inhibiting the production of aqueous humor in the eye chamber, does not affect pupil size and accommodation.
Pharmacokinetics
It is rapidly absorbed when ingested and relatively quickly eliminated from the body. Cmax in blood plasma is reached after 1-1.5 h. Bioavailability after oral administration is 30% (effect of “first passage” through the liver, microsomal oxidation), increases after meals. T1/2 is 2-3 hours. Binding to blood plasma proteins is 90-95%. Penetrates through the placental barrier. Excretion by kidneys is 90%, in unchanged form – less than 1%.
Indications
Indications
angina pectoris, unstable angina pectoris;
sinus tachycardia (including with hyperthyroidism);
supraventricular tachycardia;
arterial hypertension;
tachysystolic form of atrial fibrillation;
supraventricular and ventricular extrasystole;
essential tremor;
sympathoadrenal crises against the background of diencephalic syndrome;
cardiovascular disorders in diffuse toxic goiter;
preoperative preparation of patients with thyrotoxic goiter who cannot tolerate thyreostatic drugs
prevention of migraine attacks.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Anaprilin – antiarrhythmic, hypotensive, antianginal.
Pharmacodynamics
Reduces the automatism of the sinus node, myocardial excitability, and the occurrence of ectopic foci of excitation; has a membrane-stabilizing effect, reduces heart rate, slows AV conduction, reduces myocardial contractility and myocardial oxygen demand.
It has a hypotensive effect, which stabilizes by the end of the 2nd week of the course. Reduces the activity of the renin-angiotensin system. Increases the atherogenic properties of blood.
Strengthens uterine contractions (spontaneous and caused by agents that stimulate the myometrium), which helps reduce bleeding during childbirth and in the postoperative period.
Increases bronchial tone, causing a sedative effect in large doses.
Reduces intraocular pressure by inhibiting the production of aqueous humor in the chamber of the eye, does not affect pupil size and accommodation.
Pharmacokinetics
It is quickly absorbed when taken orally and is relatively quickly eliminated from the body. Cmax in blood plasma is reached after 1–1.5 hours. Bioavailability after oral administration is 30% (the “first pass” effect through the liver, microsomal oxidation), increases after administration after meals. T1/2 – 2-3 hours. Binding to blood plasma proteins – 90-95%. Penetrates through the placental barrier. Excretion by the kidneys is 90%, unchanged – less than 1%.
Special instructions
Special instructions
After a long course of treatment, the drug should be discontinued gradually, under the supervision of a physician.
The drug is prescribed with caution in case of impaired liver and/or kidney function, diabetes mellitus.
For pheochromocytoma, Anaprilin can be prescribed only after taking an alpha-blocker.
When using halothane, isoflurane, methoxyflurane and trichlorethylene while taking Anaprilin, the risk of depression of myocardial function and the development of hypotension may increase. In patients who are planning extensive surgical interventions, the risk of complications after abrupt withdrawal of Anaprilin is higher than with continued treatment with beta-blockers when the effects are compensated by proper management of anesthesia.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Propranolol
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
Active substance:
10 mg propranolol;
Excipients:
milk sugar;
talc;
potato starch;
calcium stearate.
Contraindications
Contraindications
hypersensitivity;
AV block II–III stage;
sinoatrial block;
sinus bradycardia (heart rate <55 beats/min);
sick sinus syndrome;
arterial hypotension;
heart failure stage II B–III;
acute heart failure;
acute myocardial infarction;
vasomotor rhinitis;
obliterating arterial diseases (including Raynaud’s disease);
metabolic acidosis;
bronchial asthma;
tendency to bronchospastic reactions;
diabetes mellitus;
pregnancy.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Possible: bradycardia, AV block, bronchospasm, heart failure, muscle weakness.
Rarely – headache, sleep disturbances, nightmares, asthenia, decreased ability for rapid mental and motor reactions, agitation, depression, paresthesia and coldness of the extremities, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, allergic skin reactions, exacerbation of psoriasis, hypoglycemia, blurred vision, keratoconjunctivitis.
Interaction
Interaction
During treatment with Anaprilin, intravenous administration of verapamil and diltiazem should be avoided.
With simultaneous use of Anaprilin with oral hypoglycemic agents or insulins, it is possible to disrupt the regulation of glucose levels in the blood plasma and increase the risk of hyperglycemia.
Anaprilin can also mask the symptoms of incipient hypoglycemia.
With the simultaneous use of Anaprilin and NSAIDs (especially indomethacin), the antihypertensive effect of Anaprilin may be reduced, probably due to the suppression of prostaglandin synthesis in the kidneys and, as a consequence, sodium and fluid retention in the body).
With the simultaneous use of Anaprilin and estrogen-containing drugs, the antihypertensive effect of Anaprilin may be reduced due to fluid retention in the body.
With the simultaneous use of Anaprilin with nitrates, the hypotensive effect may be enhanced.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: severe bradycardia, dizziness, AV block, marked decrease in blood pressure, fainting, arrhythmia, ventricular extrasystole, heart failure, cyanosis of fingernails or palms, convulsions, difficulty breathing, bronchospasm.
Treatment: gastric lavage, administration of activated carbon; if AV conduction is impaired, 1-2 mg of atropine is administered intravenously; if efficiency is low, a temporary pacemaker is installed; for ventricular extrasystole – lidocaine (class Ia drugs are not used); when blood pressure decreases, the patient should be in the Trendelenburg position.
If there are no signs of pulmonary edema, plasma-substituting solutions are administered intravenously; if ineffective, epinephrine, dopamine, dobutamine are administered; for heart failure – cardiac glycosides, diuretics, glucagon; for convulsions – intravenous diazepam; for bronchospasm – inhaled or parenteral beta-agonists.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place, protected from light
Shelf life
Shelf life
4 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Tatchimpharmpreparaty, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 4 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place |
| Manufacturer | Tatkhimpharmpreparaty, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Tatkhimpharmpreparaty |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Anaprilin, tablets 10 mg 50 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.