No products in the cart.
Warfarin, tablets 2.5mg 50 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Warfarin s belongs to the group of anticoagulants – drugs that prevent blood clotting and is intended for long-term use. It has an indirect anticoagulant effect, inhibiting in the liver the synthesis of a number of factors involved in the regulation of blood clotting. Warfarex prevents the formation of new blood clots and prevents the growth of already formed ones.
Indications
Indications
Prevention and treatment of diseases caused by the formation of blood clots in blood vessels:
deep vein thrombosis;
pulmonary embolism;
atrial fibrillation;
myocardial infarction;
prosthetic heart valves.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Warfarin belongs to the group of anticoagulants – drugs that prevent blood clotting, and is intended for long-term use. It has an indirect anticoagulant effect, inhibiting in the liver the synthesis of a number of factors involved in regulating the blood clotting process. Warfarex prevents the formation of new blood clots and prevents the expansion of already formed ones.
Special instructions
Special instructions
The use of anticoagulants increases the risk of bleeding. To monitor the condition of the blood coagulation system, during treatment with Warfarin you should regularly visit your doctor and carry out the prescribed tests. When you contact doctors, dentists or pharmacists, you must tell them that you are taking Warfarin. You should consult a doctor if digestive disorders occur, accompanied by diarrhea (diarrhea), fever. Pregnancy during treatment with Warfarin is highly undesirable, so it is necessary to use effective methods to prevent it. You must be careful when handling sharp and traumatic objects, and avoid activities associated with the risk of injury and subsequent bleeding. During the treatment period, it is necessary to refrain from drinking ethanol (risk of developing hypoprothrombinemia). The safety of the drug in children has not been sufficiently studied in clinical studies. There is no data on the adverse effects of Warfarin on the ability to drive vehicles and operate other machinery.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Warfarin
Composition
Composition
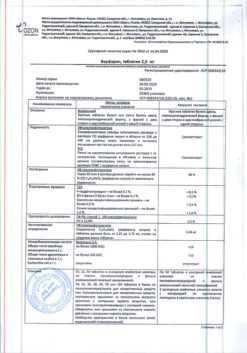
1 tablet contains warfarin sodium 2.5 mg;
excipients: lactose; corn starch; calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate; indigo carmine; povidone 30; magnesium stearate.
Contraindications
Contraindications
established or suspected hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
acute bleeding;
pregnancy (first trimester and last 4 weeks of pregnancy);
severe liver or kidney disease;
acute DIC syndrome;
deficiency of proteins C and S;
thrombocytopenia;
patients at high risk of bleeding, including patients with bleeding disorders;
varicose veins of the esophagus;
arterial aneurysm;
lumbar puncture;
peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
severe wounds (including surgical wounds)
Side Effects
Side Effects
Frequency: very often – more than 1/10, often – more than 1/100 and less than 1/10, infrequently – more than 1/1000 and less than 1/100, rarely – more than 1/10000 and less than 1/1000.
Very common: increased bleeding.
Common: increased sensitivity to warfarin after prolonged use.
Uncommon: anemia, vomiting, abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea.
Rarely: eosinophilia, increased activity of liver enzymes, jaundice, rash, urticaria, itching, eczema, skin necrosis, vasculitis, hair loss, nephritis, urolithiasis, tubular necrosis, hand-foot syndrome.
Interaction
Interaction
High levels of vitamin K in foods (spinach, broccoli, lettuce and other leafy vegetables) may reduce the effect of warfarin. However, you should not change your diet too abruptly or use vitamins and nutritional supplements without consulting your doctor. Smoking may reduce the anticoagulant effect of the drug. The effect of Warfarin may vary under the influence of a large number of drugs. NSAIDs, dipyridamole, valproic acid, cytochrome P450 inhibitors, cimetidine, chloramphenicol, laxatives – increase the risk of bleeding. The combined use of these drugs and Warfarin should be avoided (cimetidine can be replaced with ranitidine or famotidine). If treatment with chloramphenicol is necessary, anticoagulant therapy may be temporarily discontinued. Diuretics can reduce the effect of anticoagulants (in case of pronounced hypovolemic effect, which can lead to an increase in the concentration of coagulation factors). Weaken the effect: barbiturates, vitamin K, glutethimide, griseofulvin, dicloxacillin, carbamazepine, mianserin, paracetamol, retinoids, rifampicin, sucralfate, phenazone, cholestyramine. Enhance the effect: allopurinol, amiodarone, anabolic steroids (alkylated at position C-17), acetylsalicylic acid and other NSAIDs, heparin, glibenclamide, glucagon, danazol, diazoxide, disopyramide, disulfiram, isoniazid, ketoconazole, clarithromycin, clofibrate, levamisole, metronidazole, miconazole, nalidixic acid, nilutamide, omeprazole, paroxetine, proguanil, oral hypoglycemic agents – sulfonamide derivatives, sulfonamides, tamoxifen, thyroxine, quinine, quinidine, fluvoxamine, fluconazole, fluorouracil, quinolones, chloral hydrate, chloramphenicol, cephalosporins, cimetidine, erythromycin, ethacrynic acid, ethanol. When using Warfarin in combination with the above drugs, it is necessary to monitor the INR at the beginning and end of treatment and, if possible, after 2-3 weeks from the start of therapy. When using drugs that may increase the risk of bleeding due to a decrease in normal coagulation (inhibition of coagulation factors or liver enzymes), the anticoagulant strategy should be determined by the availability of laboratory monitoring. If frequent laboratory monitoring is possible, then if therapy with such drugs is necessary, the dose of Warfarin can be reduced by 5–10%. If laboratory monitoring is difficult, then treatment with Warfarin should be discontinued if these drugs are necessary.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms of chronic intoxication: bleeding from the gums, nosebleeds, excessive menstrual bleeding, heavy or prolonged bleeding from minor superficial injuries, hemorrhages in the skin, blood in the urine and feces, etc.
Treatment: for minor bleeding, reduce the dose of the drug or stop treatment for a short period. In case of severe bleeding, transfusion of prothrombin complex factor concentrates, or fresh frozen plasma, or whole blood.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
5 years.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Ozon, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 5 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. |
| Manufacturer | Ozon, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Ozon |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Warfarin, tablets 2.5mg 50 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.