No products in the cart.
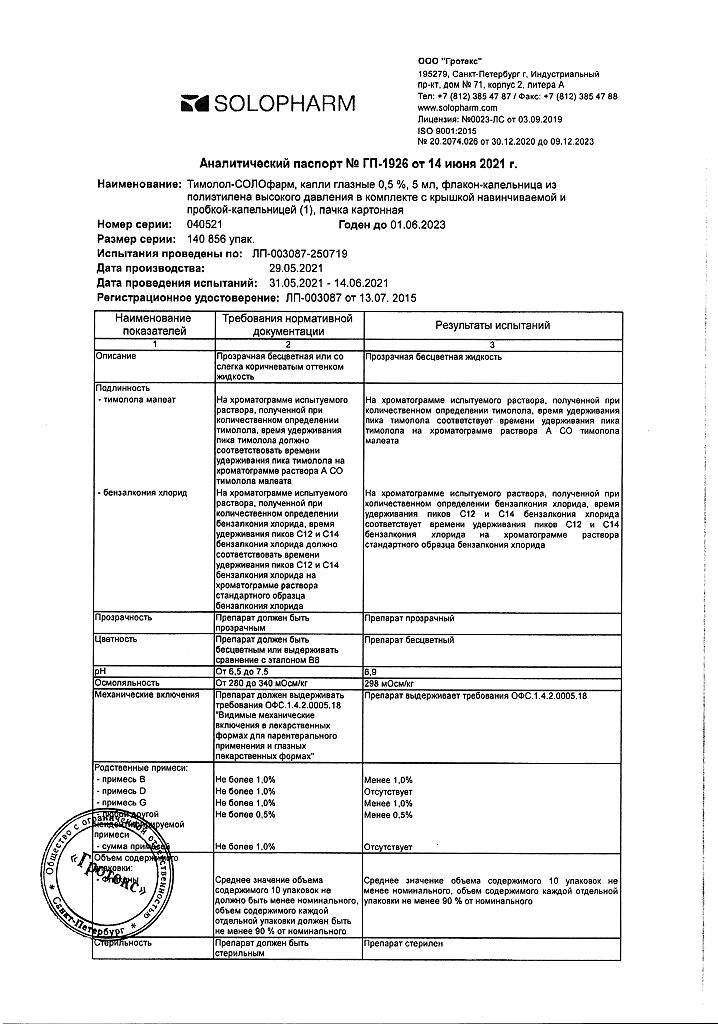
Timolol-Solofarm, eye drops 0.5% 5 ml
€1.56 €1.42
Description
A nonselective beta-adrenoblocker.
When used topically in ophthalmology it reduces both normal and elevated intraocular pressure by reducing intraocular fluid formation and improving its outflow, has no effect on accommodation and pupil size.
It has antianginal, hypotensive and antiarrhythmic effects, which appear with systemic use. It reduces automatism of sinus node, decreases heart rate, slows down AV conduction, reduces contractility and myocardial oxygen demand.
Indications
Indications
Increased intraocular pressure (ophthalmohypertension), open-angle glaucoma, glaucoma on the non-actual eye and other types of secondary glaucoma, congenital glaucoma (if other drugs are not effective), as an additional means to reduce intraocular pressure in closed-angle glaucoma (in combination with miotics).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Non-selective beta blocker.
When applied topically in ophthalmology, it reduces both normal and increased intraocular pressure by reducing the formation of intraocular fluid and improving its outflow, and does not affect accommodation and pupil size.
It has antianginal, hypotensive and antiarrhythmic effects, which manifest themselves when used systemically. Reduces the automaticity of the sinus node, reduces heart rate, slows AV conduction, reduces contractility and myocardial oxygen demand.
Special instructions
Special instructions
In the postoperative period of antiglaucomatous operations and when using drugs that reduce the secretion of intraocular fluid, detachment of the choroid may develop.
The use of timolol in patients with atopy or a history of severe pathological reactions to various allergens may provoke more severe reactions in response to incidental, diagnostic or therapeutic management of allergens. Such patients may respond poorly to normal doses of epinephrine to relieve anaphylactic reactions.
Beta-blockers can mask a number of clinical symptoms of hyperthyroidism (and in particular tachycardia). Caution is required when using beta-blockers in patients with the possibility of developing thyrotoxicosis.
In patients without a history of heart failure, prolonged myocardial depression may in some cases lead to the development of heart failure. If the first signs of heart failure occur, timolol should be discontinued. Caution is required when prescribing timolol to patients with first degree atrioventricular block, Prinzmetal’s angina and peripheral circulatory disorders (Raynaud’s phenomenon).
The main pathogenetic aspect of the treatment of angle-closure glaucoma is the need to open the anterior chamber angle, which is achieved by narrowing the pupil with the help of miotics. Due to the lack of effect of timolol on pupil diameter in the treatment of wide-angle glaucoma, the drug can only be used in combination with miotics. Due to the possible effect of beta-adrenergic blockers on blood pressure and heart rate, these drugs should be used with caution in patients with cerebrovascular insufficiency. If signs or symptoms of decreased cerebral circulation develop after initiation of timolol therapy, the need for therapy with local beta-blockers should be reconsidered.
The use of timolol may increase muscle weakness in myasthenia gravis (for example, cause increased diplopia, ptosis and general weakness). Some patients with myasthenia gravis and other myasthenic diseases have experienced an increase in muscle weakness when taking timolol.
When used simultaneously with other drugs, it is necessary to maintain an interval between instillations of at least 15 minutes.
When using it, it is necessary to monitor the function of the eyes, the condition of the cornea and evaluate the size of the visual fields at least once every 6 months.
The drug contains the preservative benzalkonium chloride, which can cause eye irritation, be absorbed by soft contact lenses, causing discoloration and have an adverse effect on eye tissue. Contact lenses should be removed before using the drug and, if necessary, put them on again no earlier than 15 minutes after instillation.
With long-term use of the drug, a toxic effect of the preservative benzalkonium chloride on the corneal epithelium (development of punctate keratopathy and/or toxic ulcerative keratopathy) is possible.
There have been cases of the development of bacterial keratitis in patients who used timolol in containers for multiple dosing of ophthalmic drugs. These containers were inadvertently contaminated by patients with underlying corneal diseases.
When transferring patients to treatment with timolol, it may be necessary to correct changes in refraction caused by previously used miotics.
The drug, like other beta-blockers, can hide possible symptoms of hypoglycemia in the blood in patients with diabetes.
In case of upcoming surgery under general anesthesia, it is necessary to discontinue the drug 48 hours before surgery, as it enhances the effect of muscle relaxants and general anesthetics.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles. Wed and fur.:
During the treatment period, care must be taken when driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions due to the profile of side effects (in particular, from the organ of vision and nervous system).
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Timolol
Composition
Composition
1 ml timolol maleate 6.84 mg, which corresponds to the content of timolol 5 mg
Excipients:
benzalkonium chloride – 0.1 mg,
sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate – 6.1 mg,
sodium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate – 15.16 mg,
water for d/i – up to 1 ml.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Bronchial asthma, sinus bradycardia, atrioventricular block II and III degrees without a pacemaker, decompensated chronic heart failure, cardiogenic shock, severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, sick sinus syndrome. hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
With caution:
Cerebrovascular insufficiency, arterial hypotension, diabetes mellitus, hypoglycemia, pulmonary insufficiency, thyrotoxicosis, myasthenia gravis, sinoatrial blockade, peripheral circulatory disorders (including Rsipo syndrome), pregnancy, simultaneous administration of other beta-blockers.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Adverse reactions that occurred after oral administration of timolol and other beta-blockers can be regarded as potential adverse reactions for timolol prep phates in the dosage form of eye drops.
Adverse reactions, information about which was obtained during clinical trials and during post-marketing surveillance of timol)l medicinal products in the dosage form of eye drops
The frequency of side effects identified both during studies and during market surveillance was assessed as follows: very often (>1/10); often (>1/100 to 1/1000 to 1/10000 to <1/1000); very rare (< 1/10000), frequency unknown (available data cannot be estimated).
General reactions
With unknown frequency: headache, asthenia/fatigue, chest pain.
From the side of the organ of vision
Common: blurred vision, eye pain, burning and itching of the eyes, eye discomfort, conjunctival injection.
Uncommon: blepharitis, punctate keratitis, keratitis, conjunctivitis, iritis, diplopia, corneal erosion, corneal ulcer, lacrimation or decreased lacrimation, photophobia, feeling of “sand” in the eyes, eyelid edema, conjunctival edema, ptosis.
Rarely: uveitis, double vision, corneal pigmentation, eyelid erythema.
Very rare: development of corneal calcification with significant damage due to the presence of phosphates in the drops.
With unknown frequency: decreased sensitivity of the cornea, detachment of the choroid in the postoperative period of antiglaucomatous surgery.
From the cardiovascular system: Uncommon: bradycardia, hypotension.
Rarely: myocardial infarction, decreased or increased blood pressure, intermittent claudication.
With unknown frequency: cardiac arrest, atrioventricular block, arrhythmia, palpitations, congestive heart failure, Raynaud’s phenomenon.
From the digestive system: Uncommon: dysgeusia.
Rarely: dyspepsia, dry oral mucosa, abdominal pain.
With unknown frequency: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea.
From the immune system With unknown frequency: systemic lupus erythematosus.
Mental disorders Rare: depression.
With unknown frequency: insomnia, memory loss, nightmares.
From the nervous system: uncommon: headache.
Rarely: cerebral ischemia, dizziness, migraine.
With unknown frequency: cerebrovascular accident, fainting, paresthesia, dizziness, worsening myasthenia gravis.
From the side of the rut and subcutaneous tissues of the face: swelling of the face, erythema.
With unknown frequency: psoriasis or worsening of psoriasis, localized rash, and elopice.
Connective tissue disorders Unknown frequency: arthropathy. muscle pain.
Allergic reactions
With unknown frequency: systemic allergic reactions, including anaphylaxis, angioedema, urticaria, local or generalized rash. itching
From the respiratory system and mediastinal organs: Uncommon: respiratory failure, shortness of breath, bronchitis.
Rarely: bronchospasm (mainly in patients with existing bronchospastic conditions), cough, nasal congestion, upper respiratory tract infections.
From the endocrine system
With unknown frequency: subclinical hypoglycemia in patients with diabetes mellitus (see section “Special instructions”).
From the genitourinary system
Not known: retroperitoneal fibrosis, sexual dysfunction (including impotence), decreased libido, Peyronie’s disease.
From the ENT organs With unknown frequency: ringing in the ears.
Adverse reactions that occurred after taking timolol or other beta-a) repoblockers orally
Allergic reactions: erythematous rash, fever accompanied by sore throat, laryngosiasm accompanied by distress syndrome.
General reactions and reactions at the injection site: pain in the extremities, decreased exercise tolerance, weight loss.
From the cardiovascular system: worsening arterial insufficiency, dilatation.
From the digestive system: gastrointestinal ool. hepatomegaly. vomiting. thrombosis of mesenteric arteries, ischemic colitis.
From the blood and lymphatic system: non-thrombocytopenic purpura, thrombocytopenic purpura, agranulocytosis.
From the endocrine system: hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia.
From the skin and subcutaneous tissues: itching, skin irritation, increased pigmentation, sweating.
From the musculoskeletal system: arthralgia.
From the nervous system/mental disorders: vertigo, decreased concentration, reversible depression of mental functions progressing to catatonia, acute reversible syndrome characterized by impaired orientation in time and space, emotional lability, some difficulty in perception and a reduced ability to perform neuropsychological tests.
From the respiratory system: wheezing, bronchial obstruction.
From the genitourinary system: difficulty urinating.
Interaction
Interaction
Combined use of the drug with eye drops containing adrenaline may cause pupil dilation.
The specific effect of the drug is a decrease in intraocular pressure, which can increase with the simultaneous use of eye drops containing epinephrine and pilocarpine.
Two different blocking agents should not be instilled into the same eye. Arterial hypotension and bradycardia may increase with simultaneous use of the drug with cation antagonists, reserpine and systemic beta-blockers.
CYP2D6 inhibitors such as quinidine and cimetidipe may increase plasma concentrations of timolol.
Concomitant use with insulin or oral antidiabetic agents may lead to hypoglycemia.
Timolol enhances the effect of muscle relaxants, so it is necessary to discontinue the drug 48 hours before the planned surgery under general anesthesia.
These data may also apply to medications that were used shortly before.
Overdose
Overdose
The development of systemic effects characteristic of beta-blockers is possible: dizziness, headache, arrhythmia, bradycardia, bronchospasm, nausea and vomiting, loss of consciousness, hypotension, shortness of breath, generalized convulsions, cardiogenic shock, heart failure and cardiac arrest.
In case of accidental ingestion of timolol, gastric lavage and activated charcoal intake are necessary. It has been shown that the drug cannot be removed from the body by hemodialysis.
With the development of bradycardia and bradyarrhythmia (with atrioventricular block II and III degrees), intravenous administration of atropine sulfate in a dose of 0.25 to 2 mg is recommended; and if bradycardia is partially relieved, the administration of isoprenaline is indicated. For difficult-to-control bradycardia, consideration should be given to installing a pacemaker. For hypotension, it is recommended to take simiatomimetics, such as dopamine, dobutamine, nerepinephrine. If there is no effect, administer glucagon.
With the development of acute heart failure, the use of digitalis and diuretics, as well as oxygen therapy, is recommended; if ineffective, intravenous administration of aminophylline is recommended.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Grotex LLC, Russia
Additional information
| Manufacturer | Grotex Ltd, Russia |
|---|---|
| Medication form | eye drops |
| Brand | Grotex Ltd |
Related products
Buy Timolol-Solofarm, eye drops 0.5% 5 ml with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.