No products in the cart.
Solpadein Fast, 65 mg+500 mg 12 pcs
€9.63 €8.43
Description
Analgesic-antipyretic of combined composition, contains a combination of two active ingredients: paracetamol and caffeine.
It has antipyretic and analgesic effect.
Paracetamol blocks COX in the CNS, affecting the centers of pain and thermoregulation (in inflamed tissues cellular peroxidases neutralize the effect of paracetamol on COX), which explains the almost complete absence of anti-inflammatory effects.
Indications
Indications
Headache;
migraine;
toothache;
lower back pain;
neuralgia;
muscle and rheumatic pain;
painful menstruation;
sore throat;
symptomatic treatment of colds and flu (to reduce elevated body temperature).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
An analgesic-antipyretic of a combined composition, contains a combination of two active ingredients: paracetamol and caffeine.
Has antipyretic and analgesic effects.
Paracetamol blocks COX in the central nervous system, affecting the centers of pain and thermoregulation (in inflamed tissues, cellular peroxidases neutralize the effect of paracetamol on COX), which explains the almost complete absence of anti-inflammatory effect.
Special instructions
Special instructions
If no improvement is observed while taking the drug or the headache becomes constant, you should consult a doctor.
While taking the drug, excessive consumption of caffeine-containing foods (including tea, coffee) is not recommended, because this can lead to restlessness, anxiety, irritability, insomnia, headache, gastrointestinal disorders, tachycardia, cardiac arrhythmia.
In cases of long-term use in high doses, monitoring of the blood picture is necessary.
Glutathione deficiency due to eating disorders, cystic fibrosis, HIV infection, starvation, exhaustion makes it possible to develop severe liver damage with small overdoses of paracetamol (5 g or more).
The drug should not be taken simultaneously with other paracetamol-containing drugs.
To avoid toxic liver damage, paracetamol should not be combined with alcoholic beverages, or taken by persons prone to chronic alcohol consumption.
Patients suffering from atonic bronchial asthma and hay fever have an increased risk of developing allergic reactions. In patients with renal impairment, the drug should be used with caution and only after consultation with a doctor. When taking the drug in patients with non-alcoholic cirrhosis of the liver there is a high risk of overdose.
When conducting tests to determine uric acid and blood glucose levels, you should inform your doctor about taking the drug.
While taking the drug, it is possible that the results of doping control tests for athletes may change.
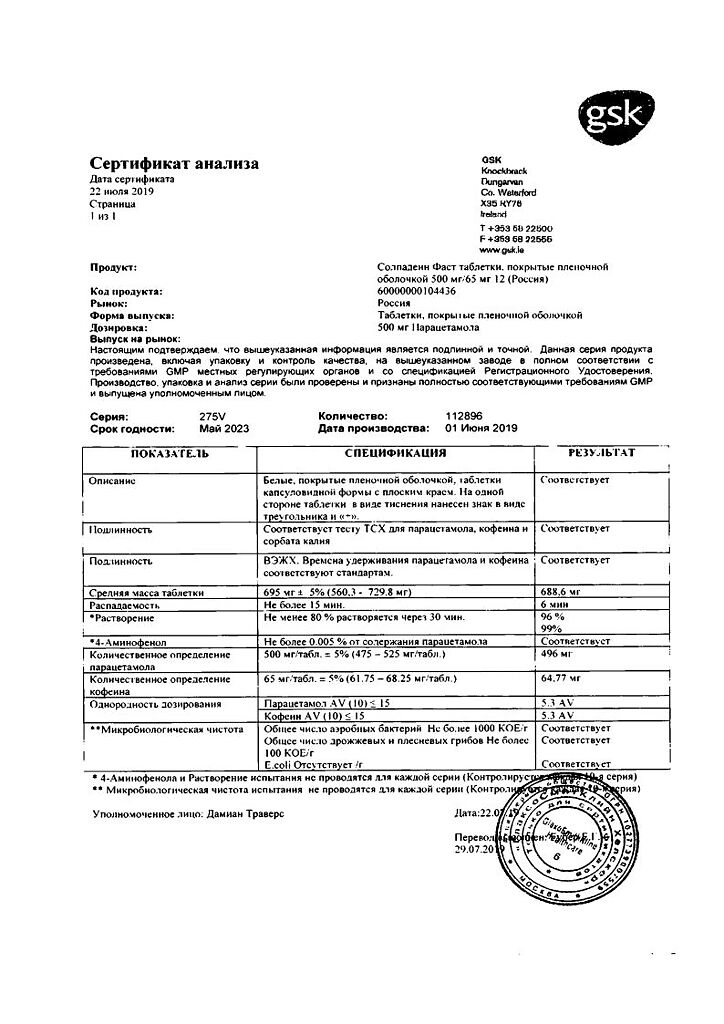
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Caffeine, Paracetamol
Composition
Composition
Active ingredients:
– paracetamol 500 mg;
– caffeine 65 mg.
Excipients:
pregelatinized starch 50 mg,
corn starch 41.4 mg,
povidone 2 mg,
potassium sorbate 0.6 mg,
talc 15 mg,
stearic acid 5 mg,
croscarmellose sodium 10 mg,
hypromellose 5 mg,
triacetin 1 mg.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Solpadeine Fast contains caffeine. When taking caffeine, there is a high risk of having a low birth weight baby and a risk of spontaneous abortion.
Contraindications
Contraindications
severe liver dysfunction;
severe renal dysfunction;
arterial hypertension;
glaucoma;
sleep disorders;
epilepsy;
children under 12 years of age;
hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
The drug should be used with caution in cases of benign hyperbilirubinemia (including Gilbert’s syndrome), viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver damage, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, alcoholism.
Side Effects
Side Effects
At recommended doses, the drug is usually well tolerated.
Determination of the frequency of side effects: very often (≥1/10), often (≥1/100 and <1/10), infrequently (≥1/1000 and <1/100), rarely (≥1/10,000 and <1/1000), very rarely (≥1/100,000 and <1/10,000).
The following side effects were detected spontaneously during post-registration use of the drug.
Paracetamol
Allergic reactions: very rarely – skin rash, angioedema (Quincke’s edema), Stevens-Johnson syndrome, anaphylaxis.
From the hematopoietic system: very rarely – leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, methemoglobinemia, agranulocytosis, hemolytic anemia.
From the respiratory system: very rarely – bronchospasm (in patients with hypersensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid and NSAIDs).
From the hepatobiliary system: very rarely – liver dysfunction.
With long-term use in high doses, the likelihood of hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity and pancytopenia increases. Also, in cases of long-term use in high doses, monitoring of the blood picture is necessary.
Caffeine
Possible: dyspeptic symptoms (including nausea, epigastric pain), increased excitability, dizziness, sleep disturbances, tachycardia. Excessive consumption of caffeine-containing foods (including tea, coffee) while taking the drug may cause restlessness, anxiety, irritability, insomnia, headache, disorders of the digestive system, tachycardia, cardiac arrhythmia.
If any of the listed side effects occur, you should stop taking the drug and consult a doctor immediately.
Interaction
Interaction
When taken regularly over a long period of time, the drug enhances the effect of indirect anticoagulants (warfarin and other coumarins), which increases the risk of bleeding. Occasional administration of a single dose of the drug does not have a significant effect on the effect of indirect anticoagulants.
The drug enhances the effect of MAO inhibitors. Barbiturates, carbamazepine, phenytoin, primidone, ethanol, rifampicin, phenylbutazone, St. John’s wort, tricyclic antidepressants and other inducers of microsomal oxidation increase the production of hydroxylated active metabolites, causing the possibility of developing severe liver damage with small overdoses of paracetamol (5 g or more).
Microsomal oxidation inhibitors (cimetidine) reduce the risk of hepatotoxicity.
Under the influence of paracetamol, the elimination time of chloramphenicol increases 5 times.
Caffeine accelerates the absorption of ergotamine.
Concomitant use of paracetamol and alcoholic beverages increases the risk of developing hepatotoxic effects and acute pancreatitis.
Metoclopramide and domperidone increase, and cholestyramine reduces the rate of absorption of paracetamol.
The drug may reduce the effectiveness of uricosuric drugs.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms caused by paracetamol: pale skin, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, stomach pain are possible within 24 hours; after 1-2 days, signs of liver damage may appear (pain in the liver area, increased activity of liver enzymes). Possible disturbances in carbohydrate metabolism and signs of metabolic acidosis.
Clinical pharmacology
Clinical pharmacology
Paracetamol is quickly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, distribution in body fluids is relatively even. The binding of paracetamol to plasma proteins is minimal at therapeutic concentrations.
Short product description
Short product description
Solpadeine Fast in soluble form has an analgesic effect for migraines, headaches, toothaches and periodic pain.*
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store out of the reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
4 years.
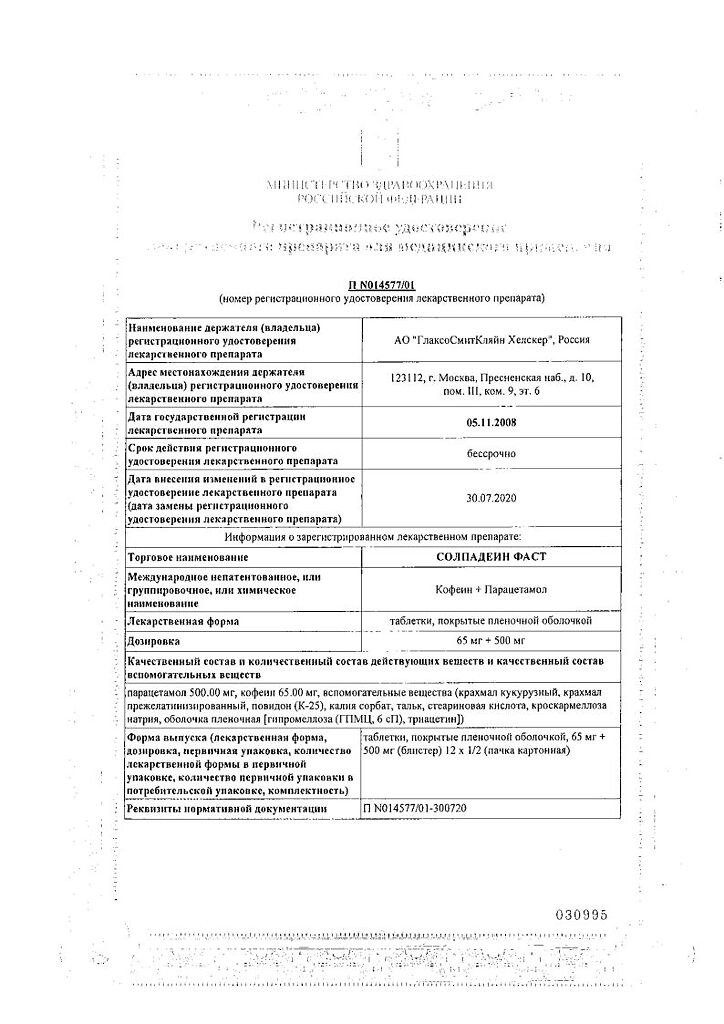
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
GlaxoSmithKline Dungarvan Limited, Ireland
Additional information
| Shelf life | 4 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Keep out of reach of children at temperatures under 25°C. |
| Manufacturer | GlaxoSmithKlein Dungarvan Limited, Ireland |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | GlaxoSmithKlein Dungarvan Limited |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Solpadein Fast, 65 mg+500 mg 12 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.