No products in the cart.
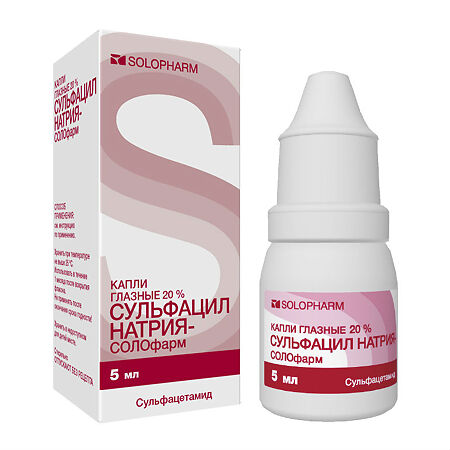
Sodium sulfacyl-SOLOPHARM, eye drops 20% 5 ml
€4.25 €3.78
Description Pharmacotherapeutic group: Antimicrobial agent – sulfonamide. Pharmacokinetics:
ATC: A.07.A.B Sulfonamides
Pharmacodynamics:
Antimicrobial bacteriostatic agent, sulfonamide. Mechanism of action is based on competitive antagonism with paraaminobenzoic acid, inhibition of dihydropteroat synthetase and disruption of tetrahydrofolic acid synthesis, necessary for purines and pyrimidines synthesis.
Active against Gram-positive and Gram-negative cocci, Escherichia coli, Shigella spp, Vibrio cholerae, Clostridium perfringers, Bacillus anthracis, Corynoebacterium diphtheriae, Yersinia pestis, Chlamydia spp, Actinomyces israelii, Toxoplasma gondii.
The development of resistance to sulfacetamide is possible.
It penetrates into the eye tissue, where it has its specific antibacterial effect. It acts mainly locally, but part of the drug is absorbed through the inflamed conjunctiva and enters the systemic bloodstream. The amount of the drug that enters the systemic bloodstream is not sufficient for development of the systemic therapeutic effect, but it is sufficient for sensitization during re-injection. When applied topically, the maximum concentration (Cmax) of sulfonamides in the cornea (about 3 mg/ml), anterior chamber humour (about 0.5 mg/ml) and iris (about 0.1 mg/ml) is reached within the first 30 minutes after application. Some amount (less than 0.5 mg/ml) persists in the eyeball tissues for 3-4 hours. When corneal epithelium is damaged sulfonamide penetration increases.
Sulfacetamide is metabolized in the liver by N-acetylation, metabolites have antibacterial activity.
Excretion of sulfacetamide occurs in the kidneys by glomerular filtration.
Indications
Indications
In the complex treatment of diseases of the eyelids, conjunctiva, cornea, anterior segment of the choroid and lacrimal ducts caused by microorganisms sensitive to sulfacetamide.
For the prevention of infectious complications in the complex treatment of burns and injuries of the organ of vision.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group: Antimicrobial agent – sulfanilamide.
ATC: A.07.A.B Sulfonamides
Pharmacodynamics:
Antimicrobial bacteriostatic agent, sulfanilamide. The mechanism of action is due to competitive antagonism with para-aminobenzoic acid, inhibition of dihydropteroate synthetase, disruption of the synthesis of tetrahydrofolic acid, necessary for the synthesis of purines and pyrimidines.
Active against gram-positive and gram-negative cocci, Escherichia coli, Shigella spp., Vibrio cholerae, Clostridium perfringers, Bacillus anthracis, Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Yersinia pestis, Chlamydia spp., Actinomyces israelii, Toxoplasma gondii.
Resistance to sulfacetamide may develop.
Pharmacokinetics:
Penetrates into the tissues of the eye, where it exerts its specific antibacterial effect. It acts predominantly locally, but part of the drug is absorbed through the inflamed conjunctiva and enters the systemic bloodstream. The amount of the drug entering the systemic circulation is not enough to develop a systemic therapeutic effect, but is sufficient to cause sensitization upon repeated administration. When applied topically, the maximum concentration (Cmax) of sulfonamides in the cornea (about 3 mg/ml), anterior chamber fluid (about 0.5 mg/ml) and iris (about 0.1 mg/ml) is achieved within the first 30 minutes after application. A certain amount (less than 0.5 mg/ml) remains in the tissues of the eyeball for 3-4 hours. When the corneal epithelium is damaged, the penetration of sulfonamides increases.
Sulfacetamide is metabolized in the liver by N-acetylation, the metabolites have antibacterial activity.
Excretion of sulfacetamide occurs in the kidneys by glomerular filtration.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Patients with hypersensitivity to furosemide, thiazide diuretics, sulfonylureas, or carbonic anhydrase inhibitors may have increased sensitivity to sulfacetamide.
Excessive growth of microorganisms that are insensitive to sulfanilamide, as well as fungal flora, is possible.
Reduced antibacterial activity of sulfonamides in the presence of high concentrations of nara-aminobenzoic acid in the presence of a large amount of purulent discharge.
It is necessary to stop therapy with sulfonamides if allergy symptoms appear, as well as if pain and other signs of an infectious inflammatory process increase, or the amount of purulent discharge increases.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles. Wed and mech.: If blurred vision develops after installation, it is necessary to refrain from driving vehicles and engaging in potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions until vision clarity is restored.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Sulfacetamide
Composition
Composition
1 ml contains:
Active substances:
sodium sulfacetamide monohydrate (in terms of sodium sulfacetamide) 200 mg
Excipients:
sodium thiosulfate pentahydrate – 1 mg,
hydrochloric acid 1M solution – up to pH 8.0,
water for d/i – up to 1 ml.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
The use of the drug during pregnancy is possible only if the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. You should refrain from breastfeeding while using the drug due to the lack of relevant clinical data.
It is possible to develop kernicterus in newborns whose mothers took tablet forms of sulfonamides during pregnancy, so it is impossible to exclude the risk of developing jaundice when taking sulfonamide in the dosage form of eye drops.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Individual hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, children’s age (up to 2 months).
Side Effects
Side Effects
Allergic reactions, burning, lacrimation, pain, itching in the eyes, transient blurred vision after instillation, nonspecific conjunctivitis, development of superinfection, severe allergic reactions to sulfonamides (Steven-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermolysis, fulminant liver necrosis, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia).
If any of the side effects indicated in the instructions get worse or you notice any other side effects not listed in the instructions, tell your doctor.
Interaction
Interaction
Sulfacetamide enhances the effect of indirect anticoagulants. Combined use with procaine. tetracaine, benzocaine reduces the bacteriostatic effect of sulfacetamide.
Diphenin, para-aminosalicylic acid (PAS), salicylates increase its toxicity.
Incompatible with silver salts.
Overdose
Overdose
Cases of drug overdose have not been described.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not higher than 15 °C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years.
After opening the bottle – 1 month. Do not use after the expiration date!
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Grotex LLC, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years. After opening the bottle – 1 month. Do not use after the expiration date! |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not higher than 15 ° C. Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Grotex Ltd, Russia |
| Medication form | eye drops |
| Brand | Grotex Ltd |
Related products
Buy Sodium sulfacyl-SOLOPHARM, eye drops 20% 5 ml with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.