No products in the cart.
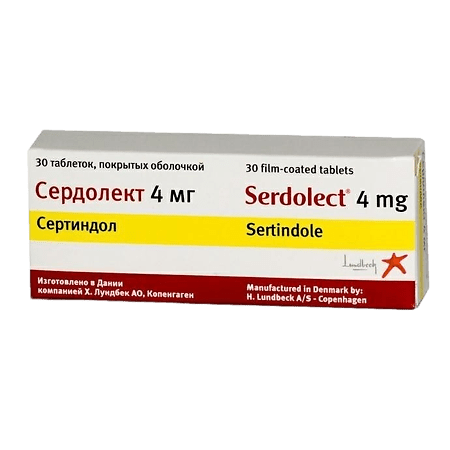
Serdollect, 4 mg 30 pcs
€61.40 €51.17
Description
Cardoleptic is an atypical neuroleptic, phenylindole derivative, selectively acting on limbic structures. It has antipsychotic effect.
Pharmacodynamics
. The neuropharmacological profile of sertindole as an antipsychotic is due to selective blockade of mesolimbic dopaminergic neurons and a balanced inhibitory effect on central dopamine D2 receptors and serotonin 5-HT2 receptors as well as α1 -adrenergic receptors.
Antipsychotics increase serum prolactin levels due to blockade of dopamine receptors. In patients taking Seardolect on short-term therapy and during long-term treatment (1 year), prolactin levels remained within normal limits.
Sertindol has no effect on muscarinic and histamine H1 receptors, which is confirmed by the absence of anticholinergic and sedative effects that are associated with effects on these receptors.
Pharmacokinetics
Sertindol is well absorbed from the gut, with maximum concentration reached approximately 10 hours after ingestion. Food intake has no effect on the speed and magnitude of absorption.
The apparent volume of distribution of sertindol after repeated administration is about 20 l/kg. Sertindol is 99.5% bound to plasma proteins. Sertindol penetrates through the blood-brain barrier and the placental barrier.
Sertindol is metabolized in the liver with the participation of cytochromes P450 2D6 and P450 3A.
The metabolites have no neuroleptic activity.
The elimination half-life is about 3 days.
Sertindol and its metabolites are excreted mainly in the feces and partially in the urine.
Indications
Indications
Treatment of schizophrenia.
Sertindole is not recommended for use in emergency situations for the treatment of acute psychotic disorders.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Serdolect is an atypical antipsychotic, a phenylindole derivative, selectively affecting limbic structures. Has antipsychotic effect.
Pharmacodynamics
The neuropharmacological profile of sertindole as an antipsychotic drug is due to the selective blockade of mesolimbic dopaminergic neurons and a balanced inhibitory effect on central dopamine D2 receptors and serotonin 5-HT2 receptors, as well as on α1 adrenergic receptors.
Antipsychotics increase serum prolactin levels due to blockade of dopamine receptors. In patients taking Serdolect during short-term therapy and during long-term treatment (1 year), prolactin levels remained within the normal range.
Sertindole does not affect muscarinic and histamine H1 receptors, which is confirmed by the lack of anticholinergic and sedative effects that are associated with effects on these receptors.
Pharmacokinetics
Sertindole is well absorbed from the intestine, with maximum concentrations achieved approximately 10 hours after administration. Food intake does not affect the rate and magnitude of absorption.
The apparent volume of distribution of sertindole after repeated use is about 20 l/kg. Sertindole is 99.5% bound to plasma proteins. Sertindole penetrates the blood-brain and placental barriers.
Sertindole is metabolized in the liver with the participation of cytochromes P450 2D6 and P450 3A.
Metabolites do not have neuroleptic activity.
The half-life is approximately 3 days.
Sertindole and its metabolites are excreted mainly in feces and partly in urine.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Due to precautions related to QT prolongation and ECG monitoring, sertindole should be prescribed in cases where at least one other antipsychotic is already intolerant.
The risk of QT interval prolongation is greater when taking higher doses (20-24 mg/day). Prolongation of the QT interval when taking a number of drugs can lead to the development of paroxysms of ventricular tachycardia and sudden death.
Blood pressure monitoring is necessary during the dose titration period and at the beginning of the maintenance therapy period.
Cardiovascular system
Before prescribing Serdolect, it is necessary to conduct an ECG study. When the QT interval exceeds 450 ms in men and 470 ms in women, Serdolect should not be prescribed.
An ECG study should be carried out before prescribing the drug, when equilibrium concentration is reached approximately 3 weeks after the start of administration or a daily dose of 16 mg, as well as 3 months after the start of treatment. During maintenance therapy, ECG examinations must be performed every 3 months.
During maintenance treatment, an ECG study should be performed before and after increasing the dose of sertindole or after adding/increasing the dose of a drug that may increase the concentration of sertindole in the blood.
If the QT interval prolongs beyond 500 ms, sertindole should be discontinued.
If a patient develops symptoms such as palpitations, convulsions, fainting, indicating the possibility of an arrhythmia, the attending physician should immediately begin examining the patient, including an ECG.
It is preferable to conduct an ECG study in the morning.
Electrolyte disturbances
In patients at risk of developing severe electrolyte disturbances, the level of potassium and magnesium in the blood serum should be measured before starting treatment with Serdolect. Hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia should be corrected before starting sertindole. It is recommended to monitor the concentration of potassium in the blood plasma in patients with vomiting and diarrhea, in patients taking potassium-sparing diuretics, as well as in other electrolyte disturbances.
Parkinson’s disease
Antipsychotics may inhibit the effects of dopamine agonists. Serdolect should be used with caution in patients with Parkinson’s disease.
Decreased liver function
With a slight or moderate degree of liver dysfunction, careful monitoring of the patient’s condition is necessary. A slower dosage increase and a lower maintenance dose are recommended.
Seizures
Serdolect should be prescribed with caution in patients with a history of seizures.
Tardive dyskinesia
Long-term use of antipsychotic drugs, especially in high doses, is associated with the risk of developing tardive dyskinesia. If symptoms appear while taking sertindole, the dosage should be reduced or the drug should be discontinued completely.
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS)
In cases of development of NMS, immediate discontinuation of the drug is necessary.
Withdrawal syndrome
Abrupt withdrawal of antipsychotics may cause nausea, vomiting, increased sweating, and insomnia. The return of psychotic symptoms and the appearance of involuntary movement disorders (akathisia, dystonia, dyskinesia) are also possible. Gradual withdrawal of the drug is necessary.
Excipients
The tablets contain lactose monohydrate. Patients with hereditary galactose intolerance, lactase deficiency or impaired absorption of glucose and galactose should not be prescribed the drug.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding
Since the safety of Serdolect during pregnancy in humans has not been studied, this drug should not be prescribed to pregnant women.
The safety of Serdolect in breastfeeding women has not been studied. In cases where the use of sertindole is considered necessary, breastfeeding should be discontinued.
Children and youth (up to 18 years old)
The safety and effectiveness of Serdolect in children and adolescents has not been studied, therefore the drug should not be used in children and adolescents.
Effect on the ability to drive a car or use other machinery
Although Serdolect does not have a sedative effect, patients are not recommended to drive a car or use other machinery while taking it until individual tolerance to the drug has been established.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Sertindole
Composition
Composition
active ingredient:
sertindole 4 mg.
excipients
– corn starch,
lactose monohydrate,
microcrystalline cellulose,
hyprolose, magnesium stearate,
sodium croscarmellose.
shell – hypromellose,
titanium dioxide (E171),
Macragol 400 and iron oxide yellow (E172)
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
The safety of using the drug Serdolect during pregnancy and lactation has not been studied.
Prescription during pregnancy is contraindicated.
If it is necessary to use Serdolect during lactation, breastfeeding should be stopped.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the drug Serdolect or its components.
Serdolect is contraindicated in case of uncorrectable hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia.
Serdolect should not be prescribed if patients have a status or history of severe cardiovascular diseases, congestive heart failure, myocardial hypertrophy, arrhythmia or bradycardia (less than 50 beats per minute).
The drug should not be prescribed to patients with congenital long QT interval syndrome or if this syndrome is present in the patient’s relatives, as well as in cases of acquired long QT interval (over 450 ms in men and 470 ms in women).
Serdolect should not be prescribed together with drugs that prolong the QT interval: class IA and III antiarrhythmics (quinidine, sotalol, amiodarone, dofetilide, etc.), some antipsychotics (thioridazine), some macrolide antibiotics (erythromycin) and quinolone antibiotics (gatifloxacin), some antihistamines (terfenadine, astemizole), as well as cisapride, lithium and other drugs that increase the QT interval.
Serdolect should also not be prescribed together with drugs that inhibit cytochrome P450 3A: azole antifungals (ketoconazole, itraconazole), macrolide antibiotics (erythromycin, clarithromycin), HIV proteinase inhibitors (indinavir), some calcium channel blockers (verapamil, diltiazem), as well as cimetidine and other drugs, which are inhibitors of cytochrome P450 3A.
Serdolect is contraindicated in cases of severe liver failure. Pregnancy, lactation, age under 18 years (the safety and effectiveness of the drug in these groups of patients have not been established).
Side Effects
Side Effects
The following side effects are observed (in order of decreasing frequency):
rhinitis and difficulty breathing through the nose,
reduction in ejaculate volume,
dizziness,
dry mouth,
postural hypotension,
weight gain,
peripheral edema,
dyspnea,
paresthesia,
prolongation of the QT interval,
leukocyturia and hematuria,
hyperglycemia,
syncope,
seizure disorders,
movement disorders, including tardive dyskinesia,
paroxysms of ventricular tachycardia (such as “torsade de pointes”).
Extrapyramidal symptoms with sertindole occur with the same frequency as with placebo.
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome is very rare.
Some side effects, such as postural hypotension, are transient and occur early in therapy.
Interaction
Interaction
The risk of QT interval prolongation increases with concomitant treatment with drugs that prolong the QT interval or inhibit the metabolism of sertindole. The use of Serdolect simultaneously with such drugs is prohibited. Sertindole is metabolized by cytochromes P450 2D6 and P450 3A.
The concentration of sertindole in plasma increases when taken simultaneously with drugs that inhibit cytochrome P450 2D6 (fluoxetine, paroxetine, quinidine, etc.). It may be necessary to prescribe a lower maintenance dose, as well as perform an ECG examination before and after changing the dose of these drugs.
In turn, sertindole and its main metabolites have a weak inhibitory effect on the activity of cytochrome P4502D6, through which β-blockers, antiarrhythmics, some antihypertensive drugs, and a large number of antipsychotic drugs and antidepressants are metabolized.
The simultaneous use of sertindole and macrolide antibiotics (erythromycin) and calcium channel blockers (diltiazem, verapamil) may lead to a slight increase (4502D6). Since it is quite difficult to routinely identify these patients, the simultaneous use of sertindole and drugs that inhibit cytochrome P450 3A is contraindicated, as this can lead to a significant increase in the level of sertindole plasma concentration.
The metabolism of sertindole can be significantly enhanced, leading to a decrease in its concentration in the blood plasma, under the influence of the following drugs – rifampicin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, phenobarbital. A decrease in the antipsychotic activity of sertindole in such cases may require an increase in its dose.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms.
Drowsiness, slurred speech, tachycardia, decreased blood pressure and transient increase in QT interval. The development of paroxysms of ventricular tachycardia (such as “torsade de pointes”) is possible, especially in cases where sertindole is used in conjunction with drugs that can cause this type of side effect.
Treatment.
In case of overdose, the drug should be discontinued immediately and measures should be taken to maintain airway patency and adequate oxygenation.
Monitoring of ECG and vital signs should be started immediately. In cases of increased QT interval, ECG monitoring is carried out until this indicator normalizes, and the half-life of sertindole should be taken into account (from 2 to 4 days).
An intravenous catheter should be installed, gastric lavage, activated charcoal and laxatives should be prescribed.
There is no specific antidote and the drug cannot be removed by dialysis. Therefore, maintenance therapy should be prescribed. Correction of decreased blood pressure and manifestations of vascular collapse is carried out using intravenous solutions. If sympathomimetics are used, adrenaline or dopamine should be used with caution, since stimulation of β-adrenergic receptors, together with the antagonistic effect on α1-adrenergic receptors inherent in sertindole, can lead to a pronounced decrease in blood pressure.
If antiarrhythmics are used, it should be taken into account that drugs such as quinidine, disopyramide, procainamide can potentially increase the QT interval.
In case of severe extrapyramidal disorders, anticholinergic drugs should be prescribed. The patient should be under constant medical supervision until complete recovery.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
5 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
H. Lundbeck A/O, Denmark
Additional information
| Shelf life | 5 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a light-protected place, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Х. Lundbeck A/O, Denmark |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Х. Lundbeck A/O |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Serdollect, 4 mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.