No products in the cart.
Sedalgin Plus, tablets 10 pcs
€9.75 €8.53
Description
Sedalgin Plus is a combined drug with analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effect.
Sodium metamizole is a derivative of pyrazolone and has analgesic, antipyretic and mild anti-inflammatory effects, the mechanism of which is associated with inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis by inhibiting cyclooxygenase.
Caffeine has a stimulating effect on the central nervous system (CNS), mainly on the cerebral cortex, respiratory and vasomotor centers.
It increases mental and physical performance, reduces sleepiness and fatigue. Caffeine increases permeability of histohematic barriers and increases bioavailability of non-narcotic analgesics, thus strengthening the therapeutic effect.
Thiamine (vitamin B,) is involved in metabolism and helps to improve nerve-reflex
conduction.
Indications
Indications
Moderate or mild pain syndrome of various origins: headache (including migraine), toothache, neuralgia, muscle pain (myalgia), joint pain (arthralgia), radicular syndrome, menstrual pain (algodismenorrhea).
Feverish syndrome with “colds” and other infectious and inflammatory diseases (with an established diagnosis).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Sedalgin Plus is a combined drug that has analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects.
Metamizole sodium is a pyrazolone derivative and has an analgesic, antipyretic and weak anti-inflammatory effect, the mechanism of which is associated with inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis due to inhibition of cyclooxygenase.
Caffeine has a stimulating effect on the central nervous system (CNS), mainly on the cerebral cortex, respiratory and vasomotor centers.
Increases mental and physical performance, reduces drowsiness and fatigue. Caffeine increases the permeability of histohematological barriers and increases the bioavailability of non-narcotic analgesics, thereby enhancing the therapeutic effect.
Thiamine (vitamin B) is involved in metabolism and helps improve neuro-reflex
conductivity.
Special instructions
Special instructions
When treating patients receiving cytotoxic drugs, the drug should only be taken under medical supervision.
Anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions
The following conditions cause an increased risk of developing hypersensitivity reactions to metamizole sodium:
bronchial asthma induced by analgesics;
intolerance to analgesics such as urticaria or angioedema;
complete or incomplete combination of bronchial asthma, recurrent polyposis of the nose and paranasal sinuses and intolerance to acetylsalicylic acid or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (including a history);
chronic urticaria;
alcohol intolerance (increased sensitivity to alcohol), against the background of which, even when taking a small amount of certain alcoholic beverages, patients experience sneezing, lacrimation and severe redness of the face. Alcohol intolerance may indicate a previously unidentified syndrome of bronchial asthma associated with analgesics (aspirin asthma);
intolerance or hypersensitivity to dyes (for example, tartrazine) or to preservatives (for example, benzoates);
history of anaphylactic or other immunological reactions to other pyrazolones, pyrazolidines and other non-narcotic analgesics (see section “Contraindications”).
If the patient is at particular risk of developing anaphylactoid reactions, the drug should be prescribed only after carefully weighing the possible risks and expected benefits. If a decision is made to use the drug in such patients, strict medical monitoring of their condition will be required, and it is necessary to have the means to provide emergency care for them in the event of anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions.
In predisposed patients, anaphylactic shock may occur, so patients with bronchial asthma or atopy should be prescribed metamizole sodium with caution.
Severe skin reactions
Life-threatening skin reactions, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS) and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), have been described with the use of metamizole sodium. If symptoms of SJS or TEN (such as a progressive skin rash, often with blistering or mucosal lesions) appear, treatment with the drug should be stopped immediately. It is prohibited to ever repeat treatment with the drug.
Skin reactions should be carefully monitored, especially during the first weeks of treatment.
Agranulocytosis
Agranulocytosis, which develops during treatment with metamizole, is of immunoallergic origin and lasts for at least one week. This reaction occurs very rarely and can be severe, life-threatening and even fatal. This reaction is not dose-related and may occur at any time during treatment.
It is necessary to stop using the drug and immediately consult with your doctor if the following subjective or objective symptoms, possibly associated with neutropenia, appear: fever, chills, sore throat, mouth ulcers. In case of development of neutropenia (number of neutrophils <1500 per mm3), it is necessary to immediately stop treatment, urgently perform a detailed general blood test and continue monitoring the blood composition until the number of formed elements returns to normal values.
Pancytopenia
If pancytopenia develops, treatment should be stopped immediately, and complete blood count parameters should be monitored until they return to normal.
It is necessary to immediately seek medical help if subjective or objective symptoms appear during treatment with the drug that suggest pathological changes in the blood (for example, general malaise, infections, persistent fever, hematoma formation, bleeding, pallor).
Isolated hypotensive reactions
The use of metamizole sodium may cause isolated hypotensive reactions. These reactions may be dose dependent and occur more often after parenteral administration.
Acute abdominal pain
It is inadmissible to use the drug Sedalgin® Plus to relieve acute abdominal pain (until the cause is determined).
Liver and kidney dysfunction
In patients with impaired liver or kidney function, Sedalgin® Plus should be used only after consulting a doctor, since in these patients the rate of elimination of the drug is reduced.
Impact on laboratory results
In patients treated with metamizole sodium, changes in the results of laboratory tests performed using the Trinder test and similar tests (for example, analysis of serum creatinine, triglycerides, HDL cholesterol and uric acid concentrations) were recorded.
Caffeine may interfere with test results using adenosine or dipyridamole, so you should not take Sedalgin® Plus less than 12 hours before the test.
The wheat starch in Sedalgin® Plus contains a trace amount of gluten (considered gluten-free) and is unlikely to cause problems in patients with celiac disease. One tablet contains no more than 0.01 micrograms of gluten. Patients with allergies to wheat (except celiac disease) should not take this medicine. Effect on the ability to drive vehicles, operate machinery
There is no evidence that the drug Sedalgin® Plus, used in recommended doses, has an undesirable effect on the ability to concentrate and on the speed of reactions.
However, when treating the drug in high doses, the possibility of impaired concentration and decreased reaction speed should be taken into account, which may pose a risk in situations where these abilities are especially important (for example, driving a car or moving machinery), especially with concomitant alcohol use.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
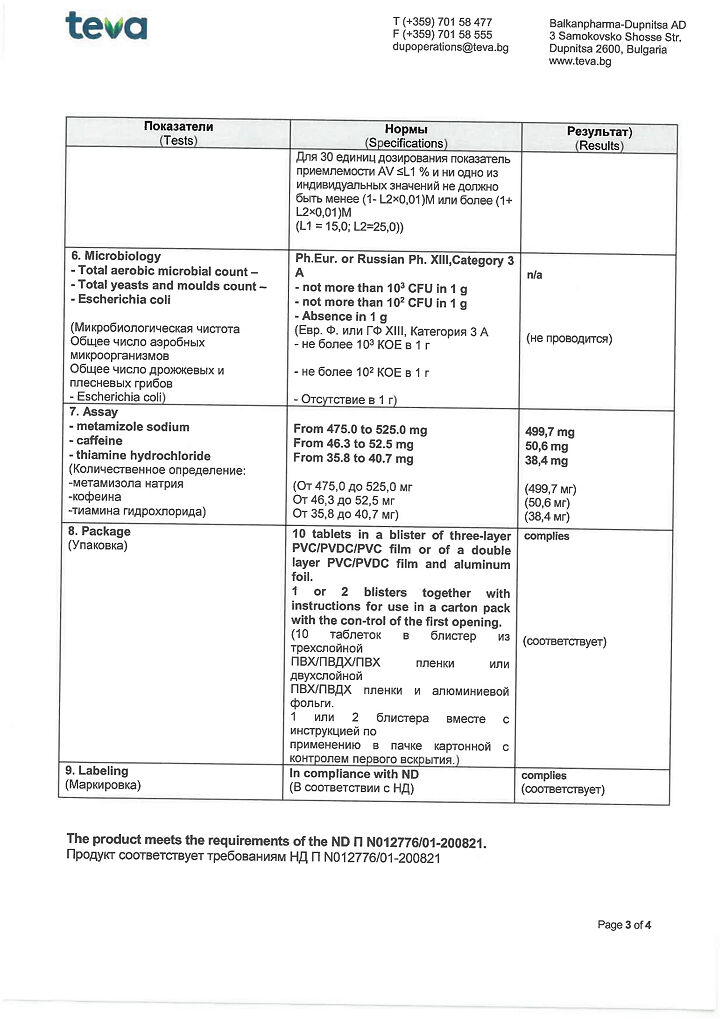
Metamizole Sodium, Caffeine, Thiamine
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
active ingredients:
metamizole sodium 500 mg,
caffeine 50 mg,
thiamine hydrochloride 38.75 mg;
excipients:
microcrystalline cellulose 45.75 mg,
wheat starch 11.00 mg,
gelatin 4.00 mg,
colloidal silicon dioxide 2.50 mg,
talc 12.00 mg,
magnesium stearate 6.00 mg.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Data related to metamizole
Pregnancy
There is no data on the negative effect of metamizole on the fetus: in rats and rabbits, metamizole did not have a teratogenic effect, and a toxic effect on the fetus was observed only at high doses that are toxic to the mother’s body. However, there is insufficient clinical data on the use of Sedalgin® Plus during pregnancy.
Metamizole crosses the placenta.
The use of Sedalgin® Plus during pregnancy is contraindicated. This is due to the fact that, although metamizole is a weak inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis, it is impossible to completely exclude the possibility of premature closure of the ductus arteriosus and complications in the perinatal period associated with impaired aggregation ability of platelets of the mother and newborn.
Breastfeeding period
Metamizole metabolites pass into breast milk. Breastfeeding is not allowed during treatment with Sedalgin® Plus and for 48 hours after the last dose of the drug.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to metamizole sodium, caffeine, thiamine and/or excipients, as well as to other pyrazolones (phenazole, propyphenazole, isopropylaminophenazole) or pyrazolidones (phenylbutazone, oxyphenbutazole), including, for example, a history of agranulocytosis when using one of the drugs.
Impaired bone marrow hematopoiesis (for example, after treatment with cytostatics) or diseases of the hematopoietic environment.
An indication in the medical history of the development of bronchospasm or other anaphylactic reactions (for example, urticaria, rhinitis, angioedema) when using analgesic drugs such as salicylates, paracetamol, diclofenac, ibuprofen, indomethacin, naproxen).
Acute intermittent hepatic porphyria (risk of developing exacerbations of porphyria).
Congenital deficiency of 6-phosphate dehydrogenase (risk of hemolysis).
Pregnancy.
Breastfeeding period.
Children’s age (up to 15 years).
With caution
For arterial hypotension (systolic blood pressure below 100 mm Hg), hemodynamic instability (myocardial infarction, multiple trauma, incipient shock), decreased circulating blood volume, incipient heart failure, high fever (increased risk of a sharp decrease in blood pressure).
For diseases in which a significant decrease in blood pressure may pose an increased danger (patients with severe coronary heart disease and severe stenosis of the cerebral arteries).
For alcoholism.
With an increased risk of developing severe anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions in patients with:
bronchial asthma, especially in combination with concomitant polypous rhinosinusitis;
chronic urticaria and other types of atopy (allergic diseases, in the development of which a significant role is played by a hereditary predisposition to sensitization: polynoses, allergic rhinitis, etc.);
alcohol intolerance (reaction to even small amounts of certain alcoholic beverages, with symptoms such as itching, watery eyes and severe redness of the face);
intolerance to dyes (for example, tartrazine) or preservatives (for example, benzoates).
In case of severe impairment of liver and kidney function (the use of low doses is recommended due to the possibility of slowing down the excretion of metamizole sodium).
Side Effects
Side Effects
Adverse reactions are systematized in accordance with the World Health Organization (WHO) Classification: very common (≥1/10); often (≥1/100, <1/10); uncommon (≥1/1000, <1/100); rare (≥1/10000, <1/1000); very rare (< 1/10000); frequency unknown (cannot be determined from available data).
Blood and lymphatic system disorders
Frequency unknown: transient leukopenia, agranulocytosis, hemolytic anemia, purpura, thrombocytopenia.
Immune system disorders
Frequency unknown: anaphylactic shock or other anaphylactic reactions.
Nervous system disorders
Frequency unknown: insomnia, vertigo, increased excitability.
Heart disorders
Frequency unknown: tachycardia, palpitations.
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders Frequency unknown: bronchospasm.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Frequency unknown: loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, cholestasis, jaundice.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Frequency unknown: rash, itching.
All side effects should be reported to your doctor.
Interaction
Interaction
The simultaneous use of Sedalgin® Plus with other drugs requires caution due to the content of metamizole sodium, which, with a single use, can affect the metabolism of the drug, and with long-term use is an enzyme inducer.
Sedalgin® Plus may reduce serum concentrations of cyclosporine and may compromise tissue transplantation, so cyclosporine concentrations should be monitored when used together.
The simultaneous use of Sedalgin® Plus with other non-narcotic analgesics, antipyretics and anti-inflammatory drugs can lead to mutual enhancement of toxic effects and also increases the risk of hypersensitivity reactions.
Tricyclic antidepressants, oral contraceptives and allopurinol interfere with the metabolism of metamizole sodium in the liver and increase its toxicity.
Barbiturates, phenylbutazone and other inducers of microsomal liver enzymes weaken the effect of metamizole sodium.
Neuroleptics, sedatives and tranquilizers enhance the analgesic effect of Sedalgin® Plus. When used together with chlorpromazine, severe hypothermia may develop.
Metamizole sodium, displacing oral hypoglycemic agents, indirect anticoagulants, glucocorticosteroids and indomethacin (drugs that are highly bound to plasma proteins) from binding to plasma proteins, enhances their effect.
When used simultaneously with myelotoxic drugs (for example, gold salt preparations, antitumor agents, chloramphenicol, etc.), the hematotoxicity of metamizole sodium increases and there is a risk of damage to white blood cells.
The addition of metamizole sodium to methotrexate treatment may enhance the hematotoxic effects of methotrexate, especially in elderly patients. Therefore, the combined use of these drugs should be avoided.
Thiamazole and sarcolysine, when used together with metamizole sodium, increase the risk of developing leukopenia.
Codeine, H2-histamine receptor blockers and propranolol enhance the effects of metamizole sodium.
During treatment with metamizole sodium, radiocontrast agents, colloidal blood substitutes and penicillin should not be used (increased risk of developing anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions).
When used together, metamizole sodium may reduce the effect of acetylsalicylic acid on platelet aggregation. Therefore, this combination should be used with caution when treating patients taking low doses of acetylsalicylic acid for cardioprotection (prevention of thrombus formation).
Metamizole sodium may reduce the concentration of bupropion in the blood, which should be taken into account when using metamizole sodium and bupropion simultaneously.
Concomitant use with sympathomimetics can cause overexcitation of the central nervous system.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms
In case of overdose, the following symptoms may occur: nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, decreased renal function/acute renal failure with oliguria (for example, due to the development of interstitial nephritis), more rarely, symptoms from the central nervous system (excitement, insomnia, headache, dizziness), tinnitus, melena, hematomas, as well as heart rhythm disturbances (tachycardia). In more severe cases – oliguria to anuria, epileptopharyngeal seizures, coma, convulsions, agranulocytosis, aplastic or hemolytic anemia, hemorrhagic diathesis.
After administration of very high doses of the drug, excretion through the kidneys of the non-toxic metabolite of metamizole sodium (rubazonic acid) may cause red coloration of urine.
Treatment
If you have recently taken the drug, primary detoxification measures can be taken to limit further absorption of the drug (use of emetics, gastric lavage, activated charcoal, laxatives). There is no specific antidote. The main metabolite of metamizole (4-N-methylaminoantipyrine) is eliminated by hemodialysis, hemofiltration, hemoperfusion or plasma filtration. Symptomatic treatment is used if necessary. With the development of convulsive syndrome – intravenous administration of diazepam and fast-acting barbiturates.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Keep out of the reach of children!
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Balkanpharma-Troyan AD, Bulgaria
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Keep out of reach of children! |
| Manufacturer | Balkanpharma – Troyan AD, Bulgaria |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Balkanpharma – Troyan AD |
Related products
Buy Sedalgin Plus, tablets 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.