No products in the cart.
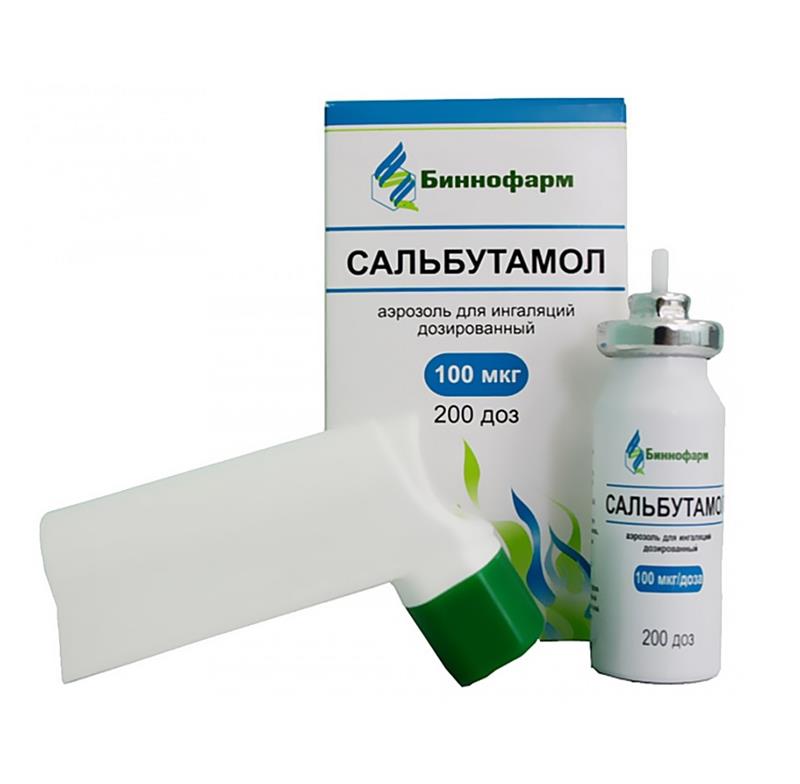
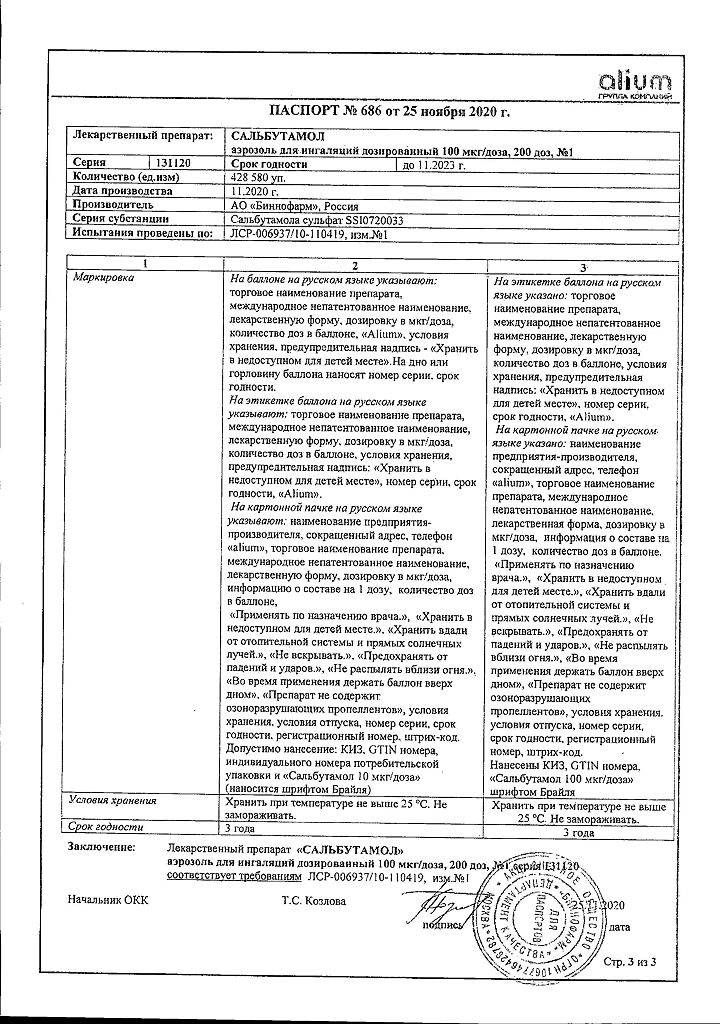
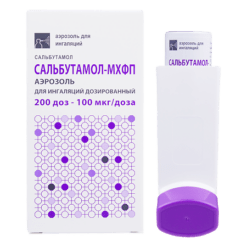
Salbutamol, 100 mcg/dose 12 ml aerosol (200 doses)
€4.52 €4.01
Description
Salbutamol is a selective β2-adrenoreceptor agonist. In therapeutic doses it acts on β2-adrenoceptors of bronchial smooth muscle, with a minor effect on β1-receptors of the myocardium. It has a pronounced bronchodilator effect, preventing or arresting bronchial spasm, reduces airway resistance. Increases the vital capacity of the lungs.
In the recommended therapeutic doses it does not have adverse effects on the cardiovascular system and does not cause increase of blood pressure.
To a lesser extent, in comparison with the drugs of this group, it has positive chrono- and inotropic effects. Causes dilation of coronary arteries.
It has a number of metabolic effects: it decreases the concentration of potassium in the plasma, affects glycogenolysis and insulin secretion, has hyperglycemic (especially in patients with bronchial asthma) and lipolytic effect, increasing the risk of acidosis.
After the use of inhaled forms, the effect is rapid, the beginning of the effect – in 5 minutes, the maximum effect – in 30-90 minutes (75% of the maximum effect is achieved within 5 minutes), duration – 4-6 hours.
Indications
Indications
1. Bronchial asthma:
– relief of attacks of bronchial asthma, including exacerbation of severe bronchial asthma;
– prevention of bronchospasm attacks associated with exposure to an allergen or caused by physical activity;
– use as one of the components in long-term maintenance therapy of bronchial asthma.
2. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), accompanied by reversible airway obstruction, chronic bronchitis.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Salbutamol is a selective β2-adrenergic receptor agonist. In therapeutic doses, it acts on β2-adrenergic receptors of bronchial smooth muscle, having a slight effect on β1-receptors of the myocardium. It has a pronounced bronchodilator effect, preventing or relieving bronchospasm, and reduces resistance in the respiratory tract. Increases vital capacity of the lungs.
In recommended therapeutic doses, it does not have a negative effect on the cardiovascular system and does not cause an increase in blood pressure.
To a lesser extent, compared with drugs of this group, it has a positive chrono- and inotropic effect. Causes dilation of the coronary arteries.
It has a number of metabolic effects: it reduces the concentration of potassium in plasma, affects glycogenolysis and insulin secretion, has a hyperglycemic (especially in patients with bronchial asthma) and lipolytic effect, increasing the risk of developing acidosis.
After using inhalation forms, the action develops quickly, the onset of the effect is after 5 minutes, the maximum is after 30-90 minutes (75% of the maximum effect is achieved within 5 minutes), the duration is 4-6 hours.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Patients should be instructed on the correct use of Salbutamol. Correct use of the drug and strict adherence to the instructions are necessary to ensure that salbutamol enters the bronchi. At the beginning of treatment, the drug should be used under the supervision of medical personnel and after training in front of a mirror.
As with other inhaled medications, the therapeutic effect may decrease as the balloon cools. Therefore, before use, the container with the drug must be warmed to room temperature (warm the container with your hands for several minutes, other methods cannot be used!).
The contents of the cylinders are under pressure and therefore the cylinders must not be heated, broken, punctured or burned, even when empty.
If you experience discomfort in the mouth or a sore throat after inhalation, rinse your mouth with water.
Bronchodilators should not be the only or main component of the treatment of unstable or severe bronchial asthma.
If the effect of the usual dose of the drug becomes less effective or shorter lasting (the effect of the drug should last at least 3 hours), the patient should consult a doctor. Increasing the dose or frequency of taking salbutamol should only be done under the supervision of a physician. Reducing the interval between taking subsequent doses is possible only in exceptional cases and must be strictly justified. An increased need for the use of inhaled β2-adrenergic receptor agonists with a short duration of action for the treatment of bronchial asthma indicates an exacerbation of the disease. In such cases, the patient’s treatment plan should be reconsidered. Taking high doses of salbutamol during exacerbation of bronchial asthma can cause “rebound” syndrome (each subsequent attack becomes more intense). In case of a severe attack of suffocation, the break between inhalations should be at least 20 minutes.
The risk of complications increases both with a significant duration of treatment and with abrupt discontinuation of the drug. Long-term use of salbutamol should be accompanied by the use of anti-inflammatory drugs for basic therapy.
A sudden and progressive deterioration of bronchial asthma can pose a threat to the patient’s life, so in such cases it is necessary to urgently decide on prescribing or increasing the dose of glucocorticosteroids. In such patients, daily monitoring of peak expiratory flow is recommended.
Salbutamol should be used with caution in patients with thyrotoxicosis.
Therapy with β2-adrenergic agonists, especially when administered parenterally or when administered via nebulizer, can lead to hypokalemia. Particular caution is recommended when treating severe attacks of bronchial asthma, since in these cases hypokalemia may increase as a result of the simultaneous use of xanthine derivatives, glucocorticosteroids, diuretics, as well as due to hypoxia. In such cases, it is necessary to monitor the level of potassium in the blood serum.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Salbutamol
Composition
Composition
1 dose of the drug contains:
Active ingredient:
salbutamol sulfate (calculated as 100% substance) 0.1208 mg (equivalent to 0.1 mg of salbutamol).
Excipients:
oleyl alcohol 0.0625 mg,
ethanol (rectified ethyl alcohol) 2.02 mg,
propellant R 134a (1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane, HFA 134a) 56.91 mg.
The drug does not contain chlorofluorocarbon propellants.
1 bottle of the drug contains:
Active ingredient:
salbutamol sulfate (calculated as 100% substance) 0.029 g (equivalent to 0.024 g of salbutamol).
Excipients:
oleyl alcohol 0.015 g,
ethanol (rectified ethyl alcohol) 0.485 g,
propellant R 134a (1,1,1,2-tetrafluoroethane, HFA 134a) 13.659 g (up to 12.00 ml).
The drug does not contain chlorofluorocarbon propellants.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to any component of the drug.
Children under 2 years of age.
With caution:
If there is a history of tachyarrhythmia, myocarditis, heart defects, aortic stenosis, coronary heart disease, severe chronic heart failure, arterial hypertension, thyrotoxicosis, pheochromocytoma, decompensated diabetes mellitus, glaucoma, seizures, renal or liver failure.
With simultaneous use of non-selective β2-blockers, pregnancy, and lactation.
Side Effects
Side Effects
By frequency, side effects can be divided into the following categories: very common (1/10), common (1/100 and <1/10), uncommon (1/1000 and <1/100), rare (1/10,000 and <1/100), very rare (<1/10,000).
From the immune system: rarely – dermatitis, very rarely – hypersensitivity reactions, including angioedema, skin rash.
From the side of metabolic processes: rarely – hypokalemia.
From the nervous system: often – tremor, headache, anxiety; rarely – dizziness, drowsiness, fatigue; very rarely – hyperactivity.
From the cardiovascular system: often – tachycardia, palpitations; rarely – dilatation of peripheral vessels with skin hyperemia, discomfort or chest pain; very rarely – arrhythmia, including atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia, extrasystole, decreased blood pressure and collapse.
From the respiratory system: rarely – cough, irritation of the respiratory tract; very rarely – bronchospasm (paradoxical or caused by hypersensitivity to the drug).
From the gastrointestinal tract: rarely – dryness and irritation of the mucous membrane of the mouth and pharynx, changes in taste, nausea, vomiting.
From the musculoskeletal system: rarely – muscle cramps.
Interaction
Interaction
It is not recommended to use salbutamol and non-selective β2-adrenergic receptor blockers simultaneously, such as propranolol.
Salbutamol is not contraindicated in patients receiving monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs).
Enhances the effect of central nervous system stimulants.
Theophylline and other xanthines, when used simultaneously, increase the likelihood of developing tachyarrhythmias; agents for inhalation anesthesia, levodopa – severe ventricular arrhythmias.
Simultaneous use with m-anticholinergic blockers (including inhaled ones) may increase intraocular pressure.
Diuretics and glucocorticosteroids enhance the hypokalemic effect of salbutamol.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms:
More frequent – hypokalemia, decreased blood pressure, tachycardia, muscle tremors, nausea, vomiting; less frequent – agitation, hyperglycemia, respiratory alkalosis, hypoxemia, headache; rare – hallucinations, convulsions, tachyarrhythmia, ventricular flutter, dilatation of peripheral vessels.
Treatment:
In case of salbutamol overdose, the best antidotes are cardioselective β2-blockers. However, β2-adrenergic receptor blockers must be used with caution (risk of bronchospasm).
The use of large doses of salbutamol can cause hypokalemia, therefore, if an overdose is suspected, the concentration of potassium in the blood serum should be monitored.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. Do not freeze.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Keep away from heating systems and direct sunlight.
Protect from falls and impacts.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years. Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Binnopharm, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. Do not freeze. Store out of the reach of children. Store away from heating system and direct sunlight. Please protect from falls and impacts. |
| Manufacturer | Binnopharm, Russia |
| Medication form | metered aerosol for inhalation |
| Brand | Binnopharm |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Salbutamol, 100 mcg/dose 12 ml aerosol (200 doses) with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.