No products in the cart.
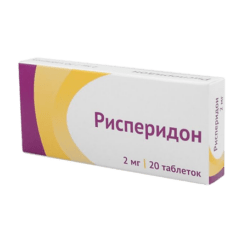
Risperidone 2 mg, 20 pcs.
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
- treatment of schizophrenia (including. Acute psychosis for the first time, acute onset of schizophrenia, chronic schizophrenia);
- psychotic conditions with pronounced productive (hallucinations, delusions, thought disorders, hostility, suspiciousness) and/or negative (blunted affect, emotional and social withdrawal, poor speech) symptomatology;
- to reduce affective symptoms (depression, guilt, anxiety) in patients with schizophrenia;
- treatment of behavioral disorders in patients with dementia when symptoms of aggression (angry outbursts, physical violence), mental disturbances (agitation, delirium) or psychotic symptoms are present;
- treatment of mania in bipolar disorders (as a mood stabilizer as an adjunctive therapy).
.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
active ingredient:
Spiridone – 2,000 mg;
excipients:
Lactose monohydrate, 145,000 mg;
Microcrystalline cellulose, 40,000 mg;
Corn starch, 10,000 mg;
colloidal silicon dioxide – 1,000 mg;
magnesium stearate – 2,000 mg;
film shell:
[hypromellose – 3,600 mg, talc – 1,200 mg, titanium dioxide – 0,660 mg, macrogol 4000 (polyethylene glycol 4000) – 0,540 mg] or [dry film coating mixture containing hypromellose (60%), talc (20%), titanium dioxide (11%), macrogol 4000 (polyethylene glycol 4000) (9%)] – 6,000 mg.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Individual.
The initial dose for adults when taken orally is 0.25-2 mg/day; on day 2, it is 4 mg/day. Thereafter, the dose can either be maintained at the same level or adjusted if necessary. Usually the optimal therapeutic dose, depending on indications, is in the range of 0.5-6 mg/day. In some cases, a slower dose increase and lower starting and maintenance doses may be warranted.
In schizophrenic patients for the elderly, as well as in patients with concomitant liver and kidney disease, an initial dose of 500 mcg 2 times/day is recommended. If necessary, the dose can be increased to 1-2 mg 2 times/day.
Maximum dose:When using risperidone at a dose greater than 10 mg/day, there is no increase in effectiveness compared to lower doses, but the risk of extrapyramidal symptoms increases. The safety of risperidone at doses greater than 16 mg/day has not been studied, so further overdosing is not allowed.
Interaction
Interaction
Risperidone decreases the effectiveness of levodopa and dopamine agonists. Phenothiazines, tricyclic antidepressants and beta-adrenoblockers increase the plasma concentration of risperidone (does not affect the concentration of the active antipsychotic fraction).
Concomitant administration of carbamazepine and other inducers of microsomal enzymes decreases the concentration of the active antipsychotic fraction of risperidone in plasma. Clozapine decreases clearance of risperidone.
When used concomitantly with risperidone, ethanol, drugs that depress the central nervous system (CNS) lead to additive suppression of CNS function.
Hypotensive drugs increase the severity of BP reduction with risperidone.
Fluoxetine may increase the plasma concentration of risperidone (to a lesser extent, its active antipsychotic fraction).
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Cautiously use in patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system (including heart failure, myocardial infarction, cardiac conduction disorders), as well as in dehydration, hypovolemia or cerebrovascular disorders. In this category of patients the dose should be increased gradually.
The risk of orthostatic hypotension is particularly increased during the initial period of dose adjustment. If hypotension occurs, dose reduction should be considered.
The occurrence of tardive dyskinesia characterized by involuntary rhythmic movements (predominantly of the tongue and/or face) has been reported with the use of drugs with dopamine receptor antagonist properties. The occurrence of extrapyramidal symptoms has been reported to be a risk factor for the development of tardive dyskinesia. Risperidone causes the occurrence of extrapyramidal symptoms to a lesser extent than classical neuroleptics. Withdrawal of all antipsychotics should be considered if symptoms of tardive dyskinesia occur.
If MNS develops, all antipsychotics, including risperidone, should be discontinued.
Risperidone should be used with caution in patients with Parkinson’s disease because it is theoretically possible to worsen this condition.
The classical neuroleptics are known to lower the seizure threshold. Given this, risperidone is recommended with caution in patients with epilepsy.
Risperidone should be used with caution in combination with other centrally acting drugs.
When carbamazepine and other hepatic enzyme inducers are withdrawn, the dose of risperidone should be reviewed and, if necessary, reduced.
Patients should be advised to refrain from overeating during treatment due to the possibility of weight gain.
There are no data on the safety of risperidone in children under 15 years of age.
Influence on driving and operating machinery
Patients should avoid driving and other activities requiring high concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions during treatment, until individual sensitivity to risperidone is determined.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to risperidone.
Side effects
Side effects
CNS side:often – insomnia, agitation, anxiety, headache; possible – drowsiness, fatigue, dizziness, impaired ability to concentrate, visual disturbances; rarely – extrapyramidal symptoms, (including tremor, rigidity, hypersalivation, bradykinesia, akathisia, acute dystonia). In patients with schizophrenia, tardive dyskinesia, ZNS, thermoregulatory disorders, and seizures are possible.
In the digestive system: constipation, dyspeptic phenomena, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, increased activity of liver enzymes.
From the sexual system: priapism, erectile dysfunction, ejaculation disorders, orgasm disorders.
Cardiovascular system disorders:rarely – orthostatic hypotension and reflex tachycardia, arterial hypertension.
Endocrine system disorders:Galactorrhea, gynecomastia, menstrual cycle disorders, amenorrhea, weight gain.
With the hematopoietic system:a slight decrease in the number of neutrophils and/or platelets.
Allergic reactions:rhinitis, skin rash, angioedema.
Others: urinary incontinence.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms:drowsiness, sedation, tachycardia, decreased BP, extrapyramidal disorders, rarely – prolongation of the QT interval.
Treatment:Maintain free airway patency to ensure adequate oxygen supply and ventilation, gastric lavage (after intubation if patient is unconscious) and administration of activated charcoal along with laxatives. Immediately begin ECG monitoring to detect possible arrhythmias.
There is no specific antidote. Symptomatic therapy aimed at maintaining vital body functions should be carried out.
In case of BP decrease and vascular collapse – intravenous infusion of infusion solutions and/or adrenostimulants. In case of development of acute extrapyramidal symptoms – anticholinergic drugs. Continuous medical observation and monitoring should be continued until the symptoms of intoxication disappear.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Manufacturer | Vertex, Russia |
|---|---|
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Vertex |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Risperidone 2 mg, 20 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.