No products in the cart.
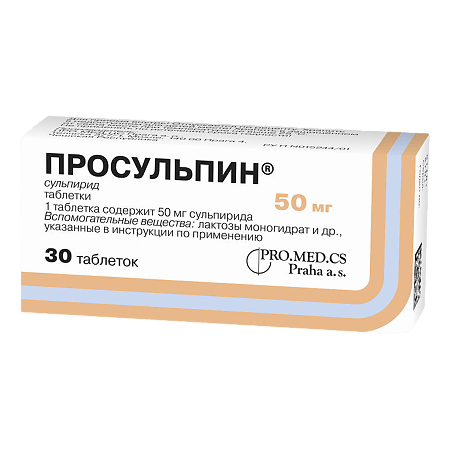
Prosulpine, tablets 50 mg 30 pcs
€3.99 €3.55
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Sulpiride is an atypical neuroleptic from the group of substituted benzamides. It has moderate neuroleptic activity in combination with stimulant and thymoanaleptic (antidepressant) action.
The neuroleptic effect is associated with antidopaminergic action. It blocks dopaminergic D2- and D3-receptors, acts insignificantly on the neostriate system, and has an antipsychotic effect. The antipsychotic effect of sulpiride is seen in doses greater than 600 mg/day, in doses up to 600 mg/day the stimulant and antidepressant effects predominate.
Sulpiride has no significant effect on noradrenergic, acetylcholine, serotonin, histamine and GABA receptors.
In low doses, sulpiride may be used as an adjunctive agent in the treatment of psychosomatic diseases, particularly gastric and duodenal ulcer. In irritable colon syndrome it reduces the intensity of abdominal pain.
Low doses of sulpiride (50-300 mg/day) are effective for dizziness.
Stimulates prolactin secretion and has a central antiemetic effect (inhibition of the vomiting center).
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration of a 200 mg dose, Cmax in plasma is reached after approximately 4.5 hours. Bioavailability is 25-35%. Binding to plasma proteins is less than 40%. It penetrates rapidly into the liver and kidneys, slower – into brain tissue (the main amount of the drug is accumulated in the pituitary gland). The concentration of sulpiride in CNS is 2-5% of the plasma concentration. It penetrates the placental barrier. It is excreted unchanged by the kidneys through glomerular filtration (92%). Total clearance is 126 ml/min. T1/2 is 6-8 hours. With breast milk 0.1% of daily dose is excreted.
Indications
Indications
— psychosomatic diseases, incl. gastric and duodenal ulcers, gastrointestinal stress ulcers, drug-induced ulcers, symptomatic ulcers, ulcerative colitis and irritable bowel syndrome;
— dysphoric disorders;
– depression of various etiologies, incl. reactive (nosogenic);
– neuroses;
– acute and chronic psychotic disorders of various etiologies (including schizophrenia);
– migraine;
– dizziness of various etiologies (vertebrobasilar insufficiency, vestibular neuritis, Meniere’s disease, condition after traumatic brain injury, otitis media);
– in children – psychosis, behavioral disorders.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Sulpiride is an atypical antipsychotic from the group of substituted benzamides. It has moderate neuroleptic activity in combination with stimulating and thymoanaleptic (antidepressive) effects.
The neuroleptic effect is associated with an antidopaminergic effect. It blocks dopaminergic D2 and D3 receptors, has a slight effect on the neostriatal system, and has an antipsychotic effect. The antipsychotic effect of sulpiride is manifested in doses of more than 600 mg/day; in doses up to 600 mg/day, the stimulating and antidepressant effect predominates.
Sulpiride does not have a significant effect on noradrenergic, acetylcholine, serotonin, histamine and GABA receptors.
In small doses, sulpiride can be used as an adjuvant in the treatment of psychosomatic diseases, in particular gastric and duodenal ulcers. In case of irritable bowel syndrome, it reduces the intensity of abdominal pain.
Low doses of sulpiride (50-300 mg/day) are effective for dizziness.
Stimulates the secretion of prolactin and has a central antiemetic effect (suppression of the vomiting center).
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, doses of 200 mg Cmax in plasma are achieved in approximately 4.5 hours. Bioavailability is 25-35%. Plasma protein binding is less than 40%. It penetrates quickly into the liver and kidneys, and more slowly into brain tissue (the main amount of the drug accumulates in the pituitary gland). The concentration of sulpiride in the central nervous system is 2-5% of the plasma concentration. Penetrates through the placental barrier. Excreted unchanged by the kidneys through glomerular filtration (92%). Total clearance – 126 ml/min. T1/2 is 6-8 hours. 0.1% of the daily dose is excreted in breast milk.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Prescribe with caution to elderly people, because this category of patients often has increased sensitivity to the drug.
Caution should also be exercised when prescribing sulpiride to patients with diseases of the cardiovascular system, parkinsonism and young women with irregular menstrual cycles.
In patients with epilepsy, before starting treatment, it is necessary to conduct a preliminary clinical and electrophysiological examination, because the drug lowers the threshold for seizure activity.
Hyperthermia that develops during sulpiride therapy may be an early sign of neuroleptic malignant syndrome. If hyperthermia develops, the drug should be discontinued!
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
During the treatment period, you should refrain from driving a car, engaging in other potentially dangerous activities that require increased attention and speed of psychomotor reactions, as well as from drinking alcohol.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Sulpiride
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
Active ingredient:
sulpiride 50 mg
Excipients:
granulated microcrystalline cellulose,
lactose monohydrate,
granulated lactose,
sodium carboxymethylamylopectin,
corn starch,
magnesium stearate,
povidone 90.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
During pregnancy and lactation, it should be used with caution and in minimally effective doses, in cases where the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. Careful monitoring of the condition of the mother, fetus, and newborn is necessary. It is possible to develop extrapyramidal disorders in newborns whose mothers have used sulpiride for a long time.
Contraindications
Contraindications
– acute poisoning with alcohol, hypnotics, analgesics;
— hypertension stage 2-3;
– pheochromocytoma;
– psychomotor agitation;
– hypersensitivity to sulpiride.
With caution – pregnancy, lactation, neonatal period, old age, cardiovascular diseases; renal failure, parkinsonism, epilepsy.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the side of the central nervous system: sedation, drowsiness, headache; rarely – tremor, akathisia, extrapyramidal disorders, dyskinesia, anxiety, irritability, insomnia.
From the digestive system: dry mouth, heartburn, vomiting, constipation.
From the cardiovascular system: possible increase in blood pressure, tachycardia; rarely – arterial hypotension, orthostatic hypertension, dizziness.
From laboratory parameters: increased activity of hepatic transamiasis and alkaline phosphatase.
From the endocrine system: hyperprolactinemia, possible menstrual irregularities, decreased sexual activity, galactorrhea, gynecomastia, weight gain.
Allergic reactions: possible skin rash, eczematous rash, itching.
Other: visual acuity impairment.
Interaction
Interaction
The simultaneous use of sulpiride and drugs that depress the central nervous system (opioid analgesics, hypnotics, antihistamines, barbiturates, tranquilizers, centrally acting antitussives) can lead to an increase in the sedative effect of these drugs.
The combination of sulpiride with alcohol can also enhance the sedative effect of ethanol. Co-administration with levodopa should be avoided due to mutual antagonism of the drugs and a decrease in the effectiveness of sulpiride.
When taking sulpiride and antihypertensive drugs simultaneously, the hypotensive effect is enhanced and the risk of developing orthostatic hypotension increases.
Sucralfate, antacids containing magnesium or aluminum reduce the bioavailability of sulpiride by 20-40%.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: dyskinesia (spasm of masticatory muscles, spastic torticollis), extrapyramidal disorders, in some cases – coma.
Treatment: symptomatic therapy, centrally acting anticholinergics.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature of 15–25 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
PRO.MED.CS Prague, Czech Republic
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at 15-25 °C |
| Manufacturer | PRO.MED.CS Prague, Czech Republic |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | PRO.MED.CS Prague |
Related products
Buy Prosulpine, tablets 50 mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.