No products in the cart.
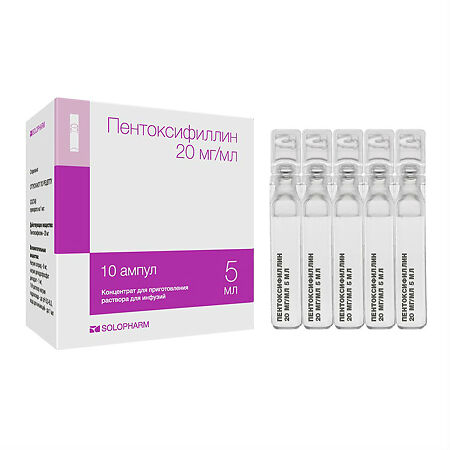
Pentoxifylline, 20 mg/ml concentrate 5 ml 10 pcs
€6.89 €6.03
Description
Pentoxifylline is a xanthine derivative. It improves microcirculation and rheological properties of blood. The mechanism of action is associated with inhibition of phosphodiesterase and increase of cyclic 3,5-adenosine monophosphate (3,5-AMP) in platelets and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in red blood cells with simultaneous saturation of energy potential, which in turn leads to vasodilation, reduction of total peripheral vascular resistance, increase of systolic and minute blood volume without significant change in heart rate.
Dilating coronary arteries increases oxygen delivery to the myocardium (minor antianginal effect), pulmonary vessels – improves blood oxygenation. When administered intravenously it leads to increased collateral circulation, increased blood volume flowing through a unit section.
Limits blood viscosity, causes platelet disaggregation, increases the elasticity of red blood cells (by influencing the pathologically altered deformability of red blood cells). Improves microcirculation in the areas of impaired circulation. In occlusive lesions of the peripheral arteries (intermittent claudication), leads to extension of walking distance, elimination of night cramps of the calf muscles and pain at rest.
Pharmacokinetics
The drug is rapidly metabolized in the liver after administration. During metabolism two main metabolites are formed: 1-(5-hydroxyhexyl)-3,7-dimethylxanthine (metabolite I) and 1-(3-carboxypropyl)-3,7-dimethylxanthine (metabolite V), which have similar activity to pentoxifylline.
1.5-2 hours after infusion, plasma concentrations of metabolites I and V are, respectively, 5 and 8 times higher than those of the parent substance. By the 8th hour, the concentration of pentoxifylline and its metabolites in blood decreases significantly (up to 10% of the initial concentration). The elimination half-life is from 30 minutes to 1.5 hours.
It is excreted mainly by the kidneys (94%) as metabolites (mainly metabolite V), the intestine (4%), in the first 4 hours it is eliminated up to 90% of the dose. 2% of the drug is excreted unchanged. Pentoxifylline and its metabolites do not bind to plasma proteins. It is excreted with breast milk.
In severe renal dysfunction, excretion of metabolites is delayed. In liver dysfunction, prolongation of the elimination half-life and increased bioavailability are noted.
Indications
Indications
– Peripheral circulation disorders due to atherosclerotic, diabetic and inflammatory processes (including intermittent claudication caused by atherosclerosis, diabetic angiopathy, obliterating endarteritis);
– trophic tissue disorders due to disruption of arterial and venous microcirculation (varicose ulcers, gangrene, frostbite);
– angioneuropathy (paresthesia, acrocyanosis, Raynaud’s disease); – acute and chronic disorders of cerebral circulation of the ischemic type (including cerebral atherosclerosis);
– conditions after hemorrhagic or ischemic stroke;
– circulatory disorders in the vessels of the eye (acute and chronic insufficiency of blood supply to the retina and choroid of the eye); – dysfunction of the middle ear of vascular origin, accompanied by hearing loss.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pentoxifylline is a xanthine derivative. Improves microcirculation and rheological properties of blood. The mechanism of action is associated with inhibition of phosphodiesterase and an increase in the content of cyclic 3,5-adenosine monophosphate (3,5-AMP) in platelets and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) in erythrocytes with simultaneous saturation of energy potential, which in turn leads to vasodilation, a decrease in total peripheral vascular resistance, an increase in systolic and minute blood volume without a significant change in heart rate abbreviations.
By expanding the coronary arteries, it increases the delivery of oxygen to the myocardium (minor antianginal effect), and the blood vessels of the lungs improve blood oxygenation. When administered intravenously, it leads to increased collateral circulation and an increase in the volume of blood flowing through a sectional unit.
Reduces blood viscosity, causes platelet disaggregation, increases the elasticity of red blood cells (due to the effect on the pathologically altered deformability of red blood cells). Improves microcirculation in areas of poor circulation. With occlusive lesions of the peripheral arteries (intermittent claudication), it leads to an increase in walking distance, elimination of night cramps of the calf muscles and pain at rest.
Pharmacokinetics
The drug after administration is quickly metabolized in the liver. During the metabolism, two main metabolites are formed: 1-(5-hydroxyhexyl)-3,7-dimethylxanthine (metabolite I) and 1-(3-carboxypropyl)-3,7-dimethylxanthine (metabolite V), which have activity similar to pentoxifylline.
1.5-2 hours after infusion, the concentration of metabolites I and V in the blood plasma is, respectively, 5 and 8 times higher than the concentration of the original substance. By the 8th hour, the concentration of pentoxifylline and its metabolites in the blood decreases significantly (up to 10% of the initial level). The half-life is from 30 minutes to 1.5 hours.
Excreted mainly by the kidneys (94%) in the form of metabolites (mainly metabolite V), intestines (4%), up to 90% of the dose is excreted in the first 4 hours. 2% of the drug is excreted unchanged. Pentoxifylline and its metabolites do not bind to plasma proteins. Excreted in breast milk.
In severe renal impairment, the elimination of metabolites is slowed down. If liver function is impaired, there is an increase in half-life and increased bioavailability.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Treatment should be carried out under blood pressure control. In patients with chronic heart failure, circulatory compensation should be achieved.
In patients with diabetes mellitus taking hypoglycemic agents, the administration of large doses of pentoxifylline may cause severe hypoglycemia (dose adjustment of hypoglycemic agents and glycemic control may be required).
When prescribed simultaneously with anticoagulants, monitoring of blood clotting parameters is necessary. In patients who have recently undergone surgery, regular monitoring of hemoglobin and hematocrit is necessary.
The administered dose should be reduced in patients with low and unstable blood pressure, as well as in patients with severe atherosclerosis of the coronary and/or cerebral arteries, because in the latter case, an additional decrease in blood pressure may lead to a deterioration in blood supply to the heart and/or brain.
In elderly patients, dose reduction may be required (increased bioavailability and decreased elimination rate). Smoking may reduce the therapeutic effectiveness of the drug.
The compatibility of pentoxifylline solution with other infusion solutions should be checked on a case-by-case basis. During therapy, monitoring of sodium content in the blood plasma is required, especially in patients on a diet with limited salt (total sodium content in a 5 ml ampoule is 11.8 mg).
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery:
Given the possible side effects (for example, dizziness), caution should be exercised when driving vehicles and engaging in potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Pentoxifylline
Composition
Composition
1 ml of the drug contains:
Active ingredient:
pentoxifylline – 20 mg.
Excipients:
sodium chloride – 6 mg,
sodium dihydrogen phosphate dihydrate – 1 mg,
1 M sodium hydroxide solution – up to pH 6.0-8.0,
water for injection – up to 1 ml.
Contraindications
Contraindications
– Hypersensitivity to pentoxifylline or other xanthine derivatives, as well as to any excipient of the drug;
– severe coronary or cerebral atherosclerosis;
– recent myocardial infarction;
– hemodynamically significant cardiac arrhythmias;
– uncontrolled arterial hypotension;
– massive bleeding (risk of increased bleeding);
– extensive hemorrhages in the retina of the eye (risk of increased bleeding);
– hemorrhages in the brain;
– peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum;
– violation of blood coagulation parameters;
– age under 18 years (efficacy and safety have not been established).
With caution:
Patients with labile blood pressure, a tendency to arterial hypotension, chronic heart failure, hemorrhagic diathesis, a tendency to bleeding (including gastric and duodenal ulcers), in a condition after recent surgical interventions, with severe hepatic and/or renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance less than 10 ml/min). Patient Pentoxifylline should be prescribed with caution in combination with direct and indirect anticoagulants due to the enhanced effect of the latter. Pregnancy and lactation: Pentoxifylline is contraindicated during pregnancy because experience with the drug in pregnant women is limited. If it is necessary to prescribe pentoxifylline during lactation, breastfeeding should be stopped due to the fact that pentoxifylline passes into breast milk.
Side Effects
Side Effects
The frequency of possible side effects listed below is determined as follows: very often (1/10); often (1/100 to <1/10); uncommon (1/1000 to <1/100); rare (1/10000 to <1/1000); very rare (< 1/10000);
frequency unknown (cannot be estimated from available data).
Blood and lymphatic system disorders:
Very rare: thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenic purpura, aplastic anemia, pancytopenia.
Rarely: bleeding (including nosebleeds, gastrointestinal bleeding, bleeding from the urinary tract, etc.).
Immune system disorders: Uncommon: hypersensitivity reactions.
Very rare: severe anaphylactic or anaphylactoid reactions, angioedema, bronchospasm, anaphylactic shock, occurring within a few minutes after administration of pentoxifylline.
Mental disorders:
Uncommon: increased excitability, insomnia.
Nervous system disorders:
Uncommon: dizziness, tremor, headache.
Very rare: paresthesia, convulsions, intracranial hemorrhage, aseptic meningitis. Visual disorders:
Uncommon: blurred vision, conjunctivitis.
Very rare: retinal hemorrhage, retinal detachment.
Cardiac disorders:
Uncommon: cardiac arrhythmia, tachycardia.
Rarely: angina pectoris, shortness of breath.
Vascular disorders:
Common: facial skin flushing.
Rarely: decreased blood pressure, peripheral edema.
Very rare: increased blood pressure.
Gastrointestinal disorders: Common: nausea, vomiting, bloating, feeling of heaviness in the stomach, diarrhea.
Disorders of the liver and biliary tract:
Very rare: intrahepatic cholestasis, increased activity of hepatic transaminases.
Disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissues:
Uncommon: pruritus, erythema, urticaria.
Very rare: toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, increased sweating.
General disorders and disorders at the injection site:
Uncommon: increased body temperature.
Interaction
Interaction
Pentoxifylline may enhance the effect of drugs that affect the blood coagulation system (indirect and direct anticoagulants, thrombolytics), antibiotics (including cephalosporins – cefamandole, cefoperazone, cefotetan), valproic acid.
When pentoxifylline is used simultaneously with ketorolac, the risk of bleeding and/or prolongation of prothrombin time increases. The joint administration of these drugs is undesirable. Increases the effectiveness of antihypertensive drugs, insulin, hypoglycemic agents for oral administration.
Cimetidine increases the concentration of pentoxifylline in the blood plasma (risk of side effects). Co-administration with other xanthines may lead to excessive nervous stimulation.
In some patients, with simultaneous use of pentoxifylline and theophylline, an increase in the concentration of theophylline in the blood is observed. This may subsequently lead to an increase or worsening of theophylline-related side effects.
In some patients, with simultaneous use of pentoxifylline and ciprofloxacin, an increase in the concentration of pentoxifylline in the blood plasma is observed. In the future, this may lead to an increase or intensification of side effects associated with the use of this combination.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: weakness, dizziness, marked decrease in blood pressure, tachycardia, drowsiness, loss of consciousness, tonic-clonic convulsions, increased nervous excitability, hyperthermia, areflexia, signs of gastrointestinal bleeding (vomiting like “coffee grounds”).
Treatment: symptomatic, aimed at maintaining respiratory function and blood pressure.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Grotex LLC, Russia
Additional information
| Manufacturer | Grotex Ltd, Russia |
|---|---|
| Medication form | concentrate for preparation of infusion solution |
| Brand | Grotex Ltd |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Pentoxifylline, 20 mg/ml concentrate 5 ml 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.