No products in the cart.
Orvis Flu, 10 pcs.
€8.15 €7.13
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group:
Pharmacotherapy for symptoms of acute respiratory diseases (ARI) and “colds” (analgesic non-narcotic + H1-histamine receptor blocker + vitamin).
The ATX code: N02BE51
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
A combination drug containing paracetamol, pheniramine and ascorbic acid.
Paracetamol is a non-narcotic analgesic, blocks cyclooxygenase, mainly in the central nervous system, affecting the centers of pain and thermoregulation; it has analgesic and antipyretic effects.
Pheniramine is a blocker of H1-histamine receptors; it reduces rhinorrhea and lacrimation, eliminates spastic phenomena, edema and hyperemia of the nasal cavity mucosa, nasopharynx and sinus cavities.
Ascorbic acid is involved in the regulation of redox processes, carbohydrate metabolism, blood coagulation, tissue regeneration, the synthesis of steroid hormones, reduces vascular permeability, reduces the need for vitamins B1, B2, A, E, folic acid, pantothenic acid.
It improves the tolerance of paracetamol and prolongs its effects (associated with prolongation of the half-life (T1/2)).
Pharmacokinetics
Paracetamol
After oral administration is quickly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract: maximum plasma concentrations of the drug are reached after 10-60 minutes.
The drug is rapidly distributed throughout the body tissues and penetrates the blood-brain barrier.
The binding to plasma proteins is insignificant and has no therapeutic value, but increases with increasing dose.
Metabolism occurs in the liver, 80% of the dose taken enters into conjugation reactions with glucuronic acid and sulfates to form inactive metabolites; 17% undergoes hydroxylation to form 8 active metabolites, which conjugate with glutathione to form inactive metabolites.
One of the hydroxylated metabolic intermediates has hepatotoxic effects.
This metabolite is neutralized by conjugation with glutathione, but it can cumulate and in case of paracetamol overdose (150 mg paracetamol/kg or 10 g of oral paracetamol) cause necrosis of hepatocytes.
Extracted by the kidneys as metabolites, mainly as conjugates. Less than 5% of the dose taken is excreted unchanged. T1/2 is 1 to 3 hours.
Pheniramine
It is almost completely absorbed in the digestive tract. The T1/2 from blood plasma is 1 to 1.5 hours. It is eliminated from the body mainly through the kidneys.
Ascorbic acid
It is absorbed in the small intestine. Bioavailability is approximately 70%. Time of reaching the maximum therapeutic concentration after oral administration – 4 hours. It is metabolized mainly in the liver. It is excreted by the kidneys, through the intestine, with sweat, unchanged and as metabolites.
Indications
Indications
Applies to:
— acute respiratory infections
— acute respiratory viral infections (ARVI)
— nasopharyngitis (runny nose)
— Flu to relieve the following symptoms:
– increased body temperature;
– chills;
– headache;
– nasal congestion;
– rhinorrhea;
– lacrimation;
– sneezing;
– pain in muscles and joints.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group:
a remedy for eliminating the symptoms of acute respiratory diseases (ARI) and “colds” (non-narcotic analgesic + H1-histamine receptor blocker + vitamin).
ATX code: N02BE51
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
A combination drug containing paracetamol, pheniramine and ascorbic acid.
Paracetamol is a non-narcotic analgesic that blocks cyclooxygenase, mainly in the central nervous system, affecting the centers of pain and thermoregulation; has analgesic and antipyretic effects.
Pheniramine is a blocker of H1-histamine receptors, reduces rhinorrhea and lacrimation, eliminates spastic phenomena, swelling and hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity, nasopharynx and paranasal sinuses.
Ascorbic acid is involved in the regulation of redox processes, carbohydrate metabolism, blood clotting, tissue regeneration, and in the synthesis of steroid hormones; reduces vascular permeability, reduces the need for vitamins B1, B2, A, E, folic acid, pantothenic acid.
Improves the tolerability of paracetamol and prolongs its effect (associated with an extension of the half-life (T1/2)).
Pharmacokinetics
Paracetamol
After oral administration, it is quickly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract: maximum concentrations of the drug in the blood plasma are reached after 10-60 minutes.
It is quickly distributed throughout the tissues of the body and penetrates the blood-brain barrier.
The connection with blood plasma proteins is insignificant and has no therapeutic significance, but increases as the dose increases.
Metabolism occurs in the liver, 80% of the dose taken enters into conjugation reactions with glucuronic acid and sulfates to form inactive metabolites; 17% undergoes hydroxylation to form 8 active metabolites, which conjugate with glutathione to form inactive metabolites.
One of the hydroxylated metabolic intermediates exhibits hepatotoxic effects.
This metabolite is neutralized by conjugation with glutathione, however, it can accumulate and in case of an overdose of paracetamol (150 mg paracetamol/kg or 10 g paracetamol orally) cause necrosis of hepatocytes.
It is excreted by the kidneys in the form of metabolites, mainly in the form of conjugates. Less than 5% of the dose taken is excreted unchanged. T1/2 is from 1 to 3 hours.
Pheniramine
Almost completely absorbed in the digestive tract. T1/2 from blood plasma is from 1 to 1.5 hours. It is excreted from the body primarily through the kidneys.
Ascorbic acid
Absorbed in the small intestine. Bioavailability is approximately 70%. Time to reach maximum therapeutic concentration after oral administration –
4 hours. Metabolized predominantly in the liver. It is excreted by the kidneys, through the intestines, with sweat, unchanged and in the form of metabolites.
Special instructions
Special instructions
The drug does not contain sugar and can be used by patients with diabetes.
The drug should not be used simultaneously with other medications containing paracetamol.
To avoid toxic liver damage, paracetamol should not be combined with alcoholic beverages, or taken by patients prone to alcohol abuse.
The risk of developing liver damage increases in patients with alcoholic hepatitis.
If the recommended doses are exceeded and with prolonged use, mental dependence on the drug may appear.
To avoid an overdose of paracetamol, you should ensure that the total daily dose of paracetamol contained in all medications taken by the patient does not exceed 4 g.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Paracetamol, Pheniramine, [Ascorbic Acid]
Composition
Composition
1 pack:
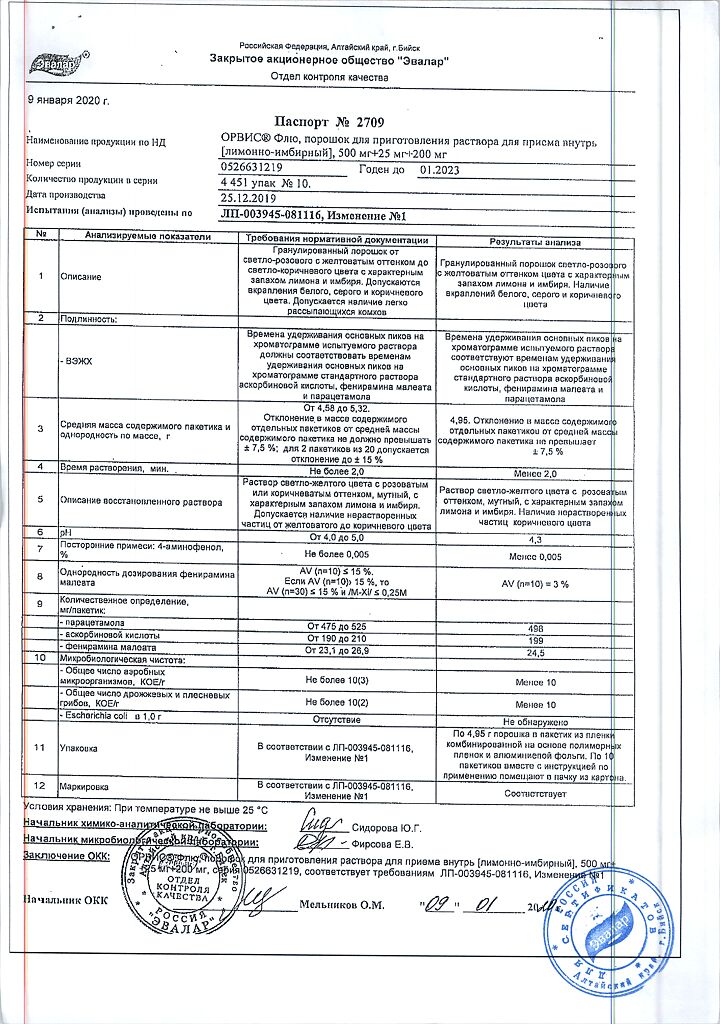
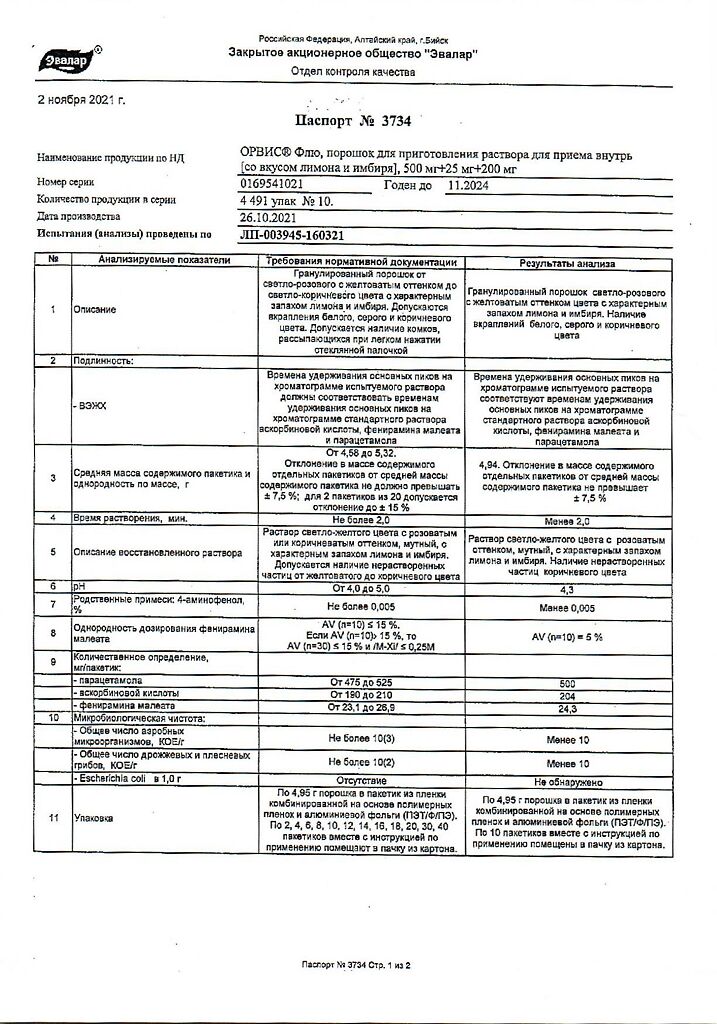
Paracetamol 500 mg
Pheniramine maleate 25 mg
Ascorbic acid 200 mg
Excipients:
Maltodextrin – 3507.25 mg
Aspartame 24.75 mg
Sodium citrate – 247.5 mg
Anhydrous citric acid – 49.5 mg
Lemon powder concentrate (lemon juice, maltodextrin, citric acid) – 247.5 mg
Ginger dry extract (ginger root extract, starch, maltodextrin, colloidal silicon dioxide) – 49.5 mg
Natural lemon flavoring “Lemon” (aromatic composition, aromatic component, maltodextrin, gum arabic) – 99 mg.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Due to the lack of animal studies and clinical studies of the use of a combination of paracetamol, ascorbic acid and pheniramine during pregnancy, taking the drug in this group of patients is not recommended.
It is not known whether the active ingredients of the drug pass into breast milk. Taking ORVIS Flue during breastfeeding is not recommended.
If use is necessary, breastfeeding should be discontinued.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to paracetamol, ascorbic acid, pheniramine or any of the excipients.
Pregnancy and breastfeeding period.
Erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract (in the acute phase).
Liver failure.
Angle-closure glaucoma.
Urinary retention associated with prostate diseases and urinary disorders.
Portal hypertension.
Alcoholism.
Phenylketonuria.
Deficiency of the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Side Effects
Side Effects
The drug is well tolerated in recommended doses.
Possible:
Dryness of the oral mucosa.
Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, constipation.
Urinary dysfunction.
Allergic reactions (erythema, skin rash, itching, urticaria, Quincke’s edema, anaphylactic shock).
Bronchospasm.
Drowsiness, impaired accommodation, palpitations, orthostatic hypotension, dizziness, loss of coordination, tremor.
Agitation, nervousness, insomnia, confusion, hallucinations, impaired concentration (more often in elderly patients), mydriasis.
Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell’s syndrome), acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis.
Hepatotoxic effect, nephrotoxicity.
Anemia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia.
If adverse reactions occur, stop taking the drug and consult a doctor.
Interaction
Interaction
Ethanol enhances the sedative effect of antihistamines (pheniramine), so its use should be avoided during treatment.
In addition, ethanol, when used simultaneously with pheniramine, contributes to the development of acute pancreatitis.
Pheniramine enhances the effect of sedatives:
morphine derivatives, barbiturates, benzodiazepine derivatives and other tranquilizers, neuroleptics (meprobamate, phenothiazine derivatives), antidepressants (amitriptyline, mirtazapine, mianserin), centrally acting antihypertensive drugs, sedatives belonging to the group of H1-histamine blockers, baclofen;
this not only increases the sedative effect, but also increases the risk of developing side effects of the drug (urinary retention, dry mouth, constipation).
The possibility of enhancing central atropine-like effects should be taken into account when used in combination with other substances with anticholinergic properties (other antihistamines, imipramine antidepressants, phenothiazine neuroleptics, m-anticholinergic antiparkinsonian drugs, atropine-like antispasmodics, disopyramide).
When using the drug together with inducers of microsomal oxidation: barbiturates, tricyclic antidepressants, anticonvulsants (phenytoin), flumecinol, phenylbutazone, rifampicin and ethanol, the risk of hepatotoxicity (due to paracetamol included in the composition) significantly increases.
Glucocorticosteroids, when used simultaneously, increase the risk of developing glaucoma.
Concomitant use with salicylates increases the risk of nephrotoxicity.
When used simultaneously with chloramphenicol (chloramphenicol), the toxicity of the latter increases.
Paracetamol contained in the drug enhances the effect of indirect anticoagulants and reduces the effectiveness of uricosuric drugs.
Overdose
Overdose
Signs of acute paracetamol poisoning are anorexia, nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, increased sweating, pale skin, drowsiness, metabolic acidosis (including lactic acidosis).
The threshold for overdose may be lowered in elderly patients and children, in patients taking certain medications (eg, liver microsomal enzyme inducers), alcohol, or who are malnourished.
After 1-2 days, signs of liver dysfunction appear.
In severe cases, liver failure, hepatonecrosis, encephalopathy and coma develop, which can be fatal.
Signs of pheniramine poisoning include convulsions, impaired consciousness, and coma.
If symptoms of poisoning appear, you should immediately stop using the drug and consult a doctor.
It is recommended to lavage the stomach, take enterosorbents (activated carbon), prescribe the antidote acetylcysteine intravenously or orally (if possible, in the first 10 hours after an overdose), and symptomatic treatment.
Recommendations for use
Recommendations for use
Orally, 1 sachet 2-3 times a day.
Before use, dissolve the contents of one sachet in a glass (200 ml) of hot water (50-60 °C).
Add sugar if necessary.
ORVIS Flue can be taken at any time of the day, but the best effect comes from taking the drug before bed, at night.
The maximum daily dose of paracetamol is 4 g (8 sachets) for body weight over 50 kg.
The interval between doses of the drug should be at least 4 hours.
In patients with impaired renal function (creatinine clearance), the maximum duration of treatment is 5 days.
If there is no relief of symptoms within 5 days after starting to take the drug, the body temperature remains elevated, or after an initial decrease it suddenly rises again, you should consult a doctor.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Evalar CJSC, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not higher than 25 ° C. Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Evalar, Russia |
| Medication form | Powder for preparation of solution for oral administration |
| Brand | Evalar |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Orvis Flu, 10 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.