No products in the cart.
Orthofen, 25 mg 20 pcs.
€1.04 €0.95
Description
Phenylacetic acid derivative NSAID. It has a pronounced anti-inflammatory, analgesic and moderate antipyretic effect. The mechanism of action is associated with inhibition of COX activity – the main enzyme of arachidonic acid metabolism, which is a precursor of prostaglandins that play an important role in the pathogenesis of inflammation, pain and fever. Analgesic effect is caused by two mechanisms: peripheral (indirectly, through inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis) and central (due to inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis in central and peripheral nervous system).
In vitro at concentrations equivalent to those achieved in the treatment of patients, it does not inhibit cartilage proteoglycan biosynthesis.
In rheumatic diseases, it reduces joint pain at rest and on movement, as well as morning stiffness and joint swelling, and helps increase range of motion. It reduces post-traumatic and post-operative pain, as well as inflammatory swelling.
In case of post-traumatic and post-operative inflammatory phenomena it quickly relieves pain (occurring both at rest and during movement), reduces inflammatory swelling and edema of the postoperative wound.
Inhibits platelet aggregation. With long-term use has a desensitizing effect.
Pharmacokinetics .
Indications
Indications
Inflammatory and degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system, including rheumatoid, psoriatic, juvenile chronic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis (Bechterew’s disease), osteoarthritis, gouty arthritis, bursitis, tenosynovitis. The drug is intended for symptomatic therapy, reducing pain and inflammation at the time of use, and does not affect the progression of the disease.
Pain syndrome: headache (including migraine) and toothache, lumbago, sciatica, ossalgia, neuralgia, myalgia, arthralgia, radiculitis, in cancer, post-traumatic and postoperative pain syndrome accompanied by inflammation.
Algodismenorrhea: inflammatory processes in the pelvis, including adnexitis.
Infectious and inflammatory diseases of ENT organs with severe pain syndrome (as part of complex therapy): pharyngitis, tonsillitis, otitis.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
NSAID, phenylacetic acid derivative. It has a pronounced anti-inflammatory, analgesic and moderate antipyretic effect. The mechanism of action is associated with inhibition of the activity of COX, the main enzyme in the metabolism of arachidonic acid, which is a precursor of prostaglandins, which play an important role in the pathogenesis of inflammation, pain and fever. The analgesic effect is due to two mechanisms: peripheral (indirectly, through suppression of prostaglandin synthesis) and central (due to inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis in the central and peripheral nervous system).
In vitro, at concentrations equivalent to those achieved when treating patients, it does not inhibit the biosynthesis of cartilage tissue proteoglycans.
For rheumatic diseases, it reduces pain in the joints at rest and during movement, as well as morning stiffness and swelling of the joints, and helps to increase range of motion. Reduces post-traumatic and postoperative pain, as well as inflammatory swelling.
In case of post-traumatic and postoperative inflammatory phenomena, it quickly relieves pain (arising both at rest and during movement), reduces inflammatory swelling and swelling of the postoperative wound.
Suppresses platelet aggregation. With prolonged use it has a desensitizing effect.
Pharmacokinetics
Special instructions
Special instructions
In patients with liver failure (chronic hepatitis, compensated cirrhosis of the liver), the kinetics and metabolism do not differ from similar processes in patients with normal liver function.
When carrying out long-term therapy, it is necessary to monitor liver function, peripheral blood patterns, and stool analysis for occult blood.
During the treatment period, the speed of mental and motor reactions may decrease, so it is necessary to refrain from driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Diclofenac
Composition
Composition
1 tab. contains:
Active substances:
diclofenac sodium 25 mg
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity (including to other NSAIDs), complete or incomplete combination of bronchial asthma, recurrent nasal polyposis and paranasal sinuses and intolerance to acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) or other NSAIDs (including a history), erosive and ulcerative lesions of the stomach and duodenum, active gastrointestinal bleeding, inflammatory bowel diseases, severe hepatic and heart failure; period after coronary artery bypass surgery; severe renal failure (creatinine clearance (CC) less than 30 ml/min), progressive kidney disease, active liver disease, confirmed hyperkalemia, pregnancy (III trimester), lactation period, children’s age (up to 6 years – for enteric-coated tablets 25 mg).
Hereditary lactose intolerance, impaired absorption of glucose-galactose, lactase deficiency.
With caution. Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, history of liver disease, hepatic porphyria, chronic heart failure, arterial hypertension, significant decrease in circulating blood volume (BCV) (including after extensive surgery), elderly patients (including those receiving diuretics, debilitated patients and patients with low body weight), bronchial asthma, simultaneous use of corticosteroids (including including prednisolone), anticoagulants (including warfarin), antiplatelet agents (including ASA, clopidogrel), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (including citalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline), coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular diseases, dyslipidemia/hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, peripheral arterial disease, smoking, chronic renal failure (creatinine clearance 30-60 ml/min), the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection, long-term use of NSAIDs, alcoholism, severe somatic diseases.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the gastrointestinal tract: more often than 1% – abdominal pain or spasm, feeling of bloating, diarrhea, nausea, constipation, flatulence, increased activity of liver transaminases, peptic ulcer with possible complications (bleeding, perforation), gastrointestinal bleeding without ulcer; less than 1% – vomiting, jaundice, melena, blood in the stool, damage to the esophagus, aphthous stomatitis, dry mucous membranes (including the oral cavity), hepatitis (possibly fulminant), liver necrosis, cirrhosis, hepatorenal syndrome, changes in appetite, pancreatitis (including with concomitant hepatitis), cholecystopancreatitis, colitis.
From the nervous system: more often than 1% – headache, dizziness; less than 1% – sleep disturbance, drowsiness, depression, irritability, aseptic meningitis (more often in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and other systemic connective tissue diseases), convulsions, general weakness, disorientation, nightmares, a feeling of fear.
From the senses: more often than 1% – tinnitus; less than 1% – blurred visual perception, diplopia, taste disturbance, reversible or irreversible hearing loss, scotoma.
From the skin: more often than 1% – skin itching, skin rash; less than 1% – alopecia, urticaria, eczema, toxic dermatitis, exudative erythema multiforme (including Stevens-Johnson syndrome), toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell’s syndrome), increased photosensitivity, pinpoint hemorrhages.
From the genitourinary system: more often than 1% – fluid retention; less than 1% – nephrotic syndrome, proteinuria, oliguria, hematuria, interstitial nephritis, papillary necrosis, acute renal failure, azotemia.
From the hematopoietic organs and immune system: less than 1% – anemia (including hemolytic and aplastic anemia), leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, eosinophilia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenic purpura, worsening of infectious processes (including the development of necrotizing fasciitis).
From the respiratory system: less than 1% – cough, bronchospasm, laryngeal edema, pneumonitis.
From the cardiovascular system: less than 1% – increased blood pressure; congestive heart failure, extrasystole, chest pain.
Allergic reactions: less than 1% – anaphylactoid reactions, anaphylactic shock (usually develops rapidly), swelling of the lips and tongue, allergic vasculitis.
Interaction
Interaction
Increases plasma concentrations of digoxin, methotrexate, lithium and cyclosporine.
Reduces the effect of diuretics; against the background of potassium-sparing diuretics, the risk of hyperkalemia increases; against the background of anticoagulants, thrombolytic agents (alteplase, streptokinase, urokinase) – the risk of bleeding (usually from the gastrointestinal tract).
Reduces the effects of antihypertensive and hypnotic drugs.
Increases the likelihood of side effects of other NSAIDs and glucocorticosteroids (bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract), methotrexate toxicity and cyclosporine nephrotoxicity.
Acetylsalicylic acid reduces the concentration of diclofenac in the blood. Concomitant use with paracetamol increases the risk of developing nephrotoxic effects of diclofenac.
Reduces the effect of hypoglycemic drugs.
Cefamandole, cefoperazone, cefotetan, valproic acid and plicamycin increase the incidence of hypoprothrombinemia.
Cyclosporine and gold preparations increase the effect of diclofenac on the synthesis of prostaglandins in the kidneys, which increases nephrotoxicity.
Concomitant use with ethanol, colchicine, corticotropin and St. John’s wort preparations increases the risk of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
Diclofenac enhances the effect of drugs that cause photosensitivity. Drugs that block tubular secretion increase the plasma concentration of diclofenac, thereby increasing its toxicity.
Antibacterial drugs from the quinolone group – the risk of developing seizures.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: vomiting, dizziness, headache, shortness of breath, confusion, in children – myoclonic convulsions, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, bleeding, impaired liver and kidney function.
Treatment: gastric lavage, administration of activated carbon, symptomatic therapy aimed at eliminating increased blood pressure, impaired renal function, seizures, irritation of the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory depression. Forced diuresis and hemodialysis are ineffective.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store the drug in a dry place, protected from light, out of reach of children, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
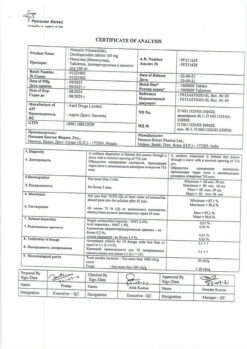
Tatchimpharmpreparaty, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store the drug in a dry, dark place out of the reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. |
| Manufacturer | Tatkhimpharmpreparaty, Russia |
| Medication form | enteric soluble tablets |
| Brand | Tatkhimpharmpreparaty |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Orthofen, 25 mg 20 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.