No products in the cart.
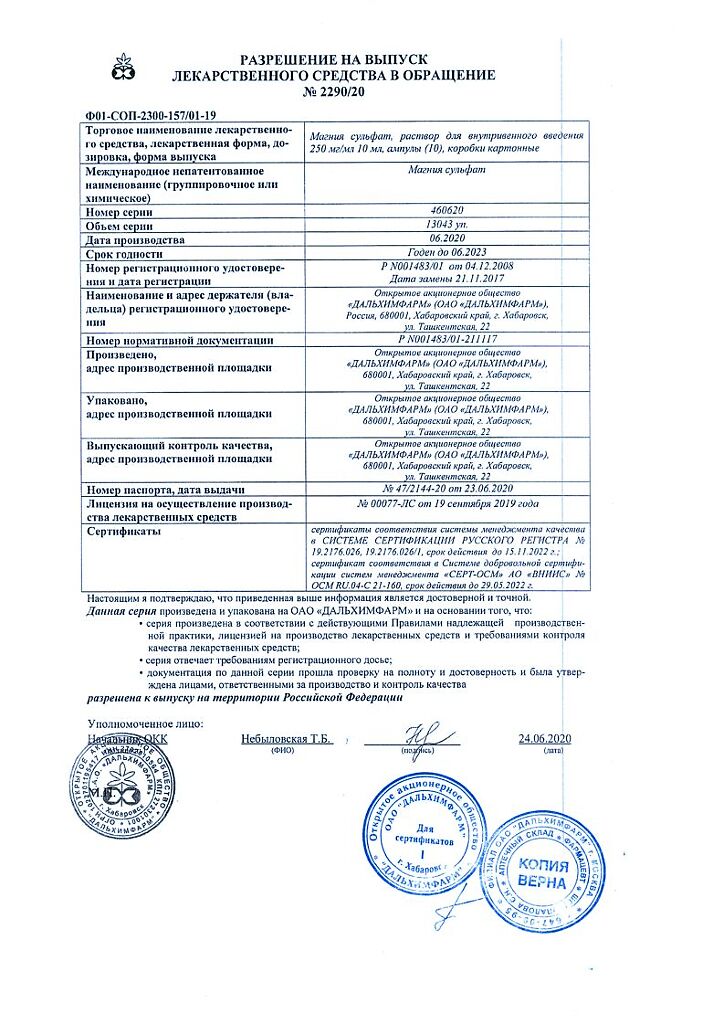
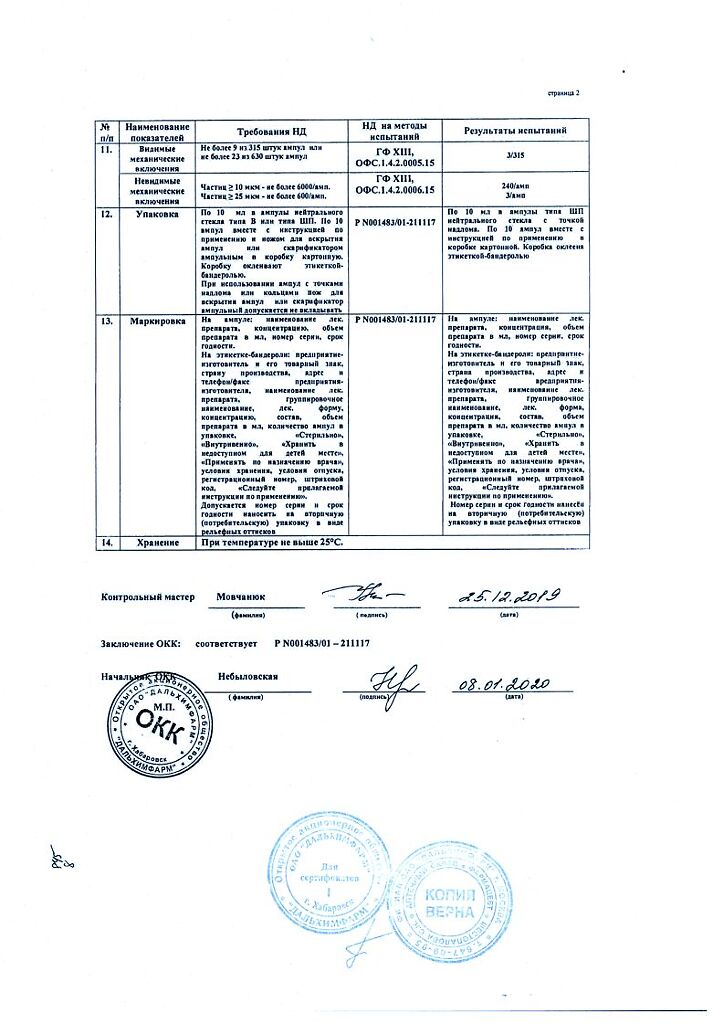
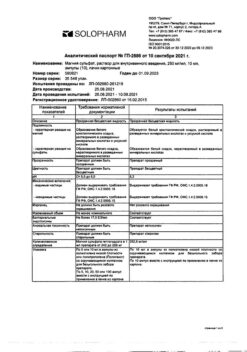
Magnesium sulfate, 250 mg/mL 10 ml 10 pcs
€4.16 €3.34
EAN: 4602824000097
SKU: 52863
Categories: Anesthesia and resuscitation, Anesthesia solutions, Medicine
Description
In parenteral administration it has anticonvulsant, antiarrhythmic, hypotensive, antispasmodic effects, in high doses it inhibits neuromuscular transmission, has tocolytic effect, inhibits respiratory center. Mg2+ is a “physiological” BMCC and is able to displace it from binding sites.
It regulates metabolic processes, inter-neuronal transmission and muscle excitability, inhibits Ca2+ entry through the presynaptic membrane, reduces the amount of acetylcholine in the peripheral nervous system and CNS. It relaxes smooth muscles, reduces BP (mostly elevated), increases diuresis.
The anticonvulsant action – Mg2+ reduces the release of acetylcholine from neuromuscular synapses, thus suppressing neuromuscular transmission, has a direct inhibitory effect on the CNS.
The antiarrhythmic action – Mg2+ reduces excitability of cardiomyocytes, restores ionic balance, stabilizes cell membranes, disrupts Na+ flow, slow incoming Ca2+ flow and one-way K+ flow.
The cardioprotective effect is due to the dilation of the coronary arteries, reduction of OPPS and platelet aggregation. Tocolytic effect – Mg2+ inhibits myometrial contractility (decreases absorption, binding and distribution of Ca2+ in smooth muscle cells), increases blood flow in the uterus as a result of the expansion of its vessels. It is an antidote for poisoning by salts of heavy metals.
The systemic effects develop almost immediately after IV and 1 h after IV/m injection. Duration of action after intravenous injection is 30 minutes, after intravenous injection – 3-4 hours.
Indications
Indications
hypertensive crisis;
late toxicosis of pregnancy;
convulsive syndrome.
relief of status epilepticus (as part of complex therapy).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
When administered parenterally, it has anticonvulsant, antiarrhythmic, hypotensive, antispasmodic effects; in large doses, it inhibits neuromuscular transmission, has a tocolytic effect, and suppresses the respiratory center. Mg2+ is a “physiological” BMCC and is capable of displacing it from binding sites.
Regulates metabolic processes, interneuronal transmission and muscle excitability, prevents the entry of Ca2+ through the presynaptic membrane, reduces the amount of acetylcholine in the peripheral nervous system and the central nervous system. Relaxes smooth muscles, reduces blood pressure (mostly elevated), increases diuresis.
Anticonvulsant effect – Mg2+ reduces the release of acetylcholine from neuromuscular synapses, while suppressing neuromuscular transmission, and has a direct inhibitory effect on the central nervous system.
Antiarrhythmic effect – Mg2+ reduces the excitability of cardiomyocytes, restores ionic balance, stabilizes cell membranes, disrupts the Na+ current, the slow incoming Ca2+ current and the one-way K+ current.
The cardioprotective effect is due to the expansion of the coronary arteries, a decrease in peripheral vascular resistance and platelet aggregation. Tocolytic effect – Mg2+ inhibits the contractility of the myometrium (decreased absorption, binding and distribution of Ca2+ in smooth muscle cells), increases blood flow in the uterus as a result of dilation of its vessels. It is an antidote for poisoning with heavy metal salts.
Systemic effects develop almost immediately after intravenous administration and 1 hour after intramuscular administration. Duration of action with intravenous administration is 30 minutes, with intramuscular administration – 3-4 hours.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Magnesium sulfate
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
magnesium sulfate
Contraindications
Contraindications
hypersensitivity to the drug;
AV block;
arterial hypotension;
conditions accompanied by calcium deficiency and depression of the respiratory center.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Early signs and symptoms of hypermagnesemia: bradycardia, diplopia, sudden “rush” of blood to the skin of the face, headache, decreased blood pressure, nausea, shortness of breath, slurred speech, vomiting, asthenia.
Signs of hypermagnesemia, ranked in order of increasing Mg2+ concentration in the blood serum: decreased deep tendon reflexes (2-3.5 mmol/l), prolongation of the P-Q interval and widening of the QRS complex on the ECG (2.5-5 mmol/l), loss of deep tendon reflexes (4-5 mmol/l), depression of the respiratory center (5-6.5 mmol/l), cardiac conduction disturbances (7.5 mmol/l), cardiac arrest (12.5 mmol/l).
In addition, hyperhidrosis, anxiety, deep sedation, polyuria, uterine atony.
Interaction
Interaction
Strengthens the effect of other drugs that depress the central nervous system. Cardiac glycosides increase the risk of conduction disturbances and AV block (especially with simultaneous intravenous administration of Ca2+ salts).
Muscle relaxants and nifedipine enhance neuromuscular blockade. When combined with parenteral magnesium sulfate and other vasodilators, the hypotensive effect may be enhanced. Barbiturates, narcotic analgesics, and antihypertensive drugs increase the likelihood of depression of the respiratory center. It interferes with the absorption of tetracycline antibiotics and weakens the effect of streptomycin and tobramycin.
Ca2+ salts reduce the effect of magnesium sulfate. Pharmaceutically incompatible (forms a precipitate) with Ca2+ preparations, ethanol (in high concentrations), carbonates, bicarbonates and phosphates of alkali metals, salts of arsenic acid, barium, strontium, clindamycin phosphate, hydrocortisone sodium succinate, polymyxin B sulfate, procaine hydrochloride, salicylates and tartrates. At Mg2+ concentrations above 10 mmol/ml in total parenteral nutrition formulas, separation of fat emulsions is possible.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: possible respiratory depression, depression of central nervous system functions, up to the development of anesthesia.
Treatment: calcium preparations – calcium chloride or calcium gluconate – are used as an antidote for an overdose of magnesium sulfate.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 30 °C (do not freeze)
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Dalkhimfarm, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 30 °C (do not freeze) |
| Manufacturer | Dalkhimpharm, Russia |
| Medication form | solution |
| Brand | Dalkhimpharm |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Magnesium sulfate, 250 mg/mL 10 ml 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.