No products in the cart.
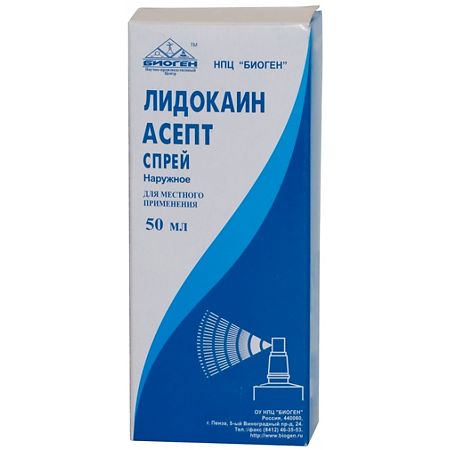
Lidocaine, 10% spray 50 ml
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
EAN: 4607006950788
SKU: 223027
Categories: Anesthesia and resuscitation, Local anesthetics, Medicine
Description
Lidocaine is a local anesthetic and antiarrhythmic drug.
The antiarrhythmic activity is due to inhibition of phase 4 (diastolic depolarization) in Purkinje fibers, reduction of automaticity, suppression of ectopic foci of excitation. The rate of rapid depolarization (phase 0) is not affected or slightly reduced. Increases membrane permeability to potassium ions, accelerates the process of repolarization and shortens the action potential. It does not change sinus-atrial node excitability and has little effect on conduction and myocardial contractility. When administered intravenously it works quickly and shortly (10-20 min).
The mechanism of local anesthetic effect consists in stabilization of neuronal membrane, reduction of its permeability to sodium ions, which prevents the emergence of action potential and impulse conduction. Antagonism with calcium ions is possible. It is rapidly hydrolyzed in a weakly alkaline environment of tissues and after a short latent period is active for 60-90 minutes. During inflammation (tissue acidosis) anesthetic activity decreases. It is effective for all types of local anesthesia. It dilates blood vessels. It has no irritating effect on the tissues.
When using the drug in pharyngeal or nasopharyngeal surgery the pharyngeal reflex is suppressed. By reaching the larynx and trachea, the drug is good at slowing down the cough reflex, which can lead to bronchopneumonia.
The action of lidocaine in aerosol form develops within 1 min and lasts 5-6 min. The desensitization achieved slowly disappears within 15 min.
It is evenly distributed in the body. It penetrates through the placental barrier.
Indications
Indications
prevention and treatment of ventricular rhythm disturbances (ventricular extrasystole, ventricular paroxysmal tachycardia) associated with the acute phase of myocardial infarction, other forms of coronary artery disease, and also caused by drugs (cardiac glycosides).
Local anesthesia: superficial, infiltration, conduction, epidural, spinal, intraligamentary for surgical interventions, painful manipulations, endoscopic and instrumental studies.
In dental practice, oral surgery:
opening of superficial abscesses;
removal of loose, falling teeth;
removal of bone fragments and suturing wounds of the mucous membranes;
gum anesthesia for fixation of a crown or bridge;
manual or instrumental removal (or excision) of an enlarged papilla of the tongue;
to reduce or suppress an increased pharyngeal reflex in preparation for an x-ray examination;
anesthesia for excision of superficial benign tumors of the oral mucosa;
in children – for frenulectomy and opening of salivary gland cysts.
In ENT practice:
before electrocoagulation (in the treatment of nosebleeds), septectomy and resection of nasal polyps;
before tonsillectomy to reduce the pharyngeal reflex and relieve pain at the injection site;
as additional anesthesia before opening a peritonsillar abscess or before puncture of the maxillary sinus;
anesthesia before washing the sinuses.
During endoscopy and instrumental examinations:
anesthesia before insertion of various probes through the nose or mouth (duodenal probe, before a fractional food test);
anesthesia before rectoscopy and in case of catheter replacement.
In obstetrics and gynecology:
perineal anesthesia for treatment and/or episiotomy;
anesthesia of the surgical field in vaginal or cervical surgery;
anesthesia for excision and in the treatment of hymen rupture;
anesthesia for suturing abscesses.
In dermatology:
anesthesia of mucous membranes during minor surgical interventions.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Lidocaine is a local anesthetic and antiarrhythmic drug.
Antiarrhythmic activity is due to inhibition of phase 4 (diastolic depolarization) in Purkinje fibers, a decrease in automaticity, and suppression of ectopic foci of excitation. The rate of rapid depolarization (phase 0) is not affected or slightly reduced. Increases membrane permeability for potassium ions, accelerates the repolarization process and shortens the action potential. Does not change the excitability of the sinoatrial node, has little effect on the conductivity and contractility of the myocardium. When administered intravenously, it acts quickly and briefly (10–20 minutes).
The mechanism of the local anesthetic effect is to stabilize the neuronal membrane, reducing its permeability to sodium ions, which prevents the occurrence of action potentials and the conduction of impulses. Antagonism with calcium ions is possible. It hydrolyzes quickly in a slightly alkaline tissue environment and, after a short latent period, acts for 60–90 minutes. With inflammation (tissue acidosis), anesthetic activity decreases. Effective for all types of local anesthesia. Dilates blood vessels. Does not irritate fabrics.
When using the drug in pharyngeal or nasopharyngeal surgery, the pharyngeal reflex is suppressed. Reaching the larynx and trachea, the drug effectively slows down the cough reflex, which can lead to bronchopneumonia.
The action of lidocaine in the form of an aerosol develops within 1 minute and lasts 5-6 minutes. The achieved reduction in sensitivity slowly disappears within 15 minutes.
Distributed evenly in the body. Penetrates through the placental barrier.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Use with caution in patients with impaired liver function, circulatory failure, arterial hypotension, renal failure, epilepsy. In these cases, a reduction in the dose of the drug is required.
With rapid intravenous administration, a sharp decrease in blood pressure and the development of collapse can occur.
In these cases, mezaton, ephedrine and other vasoconstrictors are used. Lidocaine solutions should be carefully injected into highly vascularized tissues to avoid the drug entering the lumen of the vessel (for example, in the neck area during thyroid surgery) (in such cases, smaller doses of lidocaine are indicated.
The drug should be used with particular caution in the presence of injuries to the mucous membranes, with mental retardation, as well as in very old and/or weakened patients who are already receiving drugs such as lidocaine for cardiac problems.
In dentistry and orthopedics, the drug should be used only with elastic impression materials.
Avoid ingestion of the aerosol or contact with the eyes; it is important to prevent the aerosol from entering the respiratory tract (risk of aspiration). Applying the drug to the back of the throat requires special care. It should be remembered that lidocaine suppresses the pharyngeal reflex and inhibits the cough reflex, which can lead to aspiration and bronchopneumonia.
Use in pediatrics
It should be borne in mind that in children the swallowing reflex occurs much more often than in adults.
Lidocaine in aerosol form is not recommended for local anesthesia before tonsillectomy and adenotomy in children under 8 years of age.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
If side effects after using the drug do not cause discomfort, there are no restrictions on driving vehicles or operating machinery.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Lidocaine, Chlorhexidine
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
lidocaine;
Excipients:
ethanol (96%),
peppermint oil,
propylene glycol;
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
The use of lidocaine during pregnancy should be avoided, because After intravenous administration, within a few minutes the drug passes through the placenta.
Lidocaine aerosol can be used during pregnancy, because… in recommended doses it does not pose a danger.
It is not known whether lidocaine is excreted in breast milk.
Caution should be exercised when prescribing the drug to a nursing mother.
During lactation, the use of the drug is possible after a preliminary careful assessment of the expected benefits of therapy for the mother and the potential risk for the infant.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Sick sinus syndrome.
Severe bradycardia.
2nd and 3rd degree atrioventricular block (except when a probe is inserted to simulate the ventricles).
Cardiogenic shock.
Myasthenia.
Increased individual sensitivity to lidocaine.
History of epileptiform seizures caused by lidocaine.
Severe liver dysfunction.
When using plaster of Paris as an impression material in dentistry, the aerosol is contraindicated due to the risk of aspiration.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the central nervous system: possible headaches, dizziness, drowsiness, anxiety, euphoria, tinnitus, numbness of the tongue and oral mucosa, speech and vision disorders.
From the cardiovascular system: at higher doses, arterial hypotension, collapse, bradycardia, and conduction disturbances are possible.
Allergic reactions: rarely – rash, itching, exfoliative dermatitis, anaphylactic shock, hyperthermia.
Local reactions: a slight burning sensation, which disappears as the anesthetic effect develops (within 1 minute).
Interaction
Interaction
It is not advisable to combine lidocaine with the following drugs:
With beta-blockers due to increased toxic properties of lidocaine, with digitoxin – due to a weakening of the cardiotonic effect, with curare-like drugs – muscle relaxation increases.
It is irrational to prescribe lidocaine together with ajmaline, amiodarone, verapamil or quinidine due to increased cardiodepressive effects.
The combined use of lidocaine and procainamide can cause central nervous system stimulation and hallucinations.
With intravenous administration of hexenal or thiopental sodium against the background of the action of lidocaine, respiratory depression is possible.
Under the influence of MAO inhibitors, the local anesthetic effect of lidocaine is likely to be enhanced. Patients taking MAO inhibitors should not be prescribed parenteral lidocaine.
With the simultaneous administration of lidocaine and polymyxin-B, an increased inhibitory effect on neuromuscular transmission is possible, so in this case it is necessary to monitor the patient’s respiratory function.
With the simultaneous use of lidocaine with sleeping pills or sedatives, their inhibitory effect on the central nervous system may be enhanced. When lidocaine is administered intravenously to patients taking cimetidine, undesirable effects such as stunned state, drowsiness, bradycardia, parasthesia, etc. are possible. This is due to an increase in the level of lidocaine in the blood plasma, which is explained by the release of lidocaine from binding to blood proteins, as well as a slowdown in its inactivation in the liver. If combination therapy with these drugs is necessary, the dose of lidocaine should be reduced.
Pharmaceutical interactions
When used concomitantly, the following drugs increase the concentration of lidocaine in the blood serum: aminazine, cimetidine, propranolol, pethidine, bupivacaine, quinidine, disopyramide, amitriptyline, imipramine, nortriptyline.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place protected from light
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Biogen, Netherlands
Additional information
| Conditions of storage | In a dry place protected from light |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Biogen, The Netherlands |
| Medication form | topical spray |
| Brand | Biogen |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Lidocaine, 10% spray 50 ml with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.