No products in the cart.
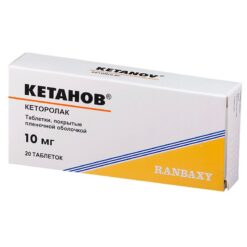
Ketorolac, 10 mg 20 pcs.
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Ketorolac has a pronounced analgesic effect, also has anti-inflammatory and moderate antipyretic effects.
The mechanism of action is related to non-selective inhibition of cyclooxygenase 1 and 2 enzyme activity, mainly in peripheral tissues, the consequence of which is inhibition of prostanglandin biosynthesis – modulators of pain sensitivity, thermoregulation and inflammation.
Ketorolac is a racemic mixture of [-]S and [+]R enantiomers, with analgesic effect due to the [-]S form.
The drug does not affect the opioid receptors, does not depress respiration, does not cause drug dependence and has no sedative and anxiolytic effects.
In its analgesic effect the drug is comparable with morphine and is considerably superior to other NSAIDs.
After oral administration the onset of analgesic effect is noted within 1 hour respectively, the maximum effect is reached after 1-2 hours and after 2-3 hours.
Indications
Indications
Pain syndrome of strong and moderate severity: trauma, toothache, pain in the postoperative period, cancer, myalgia, arthralgia, neuralgia, sciatica, sprains, sprains, rheumatic diseases.
It is intended for symptomatic therapy, to reduce pain and inflammation at the time of use, does not affect the progression of the disease.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
Composition (1 tablet):
Active substance:
Ketorolaca tromethamine – 10 mg.
Auxiliary substances:
Milk sugar (lactose),
Potato starch,
low molecular weight polyvinylpyrrolidone (povidone),
magnesium stearate,
/p>
talc,
collidone CL M;
coating:
oxypropyl methylcellulose or hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (hypromellose),
Talc,
Titanium dioxide,
Polyethylene glycol 4000,
Propylene glycol.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Ketorolac is taken orally, once or repeatedly depending on the severity of the pain syndrome.
The single dose is 10 mg, when repeatedly taken it is recommended to take 10 mg up to 4 times a day depending on the severity of pain; the maximum daily dose should not exceed 40 mg.
When taken orally, the duration of the course should not exceed 5 days.
Interaction
Interaction
Concomitant use of ketorolac with acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs, calcium preparations, glucocorticosteroids, ethanol, corticotropin may lead to formation of GI ulcers and development of gastrointestinal bleeding.
The co-administration with paracetamol increases nephrotoxicity, with methotrexate – hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity.
The co-administration of ketorolac and methotrexate is possible only when using low doses of the latter (monitor the plasma concentration of methotrexate). Probenicid decreases plasma clearance and volume of distribution of ketorolac, increases its plasma concentration and extends its half-life.
The use of ketorolac may decrease clearance of methotrexate and lithium and increase toxicity of these substances. Concomitant use with indirect anticoagulants, heparin, thrombolytics, antiaggregants, cefoperazone, cefotetan and pentoxifylline increases the risk of bleeding.
Limits the effect of hypotensive and diuretic drugs (reduces the synthesis of prostaglandins in the kidneys). When combining with opioid analgesics, the doses of the latter may be significantly reduced. Antacids do not affect the completeness of absorption of the drug.
The hypoglycemic effect of insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents increases (recalculation of the dose is necessary). Co-administration with sodium valproate causes impairment of platelet aggregation. Increases plasma concentrations of verapamil and nifedipine.
When prescribed with other nephrotoxic drugs (including gold drugs) the risk of nephrotoxicity increases. Medicinal products that block tubular secretion decrease clearance of ketorolac and increase its plasma concentration.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
When combined with other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, fluid retention, cardiac decompensation, arterial hypertension may be observed.
The effect on platelet aggregation stops after 24-48 hours. Hypovolemia increases the risk of adverse reactions from the kidneys. If necessary, can be administered in combination with narcotic analgesics.
Ketorolac is not recommended for use as an agent for premedication, maintenance anesthesia and analgesia in obstetric practice.
Do not use simultaneously with paracetamol for more than 5 days.
Patients with clotting disorders are prescribed the drug only with continuous monitoring of platelet count, especially in the postoperative period, which requires close monitoring of hemostasis.
It is recommended to avoid work requiring increased attention and rapid reaction (driving, working with machinery, etc.).
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to ketorolac, complete or incomplete combination of bronchial asthma, recurrent polyposis of the nose and sinuses and intolerance to acetylsalicylic acid or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (including history), urticaria, rhinitis caused by taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (history), dehydration.
Pyrazolone drug intolerance, hypovolemia (regardless of the cause), bleeding or high risk of bleeding, condition after coronary artery bypass grafting, confirmed hyperkalemia, inflammatory bowel disease. Ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract in the stage of exacerbation, peptic ulcers, hypocoagulation (including hemophilia). Severe hepatic and/or renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min).
Hemorrhagic stroke (confirmed or suspected), hemorrhagic diathesis, hematopoiesis disorders. Pregnancy, childbirth and lactation period. Childhood under 16 years of age.
The drug is not used for pain before and during surgical operations because of the high risk of bleeding and also for treatment of chronic pain.
Side effects
Side effects
Gastrointestinal system: often (especially in elderly patients over 65 years with a history of gastrointestinal erosive ulcers) – gastralgia, diarrhea; less frequently – stomatitis, flatulence, constipation, vomiting, feeling of stomach fullness; rarely – nausea, erosive ulcerative lesions of the GI tract (including perforation and/or bleeding – abdominal pain, spasm or burning of epigastric region, melena, vomiting like “coffee grounds”.including with perforation and/or bleeding – abdominal pain, epigastric spasm or burning, melena, “coffee grounds” type vomiting, nausea, heartburn, etc.), cholestatic jaundice, hepatitis, hepatomegaly, acute pancreatitis.
Urinary system disorders: rare – acute renal failure, lumbar pain with or without hematuria and/or azotemia, hemolytic uremic syndrome (hemolytic anemia, renal failure, thrombocytopenia, purpura), frequent urination, increased or decreased volume of urine, nephritis, edema of renal genesis.
Sensory system disorders: rare – hearing loss, tinnitus, visual impairment (including blurred vision).
Respiratory system disorders: rarely: bronchospasm or dyspnea, rhinitis, laryngeal edema (dyspnea, difficulty in breathing).
CNS disorders: often – headache, dizziness, somnolence, rarely – aseptic meningitis (fever, severe headache, cramps, neck and/or back stiffness), hyperactivity (mood changes, anxiety), hallucinations, depression, psychosis.
Cardiovascular system disorders: less frequently – BP increase, rarely – pulmonary edema, fainting.
Hematopoietic system: rarely – anemia, eosiophilia, leukopenia.
Hemostatic system disorders: rare – bleeding from the postoperative wound, nasal bleeding, rectal bleeding.
Skin disorders: less frequently – skin rash (including maculopapular rash), purpura, rarely – exfoliative dermatitis (fever with or without chills, redness, thickening or peeling of the skin, swollen and/or painful palatine tonsils), urticaria, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Lyell syndrome. Local reactions: less frequent – burning or pain at the injection site.
Allergic reactions: rarely – anaphylaxis or anaphylactoid reactions (changes in complexion, skin rash, urticaria, skin itching, tachypnea or dyspnea, edema of the eyelids, periorbital edema, shortness of breath, difficulty in breathing, heaviness in the chest, wheezing).
Others: often – edema (of face, shins, ankles, fingers, feet, weight gain); less often – increased sweating, rarely – swelling of tongue, fever.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, occurrence of peptic ulcers of the stomach or erosive gastritis, impaired renal function, metabolic acidosis.
Treatment: gastric lavage, administration of adsorbents (activated charcoal) and symptomatic therapy (maintenance of vital functions in the body). Not excreted sufficiently by dialysis.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Weight | 0.010 kg |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store in a dark, dry place out of the reach of children at up to 25°C. |
| Manufacturer | Vertex, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Vertex |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Ketorolac, 10 mg 20 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.