No products in the cart.
Heparin sodium Brown, 5000 units/ml 5 ml 10 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Heparin is a direct acting anticoagulant.
Delays the formation of fibrin, is a physiological anticoagulant, potentiating the ability of antithrombin III to inhibit activated clotting factors IXa, Ha, XIa, XIIa, and in high concentrations – and thrombin activity.
The ability to inhibit activated factor X participating in the internal and external coagulation system is of particular importance (this action is shown at a much lower dose of heparin than is required for suppression of the activity of thrombin contributing to formation of fibrin from fibrinogen, which provides justification for the possibility of subcutaneous administration of small doses of heparin for prevention of venous thrombosis and large doses – for treatment).
Heparin is not able to dissolve the thrombus (it is not a fibrinolytic), but can reduce the size of the thrombus, stopping its growth, in which case part of the thrombus dissolves under the action of natural fibrinolytic enzymes.
Inhibits the activity of hyaluronidase. Reduces surfactant activity in the lungs.
Reduces the risk of acute coronary artery thrombosis, myocardial infarction and sudden death. In high doses it is effective for pulmonary embolism and venous thrombosis, in low doses – for the prevention of venous thromboembolism, including after surgical operations.
Indications
Indications
Prevention and treatment:
– Deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary thromboembolism (including peripheral veins. In diseases of peripheral veins), coronary artery thrombosis;
– unstable angina pectoris;
– acute myocardial infarction;
– atrial fibrillation, accompanied by embolization;
– DIC (first phase).
– Prophylaxis of blood clotting during operations with the use of extracorporeal methods of blood circulation, during blood transfusions, hemodialysis, blood sampling for research.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
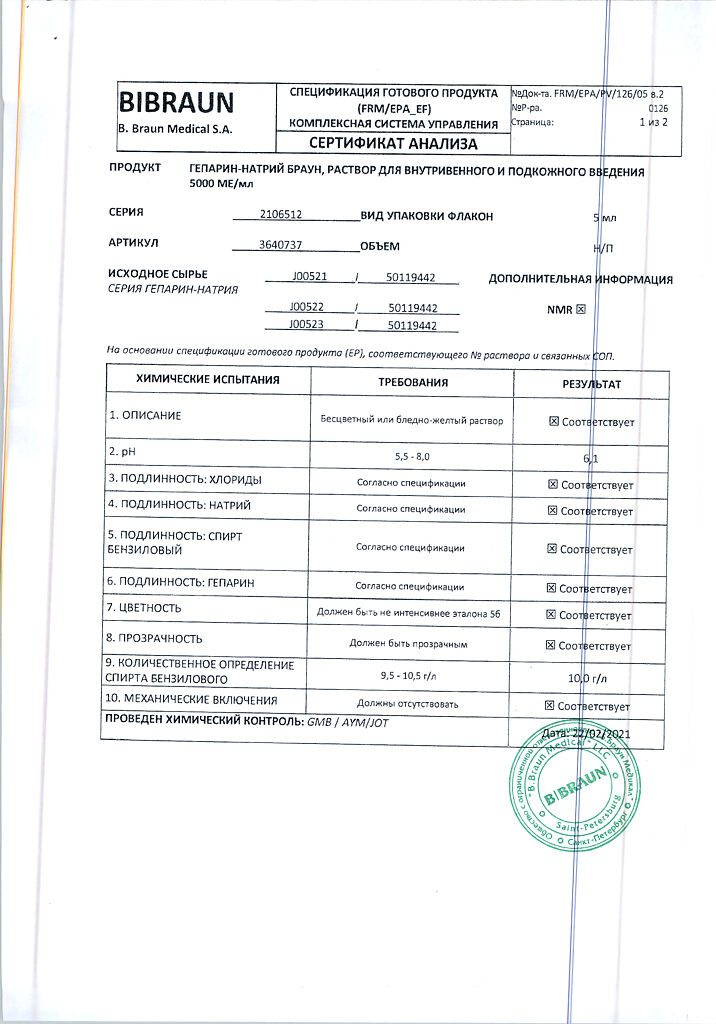
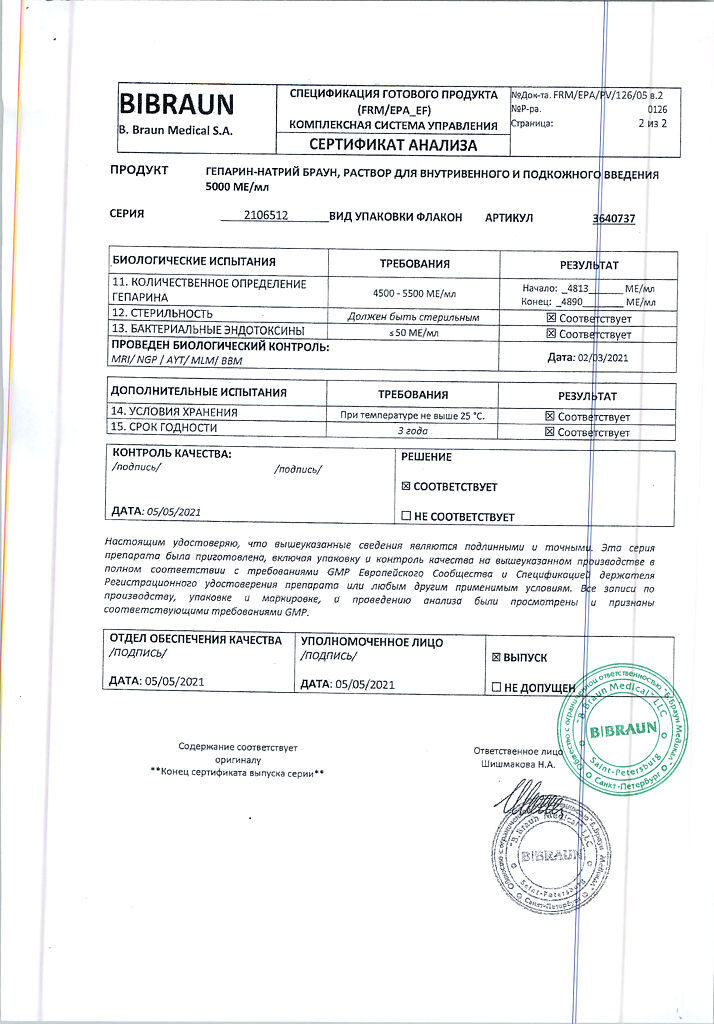
1 ml of the solution contains 5000 units of heparin sodium
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
For therapeutic purposes, Heparin is administered as an intravenous drop infusion at a dose of 15 IU/kg/h (i.e. for adults with an average body weight – 1 thousand IU/h).
Immediately prior to infusion, to achieve a rapid anticoagulant effect, the drug is administered by IV infusion in a dose of 5,000 IU (1 ml).
If by injection for any reason the drug cannot be administered, then the drug is administered by infusion – 10 thousand IU (2 ml) 4 times a day. Daily dose should not exceed 60-80 thousand IU.
The use of the drug in the maximum daily dose for more than 10 days is possible only in exceptional cases.
For prophylactic purposes to prevent thrombosis Heparin is injected under the skin of the abdomen for 5,000 IU (1 ml) 2 times a day.
Interaction
Interaction
The action of heparin increases: antibiotics (reduce the formation of vitamin K by intestinal microflora), acetylsalicylic acid, dipyridamole, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and other drugs that reduce platelet aggregation (which remains the main mechanism of hemostasis in patients treated with heparin), indirect anticoagulants.
The action of heparin reduces: antihistamines, phenothiazines, cardiac glycosides, nicotinic acid, tetracyclines, ergot alkaloids, nicotine, nitroglycerin (IV administration), thyroxine, ACTH, alkaline amines and polypeptides, protamine.
Heparin should not be mixed in the same syringe with other medicines.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Heparin should not be administered intramuscularly as hematoma may form at the site of injection.
The heparin solution may turn yellow, which does not change its activity or tolerability.
When heparin is administered for therapeutic purposes, the dose is adjusted according to the AFP value.
During the use of heparin no other drugs should be administered intramuscularly and no organ biopsy should be performed.
For heparin dilution only physiological solution is used.
Contraindications
Contraindications
– diseases accompanied by blood coagulation disorders;
– gastrointestinal ulcers (gastric, duodenal and ileum ulcers, non-specific ulcerative colitis, malignant tumors);
– subacute bacterial endocarditis;
– marked liver function disorders;
Side effects
Side effects
Allergic reactions: rhinitis, urticaria, lacrimation, fever, bronchospasm.
Other: when using the drug in high doses and/or with prolonged treatment there may be bleeding from mucous membranes and wounds, development of thrombocytopenia.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms:bleeding of varying severity.
Treatment: in case of minor bleeding the dose should be reduced or the drug should be temporarily discontinued.
In extensive bleeding, excess heparin is neutralized with protamine sulfate (1 mg protamine sulfate per 100 ME heparin).
Please note that heparin is rapidly excreted, and if protamine sulfate is administered 30 minutes after the previous dose of heparin, only half of the required dose should be administered; the maximum dose of protamine sulfate is 50 mg.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use is possible only under strict indications.
Possible to use during breastfeeding, since there is no evidence of heparin penetration into the mother’s milk.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, cool place out of the reach of children, protected from light. |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | B. Braun Melsungen AG, Switzerland |
| Medication form | solution for injection |
| Brand | B. Braun Melsungen AG |
Related products
Buy Heparin sodium Brown, 5000 units/ml 5 ml 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.