No products in the cart.
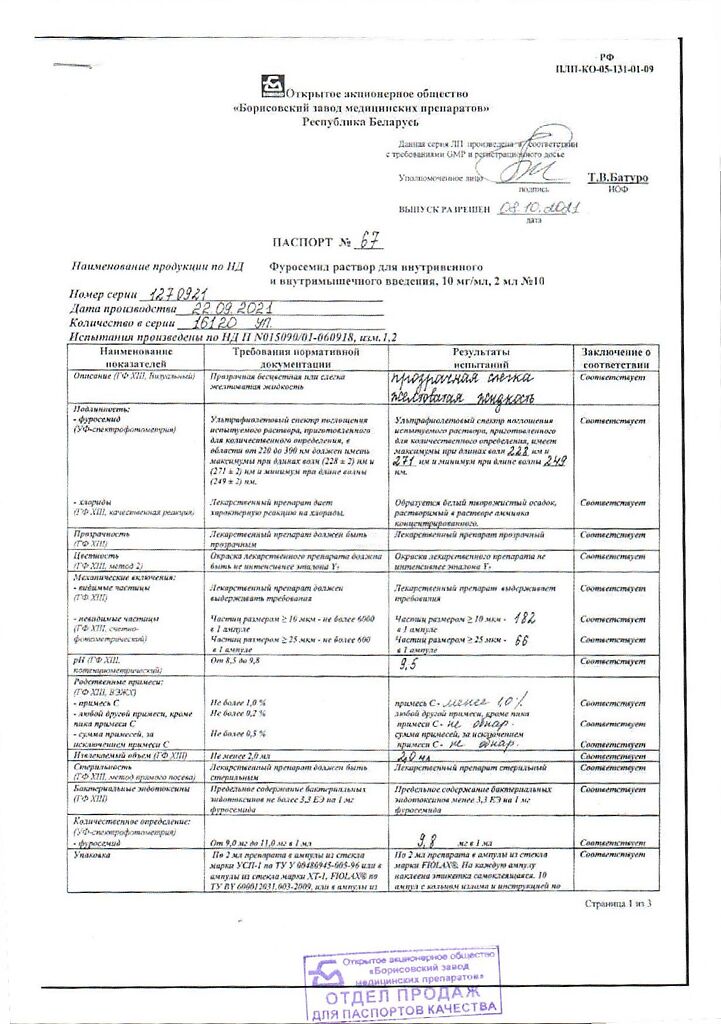
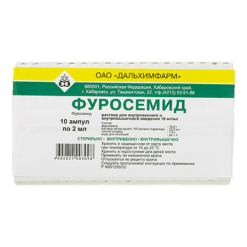
Furosemide, 10 mg/ml 2 ml 10 pcs
€1.16 €1.05
Description
A “loop” diuretic. Disrupts reabsorption of sodium, chlorine ions in the thick segment of the ascending part of the loop of Genle. Due to the increased excretion of sodium ions, there is a secondary (mediated by osmotically bound water) enhanced excretion of water and increased secretion of potassium ions in the distal part of the renal tubule.
Indications
Indications
• edema in chronic congestive heart failure (if treatment with diuretics is necessary);
• edema in acute congestive heart failure. Edema in chronic renal failure;
• acute renal failure, including in pregnant women or during childbirth;
• edema due to liver diseases (if necessary, to complement treatment with aldosterone antagonists);
• hypertensive crisis (as a supportive agent);
• support for forced diuresis.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
“Loop” diuretic. It disrupts the reabsorption of sodium and chlorine ions in the thick segment of the ascending loop of Henle. Due to an increase in the release of sodium ions, a secondary (mediated by osmotically bound water) increased excretion of water and an increase in the secretion of potassium ions occurs in the distal part of the renal tubule.
Special instructions
Special instructions
During the course of treatment, it is necessary to periodically monitor blood pressure, the content of blood plasma electrolytes (including Na+, Ca2+, K+, Mg2+), acid-base status, the content of residual nitrogen, creatinine, uric acid, liver function and, if necessary, make appropriate treatment adjustments.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Furosemide
Composition
Composition
2 ml (ampoule) contains:
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
During pregnancy, the use of furosemide is possible only for a short time and only when the expected benefit of therapy for the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to the drug (drug) Furosemide or other components included in the drug.
Patients allergic to sulfonamides (eg, sulfonamide antibiotics or sulfonylureas) may have cross-sensitivity to furosemide.
Hypovolemia or dehydration.
Renal failure in the form of anuria, if there is no therapeutic response to furosemide.
Renal failure due to poisoning with nephrotoxic or hepatotoxic drugs.
Severe hypokalemia.
Severe hyponatremia.
Precomatose or comatose states associated with hepatic encephalopathy.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the cardiovascular system: decreased blood pressure, orthostatic hypotension, collapse, tachycardia, arrhythmias, decreased blood volume.
Interaction
Interaction
When used simultaneously with aminoglycoside antibiotics (including gentamicin, tobramycin), nephro- and ototoxic effects may be enhanced. Furosemide reduces the clearance of gentamicin and increases plasma concentrations of gentamicin and tobramycin. When used simultaneously with cephalosporin antibiotics, which can cause renal dysfunction, there is a risk of increased nephrotoxicity.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: decreased blood pressure, collapse, shock, hypovolemia, dehydration, hemoconcentration, arrhythmias, acute renal failure with anuria, thrombosis, thromboembolism, drowsiness, confusion, paralysis, apathy.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Borisov Medical Preparations Plant, Belarus
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a place protected from light |
| Manufacturer | Borisov Medical Preparations Plant, Belarus |
| Medication form | solution |
| Brand | Borisov Medical Preparations Plant |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Furosemide, 10 mg/ml 2 ml 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.