No products in the cart.
Foliber, tablets 28 pcs
€11.26 €9.85
Description
Deficiency of folic acid causes impaired DNA synthesis in the cell preparing for chromosome replication.
The mechanism of action of Foliber is due to the participation of folic acid in the form of tetrahydrofolate in the synthesis of nucleic acids and cell division, as well as participation as a coenzyme in the synthesis of purines and pyrimidines, making it a critical factor in the formation of the central nervous system, which develops in humans on days 15-28 after fertilization.
The conversion of 5-methyltetrahydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate in the body can only occur as a result of the addition of a methyl group to homocysteine to form methionine by methioninesinthetase.
In this process, vitamin B12 is involved as a limiting cofactor, so vitamin B12 deficiency is similar in effect to folic acid deficiency activation; in addition, vitamin B12 is also involved in folic acid capture by cells, so when a cell has a primary vitamin B12 deficiency, it is also deficient in folate.
The pharmacological action of Foliber is that its use overcomes the metabolic blockade seen in mothers of children with neural tube defects. The specific nature of this metabolic blockade is in the metabolism of the essential amino acid methionine, in which folate and vitamin B12 are key elements because they are responsible for the re-methylation of homocysteine to methionine.
400 micrograms of folic acid is the minimum effective daily dose recommended by the Centers for Disease Prevention (US, UK and Australia) for healthy women as an additional daily intake to prevent neural tube defects in the fetus. The recommended daily intake of vitamin B12 is 2 micrograms.
Pharmacokinetics
Folic acid is rapidly absorbed in the jejunum, undergoing reduction and methylation to 5 methyltetrahydrofolate, which is present in the portal circulation. Maximum plasma concentrations are observed after 30-60 minutes. On the other hand, vitamin B12 can be absorbed after its interaction in the stomach with the “intrinsic factorKasla”, a glycoprotein that is secreted by the parietal cells of the stomach.
The maximum concentration in plasma is observed after 8-12 hours. As with folic acid, vitamin B12 undergoes significant intestinal-hepatic recirculation. Both components are largely bound to plasma proteins, with the excess accumulating in the liver. Each day, 4-5 µg of folate is excreted in the urine in the form of folic acid, 10-formyltetrahydrofolate and 5-methyltetrahydrofolate.
Folate is also excreted with the mother’s milk. The average half-life of vitamin B12 is about 6 days. Part of the administered dose is excreted with the urine during the first 8 hours, although most is excreted with the bile. 25% is excreted with the feces. In addition, vitamin B12 passes through the placenta and is present in the mother’s milk.
.
Form of release
Form of release
Pills
Additional information
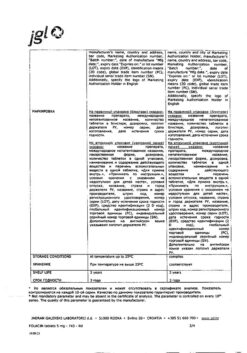
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry place, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Italpharmaco S.p.A., Italy |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Italpharmaco S.p.A. |
Related products
Buy Foliber, tablets 28 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.