No products in the cart.
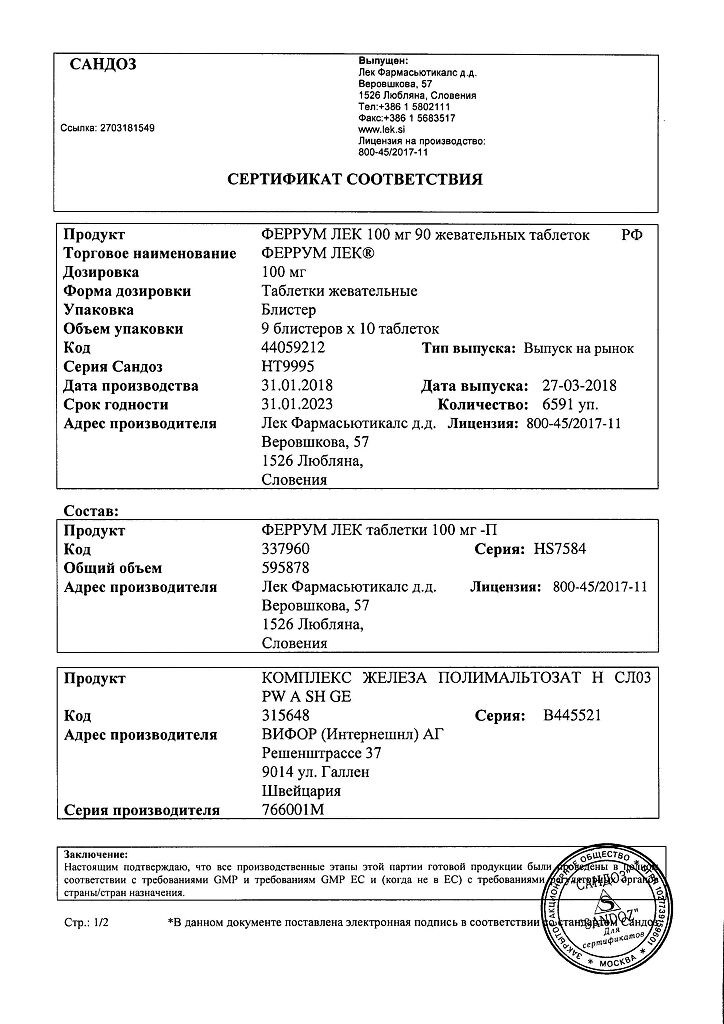
Ferrum Lek, 100 mg 90 pcs.
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Antianemic drug. A preparation of iron.
The molecular weight of the complex is so high – about 50 kDa – that its diffusion through the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract is 40 times slower than that of divalent iron. The complex is stable and does not release iron ions under physiological conditions. The iron of the multinuclear active zones of the complex is bound in a structure similar to that of the natural iron compound, ferritin.
Thanks to this similarity, iron (III) of this complex is absorbed only by active absorption. The iron-binding proteins on the surface of the intestinal epithelium and in the gastrointestinal fluid absorb iron (III) from the complex through competitive ligand exchange. Absorbed iron is mainly deposited in the liver, where it binds to ferritin. Later in the bone marrow it is incorporated into hemoglobin.
The polymaltose complex of iron (III) hydroxide, unlike iron (II) salts, has no pro-oxidant properties. The sensitivity of lipoproteins (e.g., very low-density lipoproteins and low-density lipoproteins) to oxidation is reduced.
Pharmacokinetics
. Studies using the double isotope method (55Fe and 59Fe) have shown that iron absorption, as measured by hemoglobin levels in erythrocytes, is inversely proportional to the dose taken (the higher the dose, the lower the absorption). There is a statistically negative correlation between the degree of iron deficiency and the amount of absorbed iron (the higher the iron deficiency, the better the absorption).
The maximum absorption of iron occurs in the duodenum and jejunum. Unabsorbed iron is excreted with the feces. Its excretion with the exfoliating epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract and skin, as well as with sweat, bile and urine is approximately 1 mg of iron per day. In women during menstruation there is an additional loss of iron, which must be taken into account.
Indications
Indications
treatment of latent iron deficiency;
treatment of iron deficiency anemia;
prevention of iron deficiency during pregnancy.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Antianemic agent. Iron supplement.
The molecular mass of the complex is so large – about 50 kDa – that its diffusion through the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract is 40 times slower than the diffusion of ferrous iron. The complex is stable and does not release iron ions under physiological conditions. The iron of the multinuclear active zones of the complex is bound into a structure similar to the structure of the natural iron compound – ferritin.
Due to this similarity, the iron (III) of this complex is absorbed only by active absorption. Iron-binding proteins, found on the surface of the intestinal epithelium and in the gastrointestinal fluid, absorb iron(III) from the complex through competitive ligand exchange. Absorbed iron is mainly deposited in the liver, where it binds to ferritin. Later in the bone marrow it is incorporated into hemoglobin.
The polymaltose complex of iron (III) hydroxide, unlike iron (II) salts, does not have pro-oxidant properties. The sensitivity of lipoproteins (eg, very low-density lipoproteins and low-density lipoproteins) to oxidation is reduced.
Pharmacokinetics
Studies using the dual isotope method (55Fe and 59Fe) have shown that iron absorption, as measured by red blood cell hemoglobin levels, is inversely proportional to the dose administered (the higher the dose, the lower the absorption). There is a statistically negative correlation between the degree of iron deficiency and the amount of iron absorbed (the higher the iron deficiency, the better the absorption).
Maximum absorption of iron occurs in the duodenum and jejunum. Unabsorbed iron is excreted in the feces. Its excretion in exfoliated epithelial cells of the gastrointestinal tract and skin, as well as in sweat, bile and urine is approximately 1 mg of iron per day. Women experience additional iron loss during menstruation, which must be taken into account.
Special instructions
Special instructions
In cases of anemia caused by an infectious or malignant disease, iron accumulates in the reticuloendothelial system, from which it is mobilized and utilized only after the underlying disease has been cured.
When using the drug Ferrum Lek®, the stool may turn dark, which does not have any clinical significance. The drug Ferrum Lek® does not affect the results of the occult blood test (selective for hemoglobin); therefore, it is not necessary to interrupt iron therapy.
Note for patients with diabetes: 1 chewable tablet of Ferrum Lek® contains 0.04 bread units (XE).
Note for patients with phenylketonuria: Ferrum Lek® contains aspartame (E951), which is a source of phenylalanine, in an amount equivalent to 1.5 mg per tablet.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
Ferrum Lek® does not affect the ability to drive a car or operate machinery that requires increased concentration.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Iron III hydroxide polymaltosate
Composition
Composition
1 chewable tablet contains:
Active substance:
iron (III) hydroxide polymaltosate 400 mg, in terms of iron – 100 mg.
Excipients:
macrogol 6000 – 37.0 mg;
aspartame – 1.5 mg;
chocolate flavoring – 0.6 mg;
talc – 21.0 mg;
dextrates – until 730.0 mg is obtained.
Contraindications
Contraindications
hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
iron overload in the body (for example, in cases of hemochromatosis, hemosiderosis);
impaired iron utilization (for example, anemia caused by lead intoxication, sideroachrestic anemia, thalassemia);
anemia not associated with iron deficiency (for example, hemolytic anemia, megaloblastic anemia due to vitamin B12 deficiency);
children up to 12 years of age (for this dosage form).
Side Effects
Side Effects
Ferrum Lek® is generally well tolerated. Side effects are predominantly mild and transient.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), adverse reactions are classified according to their frequency as follows: very common (≥1/10), common (≥1/100, <1/10), uncommon (≥1/1000, <1/100), rare (≥1/10000, <1/1000) and very rare (<1/10000); frequency unknown - based on available data, it was not possible to determine the frequency of occurrence.
Nervous system disorders
uncommon: headache.
Gastrointestinal disorders
very often: change in the color of feces (due to the excretion of unabsorbed iron, has no clinical significance);
often: diarrhea, nausea, dyspepsia;
very rarely: abdominal pain, constipation, vomiting, discoloration of tooth enamel.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
very rarely: urticaria, rash, itching of the skin.
Interaction
Interaction
The composition of the drug Ferrum Lek® includes complex-bound iron, which causes a low probability of ionic interactions with food components (oxalates, tannins, etc.), as well as with other drugs (for example, tetracyclines, antacids).
No interactions with other drugs or food products have been identified.
Concomitant use of polymaltosate hydroxide with parenteral iron preparations and other oral iron (III) preparations is not recommended due to the pronounced inhibition of the absorption of orally administered iron.
Overdose
Overdose
In case of an overdose of Ferrum Lek®, there were no signs of intoxication or excess iron in the body, since iron from the active substance is not present in the gastrointestinal tract in free form and is not absorbed by passive diffusion.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Lek d.d., Slovenia
Additional information
| Manufacturer | Lek d.d., Slovenia |
|---|---|
| Medication form | chewable tablets |
| Brand | Lek d.d. |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Ferrum Lek, 100 mg 90 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.