No products in the cart.
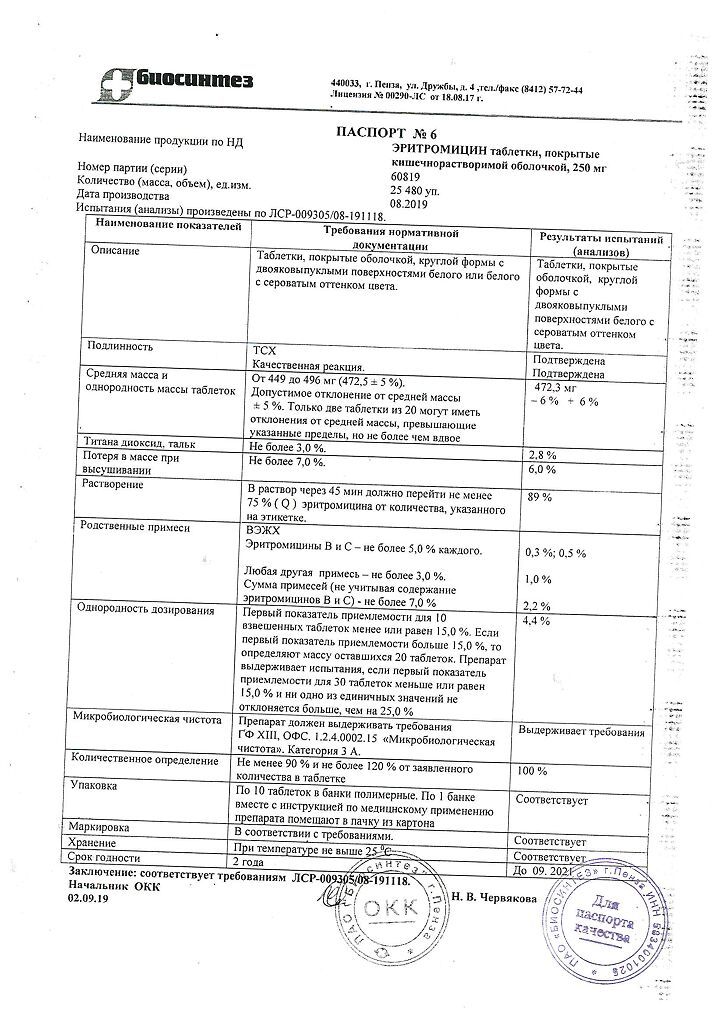
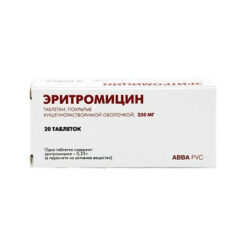
Erythromycin, 250 mg 10 pcs
€6012.00 €5.01
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Macrolide antibiotic
ATX code: S01AA17
Pharmacodynamics:
The bacteriostatic antibiotic from the group of macrolides reversibly binds to the 50S subunit of ribosomes in its donor part, which disrupts the formation of peptide bonds between amino acid molecules and blocks protein synthesis of microorganisms (does not affect nucleic acid synthesis). When used in high doses it can show bactericidal effect. Spectrum of action includes Gram-positive (Staphylococcus spp. producing and not producing penicillinase including Staphylococcus aureus; Streptococcus spp. Streptococcus pneumoniae Streptococcus pyogenes) alpha-hemolytic streptococcus (Viridans group) Bacillus anthracis Corynebacterium diphtheriae Corynebacterium minutissimum) and Gram-negative microorganisms (Neisseria gonorrhoeae Haemophilus influenzae Bordetella pertussis Brucella spp. Legionella spp. including Legionella pneumophila) and other microorganisms: Mycoplasma spp. (including Mycoplasma pneumoniae) Chlamydia spp. (including Chlamydia trachomatis) Treponema spp. Rickettsia spp. Entamoeba histolytica Listeria monocytogenes.
The following Gram-negative bacilli are resistant: Escherichia coli Pseudomonas aeruginosa as well as Shigella spp. Salmonella spp. etc. The susceptible groups include microorganisms whose growth is inhibited when the antibiotic concentration is less than 05 mg/l Medium-sensitive – 1-6 mg/l Moderately resistant and resistant – 6-8 mg/l.
Pharmacokinetics:
Absorption is high. Food intake has no effect on oral forms of erythromycin in the form of base coated with enteric coating. Maximum concentration (Cmax) is reached after oral administration in 2-4 hours. Binding with plasma proteins is 70-90%.
Bioavailability is 30-65%. It is not evenly distributed in the body. It is accumulated in large amounts in liver, spleen and kidneys. In bile and urine the concentration is ten times higher than in plasma. It penetrates well into lung lymph node tissues middle ear exudate prostatic secretion sperm pleural cavity ascitic and synovial fluid. Milk of lactating women contains 50% of the concentration in plasma.
It penetrates poorly through the blood-brain barrier into the cerebrospinal fluid (its concentration is 10% of the drug concentration in plasma). In inflammatory processes in the brain membranes their permeability to erythromycin increases slightly. It penetrates through the placental barrier and enters the fetal bloodstream where its content reaches 5-20% of the plasma content in the mother.
It is metabolized in the liver (more than 90%) partially with the formation of inactive metabolites. The elimination half-life (T1/2) is 1.4-2 hours with anuria – 4-6 hours. Excretion with bile – 20-30% unchanged by kidneys (unchanged) after oral administration – 2-5%.
Indications
Indications
– Primary syphilis (in patients allergic to penicillins) uncomplicated chlamydia in adults (with localization in the lower urinary tract and rectum) when tetracyclines are intolerant or ineffective, etc.
– Infections of ENT organs (tonsillitis otitis sinusitis).
– Infections of the biliary tract (cholecystitis);
– Infections of the upper and lower respiratory tract (tracheitis bronchitis pneumonia);
– Skin and soft tissue infections (pustular skin diseases including juvenile acne.Infections of the skin and soft tissues (pustular skin diseases including acne infected wounds decubitus burns II-III stage trophic ulcers).
– Infections of the mucous membrane of the eyes.
– Prevention of exacerbations of streptococcal infection (tonsillitis pharyngitis) in patients with rheumatism. Prevention of infectious complications during medical and diagnostic procedures (including preoperative intestinal preparation, dental interventions, endoscopy in patients with cardiac defects).
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
the active substance:
erythromycin (in terms of the active substance) 250 mg;
excipients: potato starch, calcium stearate, povidone (polyvinylpyrrolidone low molecular weight medical 12600±2700), polysorbate-80 (tween-80);
coating composition: cellacephate (acetylphthalyl cellulose), castor oil, titanium dioxide.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Ingestion.
The single dose for adults and adolescents over 14 years of age is 025-05 g daily – 1-2 g. The interval between doses is 6 hours. In severe infections the daily dose may be increased to 4 g.
In children from 3 to 14 years of age, depending on the age of body weight and the severity of the infection, 30-50 mg/kg/day in 2-4 doses. In case of severe infections the dose may be doubled.
For treatment of diphtheria carrier – 025 g 2 times a day. The course dose for the treatment of primary syphilis is 30-40 g treatment duration is 10-15 days.
In case of amebic dysentery in adults – 025 g 4 times a day in children – 30-50 mg/kg/day; course duration – 10-14 days.
In legionellosis – 05-1 g 4 times a day for 14 days.
In gonorrhea – 05 g every 6 hours for 3 days then 025 g every 6 hours for 7 days.
For preoperative preparation of the bowel for the prevention of infectious complications – orally 1 g 19 hours 18 hours and 9 hours before the operation (3 g in total).
For the prophylaxis of streptococcal infection (tonsillitis pharyngitis) in adults – 20-50 mg/kg/day in children – 20-30 mg/kg/day the course duration is at least 10 days.
To prevent septic endocarditis in patients with cardiac defects – 1 g for adults and 20 mg/kg for children 1 hour before therapeutic or diagnostic procedure and further up to 05 g for adults and 10 mg/kg for children repeatedly after 6 hours.
In pertussis, 40-50 mg/kg/day for 5-14 days.
In pneumonia in children, 50 mg/kg/day in 4 doses for at least 3 weeks.
In urinary tract infections during pregnancy, 05 g 4 times a day for at least 7 days or (if this dose is not tolerated well) 0.25 g 4 times a day for at least 14 days.
In adults with uncomplicated chlamydia and tetracycline intolerance, 05 g 4 times daily for at least 7 days.
Interaction
Interaction
Drugs that block tubular secretion prolong the elimination half-life of erythromycin.
Incompatible with lincomycin clindamycin and chloramphenicol (antagonism).
Decreases the bactericidal effect of beta-lactam antibiotics (penicillins cephalosporins carbopenems).
Concomitant use with drugs metabolized in the liver (theophylline carbamazepine valproic acid hexobarbital phenytoin alfentanil disopyramide lovastatin bromocriptine) may increase the plasma concentration of these drugs (is an inhibitor of microsomal liver enzymes).
It enhances nephrotoxicity of cyclosporine (especially in patients with concomitant renal failure). Reduces clearance of triazolam and midazolam in connection with which it may enhance the pharmacological effects of benzo-diazepines.
When concomitantly taken with terfenadine or astemizole, possibility of arrhythmia with dihydroergotamine or unhydrogenated ergot alkaloids, vasoconstriction to dysesthesia spasm.
Delays elimination (enhances the effect) of methylprednisolone felodipine and coumarin-type anticoagulants.
In co-administration with lovastatin, rhabdomyolysis increases. Increases the bioavailability of digoxin.
Decreases the effectiveness of hormonal contraception.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Laboratory measures of liver function should be monitored during long-term therapy.
Cholestatic jaundice symptoms may develop within a few days after the start of therapy; however, the risk of development increases after 7-14 days of continuous therapy. The likelihood of ototoxic effects is higher in patients with renal and hepatic impairment and in elderly patients.
Some resistant strains of Haemophilus influenzae are sensitive to simultaneous administration of erythromycin and sulfonamides.
May interfere with determination of catecholamines in urine and “hepatic” transaminase activity in blood (colorimetric determination with definylhydrazine). .
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity hearing loss concomitant administration of terfenadine or astemizole children under 3 years of age lactation.
Arrhythmias (history) prolonged QT interval jaundice (history) hepatic and/or renal failure.
Side effects
Side effects
Hypersensitivity reactions: skin allergic reactions (urticaria and other forms of rash) eosinophilia rarely – anaphylactic shock.
Nausea vomiting gastralgia tenesmia abdominal pain diarrhea dysbiosis rare – oral candidiasis pseudomembranous enterocolitis (both during and after treatment) hepatic dysfunction cholestatic jaundice increased “liver” transaminases activity pancreatitis hearing loss and/or tinnitus (with high doses – over 4 g/day hearing loss after discontinuation of the drug is usually reversible).
Rarely, tachycardia prolongation of the QT interval on ECG ventricular arrhythmias including ventricular tachycardia (pirouette type) in patients with prolonged QT interval.
Overdose
Overdose
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Weight | 0.015 kg |
|---|---|
| Shelf life | 2 years |
| Conditions of storage | List B. Store in a dry place at room temperature. |
| Manufacturer | Biosintez, Russia |
| Medication form | enteric-soluble film-coated tablets |
| Brand | Biosintez |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Erythromycin, 250 mg 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.