No products in the cart.
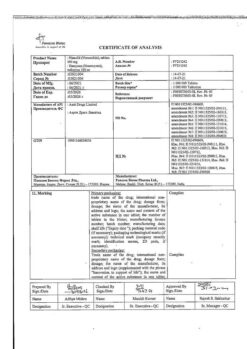
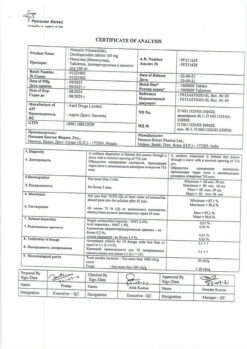
Citramon P, tablets 10 pcs
€1.92 €1.75
Description
A combination drug.
Acetylsalicylic acid has antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects, reduces pain, especially caused by inflammation, and moderately inhibits platelet aggregation and thrombosis, improves microcirculation in the inflammation focus.
Caffeine increases reflex excitability of the spinal cord, excites respiratory and vasomotor centers, dilates blood vessels of skeletal muscles, brain, heart and kidneys, decreases platelet aggregation; it reduces sleepiness and fatigue. In this combination, low-dose caffeine has practically no stimulating effect on the central nervous system, but helps to regulate the tone of the brain vessels.
Paracetamol has analgesic, antipyretic and weak anti-inflammatory effects, due to its effect on the thermoregulation center in the hypothalamus and a weak ability to inhibit the synthesis of prostaglandins (Pd) in peripheral tissues.
Indications
Indications
Pain syndrome of mild and moderate severity (of various origins): headache, migraine, toothache, neuralgia, myalgia, arthralgia, algodismenorrhea. Feverish syndrome: for acute respiratory diseases (ARI), influenza.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Combined drug.
Acetylsalicylic acid has an antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effect, relieves pain, especially caused by the inflammatory process, and also moderately inhibits platelet aggregation and thrombus formation, improves microcirculation at the site of inflammation.
Caffeine increases the reflex excitability of the spinal cord, stimulates the respiratory and vasomotor centers, dilates the blood vessels of skeletal muscles, brain, heart, kidneys, reduces platelet aggregation; reduces drowsiness, feeling of fatigue. In this combination, caffeine in a small dose has virtually no stimulating effect on the central nervous system, but helps regulate cerebral vascular tone.
Paracetamol has an analgesic, antipyretic and weak anti-inflammatory effect, which is associated with its effect on the thermoregulation center in the hypothalamus and a weak ability to inhibit the synthesis of prostaglandins (Pg) in peripheral tissues.
Special instructions
Special instructions
The drug should be prescribed with caution to patients with bronchial asthma and gout.
It is not recommended to prescribe the drug to children, especially with chickenpox and influenza, due to the high risk of developing Reye’s syndrome.
Citramon should not be prescribed simultaneously with barbiturates, anticonvulsants, salicylates, and rifampicin.
Patients taking the drug Citramon should refrain from drinking alcohol.
If it is necessary to prescribe the drug during pregnancy, the expected benefit to the mother should be weighed against the potential risk to the fetus. If short-term administration of Citramon is necessary during lactation, cessation of breastfeeding is not required.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Acetylsalicylic acid, Caffeine, Paracetamol
Composition
Composition
Active substances:
acetylsalicylic acid – 240 mg,
paracetamol – 180 mg,
caffeine monohydrate or caffeine (caffeine anhydrous) – 30 mg.
Excipients:
cocoa – 14 mg,
citric acid – 5 mg,
potato starch – 63 mg,
low molecular weight povidone (medical low molecular weight polyvinylpyrrolidone) – 4 mg,
talc – 9 mg,
calcium stearate – 5 mg.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Contraindicated during pregnancy (I and III trimesters), during lactation.
Acetylsalicylic acid has a teratogenic effect; when used in the first trimester of pregnancy, it leads to a malformation – cleft palate; in the third trimester – to inhibition of labor (inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis), to closure of the ductus arteriosus in the fetus, which causes hyperplasia of the pulmonary vessels and hypertension in the vessels of the pulmonary circulation.
It is excreted in breast milk, which increases the risk of bleeding in the baby due to impaired platelet function.
Children under 15 years of age should not be prescribed medications containing acetylsalicylic acid, since in the case of a viral infection they can increase the risk of Reye’s syndrome. Symptoms of Reye’s syndrome are prolonged vomiting, acute encephalopathy, and liver enlargement.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum in the acute phase; gastrointestinal bleeding (including history); severe dysfunction of the liver and/or kidneys, gout; hemorrhagic diathesis, hypocoagulation; surgical interventions accompanied by heavy bleeding; pregnancy (I and III trimester), lactation period; deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase; glaucoma; hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, asthma induced by taking acetylsalicylic acid, salicylates and other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; childhood (up to 15 years – the risk of developing Reye’s syndrome in children with hyperthermia due to viral diseases); increased excitability, sleep disturbances; organic diseases of the cardiovascular system (including acute myocardial infarction, atherosclerosis); severe arterial hypertension; portal hypertension; vitamin deficiency K; hypoproteinemia.
With caution
Mild to moderate renal failure, liver failure with increased transaminase levels, benign hyperbilirubinemia (including Gilbert’s syndrome, alcoholic liver damage), alcoholism, epilepsy and a tendency to seizures, old age, gout, arterial hypertension.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the immune system: hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, anaphylactic shock, rhinitis, nasal congestion.
From the skin and subcutaneous tissue: itching, rash on the skin and mucous membranes, including erythematous rashes; urticaria, angioedema, erythema multiforme exudative, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Gastrointestinal disorders: dyspeptic disorders, including nausea, vomiting, epigastric discomfort and pain, heartburn, abdominal pain; inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, which can in rare cases cause gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation with corresponding laboratory and clinical manifestations.
Hepatobiliary disorders: increased activity of liver enzymes, usually without the development of jaundice, hepatonecrosis (dose-dependent effect).
Endocrine disorders: hypoglycemia, up to hypoglycemic coma.
Neurological disorders: headache, dizziness, tremor, paresthesia, fear, anxiety, agitation, irritability, sleep disturbance, insomnia, anxiety, general weakness, ringing in the ears.
Cardiac disorders: tachycardia, palpitations, arterial hypertension.
From the blood and lymphatic system: anemia, sulfate hemoglobinemia and methemoglobinemia (cyanosis, shortness of breath, pain in the heart), hemolytic anemia, due to the antiplatelet effect on platelets, acetylsalicylic acid may increase the risk of bleeding. Bleeding events such as intraoperative hemorrhage, hematoma, bleeding from the genitourinary system, nosebleeds, gum bleeding, gastrointestinal bleeding and cerebral hemorrhage have been observed.
Others: bleeding can lead to acute and chronic post-hemorrhagic anemia/iron deficiency anemia (due to the so-called hidden microbleeding) with corresponding laboratory manifestations and clinical symptoms such as asthenia, pale skin, hypoperfusion; non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema.
Interaction
Interaction
Strengthens the effect of heparin, indirect anticoagulants, reserpine, steroid hormones and hypoglycemic drugs.
Co-administration with other NSAIDs and methotrexate increases the risk of side effects.
Reduces the effectiveness of spironolactone, furosemide, antihypertensive drugs, as well as anti-gout drugs that promote the excretion of uric acid.
Barbiturates, rifampicin, salicylamide, antiepileptic drugs and other stimulants of microsomal oxidation contribute to the formation of toxic paracetamol metabolites that affect liver function.
Metoclopramide accelerates the absorption of paracetamol.
Under the influence of paracetamol, T1/2 of chloramphenicol increases 5 times. When taken repeatedly, paracetamol may enhance the effect of anticoagulants (dicoumarin derivatives).
The simultaneous use of paracetamol and ethanol increases the risk of developing hepatotoxic effects.
Caffeine accelerates the absorption of ergotamine.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms (due to acetylsalicylic acid): for mild intoxication – nausea, vomiting, gastralgia, dizziness, ringing in the ears; severe intoxication – lethargy, drowsiness, collapse, convulsions, bronchospasm, difficulty breathing, anuria, bleeding. Initially, central hyperventilation of the lungs leads to respiratory alkalosis (shortness of breath, suffocation, cyanosis, perspiration). As intoxication increases, progressive respiratory paralysis and uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation cause respiratory acidosis.
Treatment: constant monitoring of acid-base balance and electrolyte balance; depending on the state of metabolism – the introduction of sodium bicarbonate, sodium citrate or sodium lactate. Increasing reserve alkalinity enhances the excretion of acetylsalicylic acid due to alkalinization of urine.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store out of the reach of children in the original packaging at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Pharmstandard-Leksredstva, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Keep out of reach of children in the original packaging at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. |
| Manufacturer | Pharmstandard-Leksredstva, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Pharmstandard-Leksredstva |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Citramon P, tablets 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.