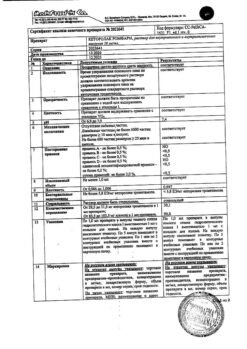
No products in the cart.
Citramon-ExtraCap, 240 mg+27, 45 mg+180 mg capsules 10 pcs.
€4.35 €3.87
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group: analgesic combined agent (NSAID + non-narcotic analgesic + psychostimulant)
ATX code: [N02BA71]
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
A combination drug.
Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) has antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects, relieves pain, especially caused by inflammation, and inhibits thrombosis, improves microcirculation in the inflamed area.
Caffeine increases reflex excitability of the spinal cord, stimulates respiratory and vasomotor centers, dilates blood vessels of skeletal muscles, brain, heart and kidneys, reduces platelet aggregation; it reduces sleepiness and fatigue and increases mental and physical efficiency. In this combination, a small dose of caffeine has practically no stimulating effect on the central nervous system; it increases the tone of cerebral blood vessels and accelerates blood flow.
Paracetamol has analgesic, antipyretic and mild anti-inflammatory effects due to its effect on the thermoregulation center in the hypothalamus and a weak ability to inhibit the synthesis of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues.
Pharmacokinetics
ASK: When taken orally, absorption is complete. During absorption it undergoes presystemic elimination in the intestinal wall and systemic elimination in the liver (deacetylated). The resorbed part is quickly hydrolyzed by cholinesterases and albumin esterase, so the half-life is no more than 15-20 minutes. Circulates in the body (75-90% in connection with albumin) and is distributed in tissues as salicylic acid anion. Time of reaching maximum concentration is 2 hours. Metabolized mainly in liver with formation of 4 metabolites found in many tissues and urine. It is excreted by active secretion in the renal tubules as salicylate (60%) and its metabolites. Excretion of unchanged salicylate depends on urine pH (when urine is alkaline, ionization of salicylates increases, their reabsorption worsens, and excretion significantly increases). The elimination rate depends on the dose: when taking small doses, the elimination half-life is 2-3 hours, with increasing doses it can increase up to 15-30 hours. In infants the elimination of salicylates is much slower than in adults.
Paracetamol: adsorption is high, the maximum concentration is reached after 0.5-2 hours and is 5-20 mcg/ml, plasma protein binding is 15%. It penetrates the blood-brain barrier. Less than 1% of the dose taken by a nursing mother penetrates into breast milk. The therapeutically effective plasma concentration of paracetamol is achieved at a dose of 10-15 mg/kg. It is metabolized in the liver (90-95%): 80% enters into conjugation reactions with glucuronic acid and sulfates to form inactive metabolites; 17% undergoes hydroxylation to form 8 active metabolites, which conjugate with glutathione to form already inactive metabolites. In glutathione deficiency, these metabolites can block hepatocyte enzyme systems and cause necrosis. The CYP2E1 isoenzyme is also involved in metabolism. The elimination half-life is 1-4 hours. It is excreted by kidneys as metabolites, mainly as conjugates. Only 3% are eliminated unchanged. In elderly patients the drug clearance is decreased and the elimination half-life is increased.
Caffeine: when taken orally absorption is good, occurs throughout the intestine. Absorption is mainly due to lipophilicity rather than water solubility. Maximum concentration is reached after 50-75 min and is 1.58-1.76 mg/l. It is rapidly distributed in all organs and tissues of the body: easily penetrates through the blood-brain barrier and the placenta. Distribution volume is 0.4-0.6 l/kg in adults and 0.78-0.92 l/kg in newborns. Blood protein (albumin) binding is 25-36%. It is metabolized in liver by more than 90 %, in children of first years of life by 10-15 %. In adults, about 80% of caffeine doses are metabolized to paraxanthine, about 10% to theobromine, and about 4% to theophylline, which are later demethylated to monomethylxanthines, and then to methylated uric acids. The half-life in adults is 3.9-5.3 hours (sometimes up to 10 hours), in infants it is 65-130 hours (by 4-7 months of life it decreases to adult values). Excretion of caffeine and its metabolites is by the kidneys (1-2% in adults is excreted unchanged, in infants – up to 85%).
Indications
Indications
Pain syndrome of mild and moderate severity (of various origins): headache, migraine, toothache, neuralgia, myalgia, arthralgia, algodismenorrhea.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group: combined analgesic (NSAID + analgesic non-narcotic + psychostimulant)
ATC code: [N02BA71]
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Combination drug.
Acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) has an antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effect, relieves pain, especially caused by the inflammatory process, and also inhibits thrombus formation, improves microcirculation in the area of inflammation.
Caffeine increases reflex excitability of the spinal cord, stimulates the respiratory and vasomotor centers, dilates the blood vessels of skeletal muscles, brain, heart, kidneys, reduces platelet aggregation; reduces drowsiness, fatigue, increases mental and physical performance. In this combination, caffeine in a small dose has virtually no stimulating effect on the central nervous system, increases cerebral vascular tone and helps accelerate blood flow.
Paracetamol has an analgesic, antipyretic and weak anti-inflammatory effect, which is associated with its effect on the thermoregulation center in the hypothalamus and a weak ability to inhibit the synthesis of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues.
Pharmacokinetics
ASA: absorption is complete when taken orally. During absorption, it undergoes presystemic elimination in the intestinal wall and systemic elimination in the liver (deacetylated). The resorbed part is quickly hydrolyzed by cholinesterases and albuminesterase, so the half-life is no more than 15-20 minutes. It circulates in the body (75-90% in connection with albumin) and is distributed in tissues in the form of salicylic acid anion. The time to reach maximum concentration is 2 hours. Metabolized primarily in the liver with the formation of 4 metabolites found in many tissues and urine. It is excreted by active secretion in the renal tubules in the form of salicylate (60%) and its metabolites. The excretion of unchanged salicylate depends on the pH of the urine (with alkalinization of the urine, the ionization of salicylates increases, their reabsorption worsens, and excretion increases significantly). The rate of elimination depends on the dose: when taking small doses, the half-life is 2-3 hours, with increasing doses it can increase to 15-30 hours. In newborns, the elimination of salicylates is much slower than in adults.
Paracetamol: adsorption is high, the maximum concentration is reached after 0.5-2 hours and is 5-20 μg/ml, binding to plasma proteins is 15%. Penetrates the blood-brain barrier. Less than 1% of the dose taken by a nursing mother passes into breast milk. The therapeutically effective concentration of paracetamol in plasma is achieved when taken at a dose of 10-15 mg/kg. Metabolized in the liver (90-95%): 80% enters into conjugation reactions with glucuronic acid and sulfates to form inactive metabolites; 17% undergoes hydroxylation to form 8 active metabolites, which conjugate with glutathione to form inactive metabolites. With a lack of glutathione, these metabolites can block the enzyme systems of hepatocytes and cause their necrosis. The CYP2E1 isoenzyme is also involved in metabolism. The half-life is 1-4 hours. It is excreted by the kidneys in the form of metabolites, mainly in the form of conjugates. Only 3% are excreted unchanged. In elderly patients, the clearance of the drug decreases and the half-life increases.
Caffeine: when taken orally, absorption is good and occurs throughout the intestine. Absorption occurs primarily due to lipophilicity rather than water solubility. The maximum concentration is reached after 50-75 minutes and is 1.58-1.76 mg/l. It is quickly distributed in all organs and tissues of the body: it easily penetrates the blood-brain barrier and the placenta. The volume of distribution in adults is 0.4-0.6 l/kg, in newborns – 0.78-0.92 l/kg. Communication with blood proteins (albumin) – 25-36%. More than 90 are metabolized in the liver, in children of the first years of life up to 10-15%. In adults, about 80% of a caffeine dose is metabolized to paraxanthine, about 10% to theobromine, and about 4% to theophylline, which are subsequently demethylated to monomethylxanthines and then to methylated uric acids. The half-life in adults is 3.9-5.3 hours (sometimes up to 10 hours), in newborns – 65-130 hours (by 4-7 months of life it decreases to the same value as in adults). Caffeine and its metabolites are excreted by the kidneys (1-2% is excreted unchanged in adults, and up to 85% in newborns).
Special instructions
Special instructions
General
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Acetylsalicylic acid, Caffeine, Paracetamol
Composition
Composition
Active ingredients:
acetylsalicylic acid – 240.0 mg,
paracetamol – 180.0 mg,
caffeine – 27.45 mg;
excipients:
citric acid (citric acid monohydrate) – 5.00 mg,
potato starch – 20.95 mg,
talc – 10.00 mg,
low molecular weight povidone (low molecular weight medical polyvinylpyrrolidone 12600±2700 or K-17) – 3.00 mg,
calcium stearate – 1.00 mg,
colloidal silicon dioxide (aerosil) – 2.60 mg.
Hard gelatin capsules No. 00.
Composition of the capsule shell (body and cap):
titanium dioxide (E 171) – 2.6666%, quinoline yellow (E 104) – 1.8394%, sunset yellow dye (E 110) – 0.0088%, gelatin – up to 100%.
Contraindications
Contraindications
– Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum in the acute phase;
– Gastrointestinal bleeding or perforation, history of peptic ulcer;
– Severe renal or liver failure;
– Hemorrhagic diathesis, hypocoagulation (including hemophilia, hypoprothrombinemia);
– Surgical interventions accompanied by heavy bleeding;
– Pregnancy, breastfeeding period;
– Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency;
– Glaucoma;
– Hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
– Complete and incomplete combination of bronchial asthma, recurrent polyposis of the nose and paranasal sinuses and intolerance to ASA or other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (including a history);
– Children up to 15 years of age as an anesthetic, for febrile syndrome – up to 18 years of age;
– Increased excitability, sleep disturbances;
– Organic diseases of the cardiovascular system (including acute myocardial infarction, atherosclerosis);
– Severe arterial hypertension;
– Portal hypertension;
– Chronic heart failure III-IV functional class according to NYHA;
– Concomitant use of methotrexate more than 15 mg per week;
– Vitamin deficiency K;
– Hypoproteinemia.
With caution:
Gout, hyperuricemia, gastric and duodenal ulcers, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, hay fever, nasal polyposis, drug allergies, simultaneous use of methotrexate at a dose of less than 15 mg/week, concomitant therapy with anticoagulants, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, glucocorticosteroids, antiplatelet agents, selective reversal inhibitors serotonin uptake.
Mild to moderate renal failure, mild to moderate liver failure with increased transaminase levels, benign hyperbilirubinemia (including Gilbert’s syndrome, alcoholic liver damage), alcoholism, epilepsy and a tendency to seizures, old age, gout, arterial hypertension, chronic heart failure of functional class I-II according to NYHA, coronary heart disease, cerebrovascular diseases, peripheral arterial diseases, smoking.
If you have one of the listed diseases/conditions, be sure to consult your doctor before taking the drug.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Gastralgia, nausea, vomiting, hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, allergic reactions (including Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Lyell), tachycardia, increased blood pressure, bronchospasm.
Interaction
Interaction
Strengthens the effect of heparin, indirect anticoagulants, reserpine, steroid hormones and hypoglycemic drugs.
Co-administration with other NSAIDs and methotrexate increases the risk of side effects.
Reduces the effectiveness of spironolactone, furosemide, antihypertensive drugs, as well as anti-gout drugs that promote the excretion of uric acid.
Barbiturates, rifampicin, salicylamide, antiepileptic drugs and other stimulants of microsomal oxidation promote the formation of toxic paracetamol metabolites that affect liver function.
Overdose
Overdose
Acetylsalicylic acid
For mild intoxications – dizziness, tinnitus, deafness, increased sweating, nausea, vomiting, headache and confusion. Occurs at plasma concentrations of 150-300 mcg/ml. Treatment is dose reduction or discontinuation of therapy. At concentrations above 300 mcg/ml, more severe intoxication occurs, manifested by hyperventilation, fever, anxiety, ketoacidosis, respiratory alkalosis and metabolic acidosis. Central nervous system depression can lead to coma, and cardiovascular collapse and respiratory failure may also occur.
The greatest risk of developing chronic intoxication is observed in children and the elderly when taking more than 100 mg/kg/day for several days.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Pharmstandard-Leksredstva, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Pharmstandard-Leksredstva, Russia |
| Medication form | capsules |
| Brand | Pharmstandard-Leksredstva |
Related products
Buy Citramon-ExtraCap, 240 mg+27, 45 mg+180 mg capsules 10 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.