No products in the cart.
Cibor 2500,2500 me 0,2 ml syringes 10 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
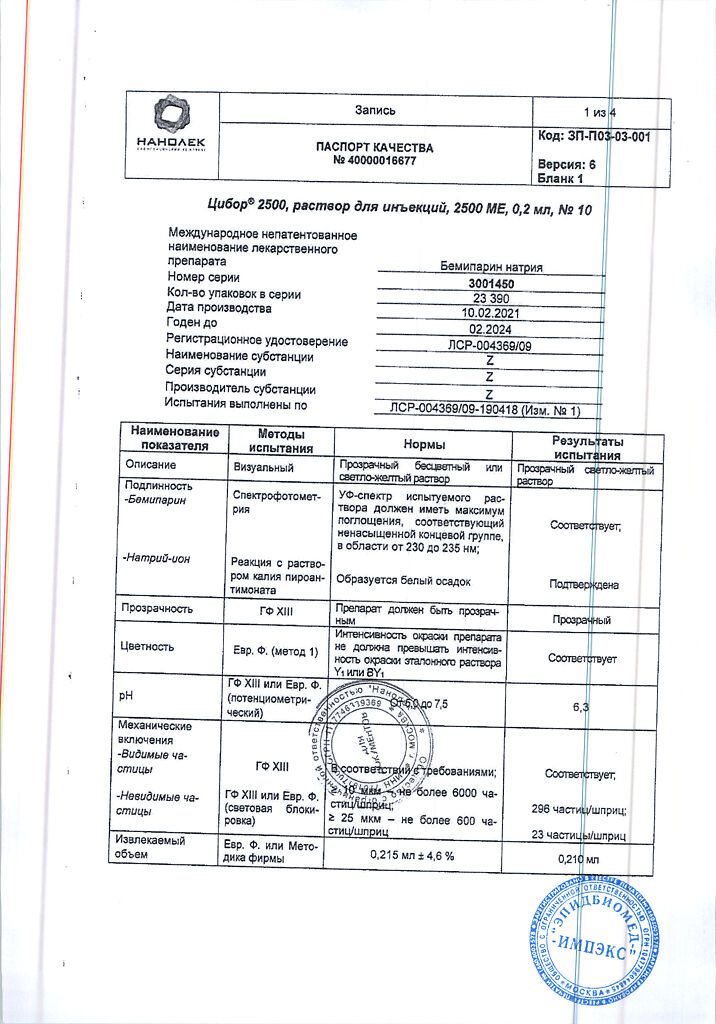
Cibor is an anticoagulant drug for parenteral administration. The drug contains the active ingredient – bemiparin sodium – a low molecular weight heparin, which is obtained by depolymerization of sodium heparin extracted from the mucous membrane of pig intestine.
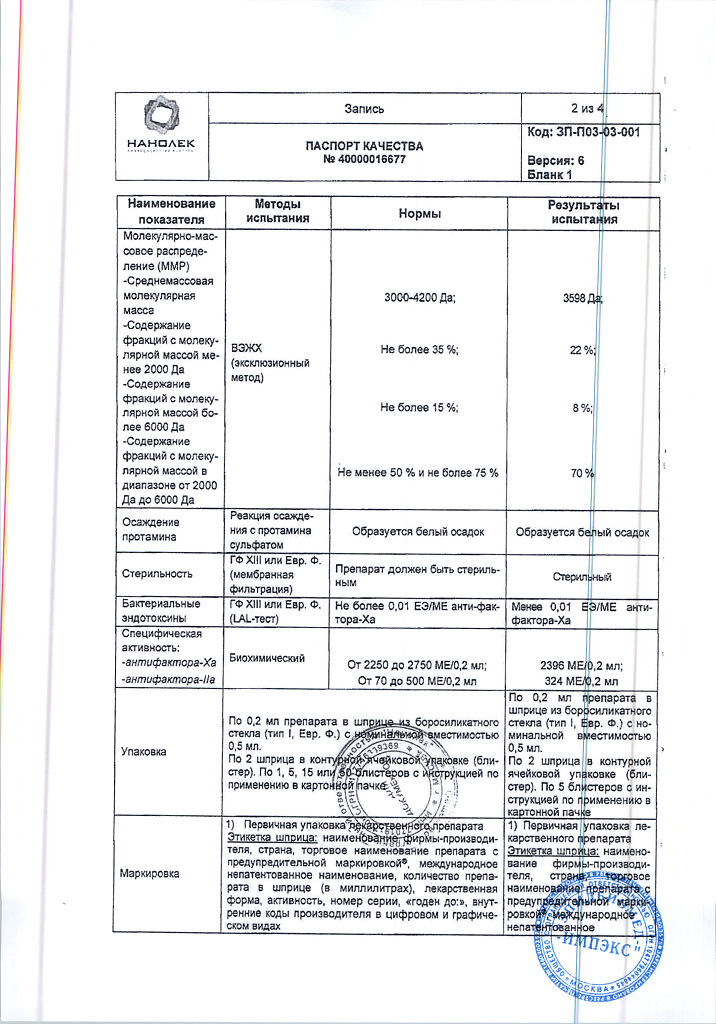
The average molecular weight of bemiparin is 3600 Da. The content of molecular chains with a molar mass of less than 2000 Da is less than 35%, with a molar mass of 2000-6000 Da – 50-75%, with a molar mass over 6000 Da – less than 15%. Bemiparin sodium has anti-Xa-factor activity of about 80-120Me of anti-Xa per 1mg of dry matter. Anti-IIa-factor activity is 5-20Me of anti-IIa-factor per 1mg of dry sodium bemiparin. The ratio of anti-Xa-factor and anti-IIa-factor activity is about 8.
Cibor has a pronounced antiplatelet effect, when used in therapeutic doses it practically does not increase the time of blood clotting.
When administered subcutaneously the bioavailability is 96%. Maximal activity is observed 2-4 hours after injection. When administering therapeutic doses the anti-IIa-factor activity is practically not manifested.
The elimination half-life with doses of 2500 to 12500 ME reaches 5-6 hours. To achieve the therapeutic effect it is sufficient to administer the drug once a day.
Indications
Indications
The drug Cibor is intended for the prevention of blood clotting in the extracorporeal circulation system during a hemodialysis session.
In addition Cibor 2500 is used for the prevention of thromboembolism during general operative interventions.
Cibor 3500 is also used for the prevention of thromboembolism during operative interventions in orthopedic practice.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
The solution for injection in ready-made syringes of 0.2 ml, 2 syringes packed in a blister, 1, 5, 15, 20 or 50 blisters placed in a carton pack.
1 ml of Cibor 2500 solution for injection contains:
Bemiparin sodium (antifactor-Xa equivalent) – 12500ME;
Additional substances.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Cibor is intended for parenteral use. The solution can be injected subcutaneously into the posterolateral lumbar region or the anterolateral region of the abdomen, alternating between the left and right sides. The needle of the syringe should be placed perpendicular to the skin fold. Do not rub the injection site. Intravenous administration of Cibor is prohibited, and intramuscular administration of other drugs during therapy with bemiparin is not recommended due to the risk of hematoma development. Doses of bemiparin are determined by the physician.
In general surgical interventions it is recommended to administer 2500 megabytes (1 syringe of Cibor 2500) 2 hours before the beginning of the surgical intervention; it is also allowed to administer the first injection 6 hours after the operation. On the next day after the first injection of the drug the use of 2500 ME of bemiparin with an interval of 24 hours should be changed.
As a prophylaxis it is recommended to use during the period of risk of thromboembolism or until restoration of the patient’s motor activity.
The minimum recommended prophylactic course is 7-10 days.
In operations with high risk of venous thromboembolism in orthopedic practice the administration of 3500 ME (1 syringe of Cibor 3500) 2 hours before surgical intervention is usually recommended; it is also possible to administer the first injection of the drug 6 hours after the operation. Afterwards, the drug should be administered at intervals of 24 hours. It is recommended to continue therapy with the drug until the patient’s motor activity is restored.
The therapy with the drug should be continued for at least 7-10 days.
In order to prevent blood clotting in the system during multiple hemodialysis of not more than 4 hours it is recommended to administer 2500-3500 ME of the drug (depending on the weight of the patient, 3500 ME is administered if the body weight is over 60 kg, 2500 ME is less than 60 kg) as a bolus injection into the arterial bed at the beginning of the hemodialysis session.
Interaction
Interaction
There are no data on pharmacological interactions of bemiparin; possible interactions should be considered on the basis of data on other low-molecular-weight heparins, so:
Bemiparin should not be used in combination with other drugs that have anticoagulant properties and can inhibit platelet aggregation, as well as with systemic glucocorticosteroid drugs and dextran, as these combinations increase the risk of bleeding. If the combined use of these drugs cannot be avoided, blood clotting and the patient’s condition should be closely monitored.
Bemiparin should also be used with caution in combination with drugs that contribute to hyperkalemia.
The simultaneous use of Cibor with nitroglycerin for intravenous administration may decrease the effectiveness of bemiparin sodium.
The solution must not be mixed with other medicinal products for parenteral use.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Cybor is not indicated in patients with hypersensitivity to bemiparin and heparin, or in patients with immunologically heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (including a history or suspected history of this condition).
The drug should not be administered to persons with clotting disorders with risk of bleeding, marked pancreatic and hepatic dysfunction, or persons with active bleeding.
Bemiparin is not prescribed in acute endocarditis of bacterial etiology, chronic endocarditis, injuries or surgical interventions in the visual, hearing and central nervous system, patients with disseminated intravascular clotting syndrome.
The drug is not recommended to patients with high risk of bleeding, particularly in case of active peptic ulcer, cerebral aneurysm, hemorrhagic stroke and brain tumors.
Cibor is not used in pediatrics.
Bemiparin is used with caution in patients with liver and kidney function disorders, thrombocytopenia, circulatory disorders of iris and retina of vascular genesis, uncontrolled arterial hypertension, urolithiasis and in patients with past history of gastric and duodenal ulcers.
Because of the increased risk of hyperkalemia, Cibor should be used with caution in patients with diabetes mellitus, metabolic acidosis, chronic renal failure and increased plasma potassium levels and in patients who receive therapy with potassium-saving diuretics (these patients should have their potassium levels determined before starting therapy with bemiparin and monitored throughout the course of treatment).
Particular caution should be exercised when performing a lumbar puncture, epidural or spinal anesthesia in patients receiving bemiparin due to the risk of spinal or epidural hematoma, the consequences of which may be permanent paralysis. The interval between taking bemiparin and carrying out these manipulations is determined by the attending physician. If symptoms of an epidural or cerebrospinal hematoma occur, a diagnosis should be made immediately and appropriate therapy administered.
Side effects
Side effects
The following undesirable effects may occur with the use of Cibor:
Hepatic disorders: transient increase in liver enzyme activity.
Hematopoietic system: thrombocytopenia of varying severity type I or II. In case of thrombocytopenia type I, the drug should not be withdrawn. If during the development of thrombocytopenia type II (usually observed on day 5-21 of therapy with bemiparin) the number of platelets decreases by 30-50% (compared with the level before the start of therapy) bemiparin should be canceled and alternative therapy should be prescribed.
Allergic reactions: urticaria, skin itching, anaphylactoid reactions. In single cases the development of skin necrosis preceded by erythema and erythematous painful spots has been noted; immediate withdrawal of bemiparin is required if such side effects develop.
Local reactions: ecchymosis, necrosis, pain and hematoma in the injection site.
Other: bleeding, including from the skin, wounds, digestive and genitourinary tract, mucous membranes. Osteoporosis.
Epidural and spinal hematoma during lumbar puncture, spinal or epidural anesthesia.
Overdose
Overdose
By using excessive doses of Cibor, bleeding has been reported in patients.
The treatment is prescribed depending on the severity of the hemorrhage as well as the risk of thrombosis. For minor bleeding, therapy is rarely needed. For more severe hemorrhages, administration of protamine sulfate is indicated, which slightly reduces the anti-Xa activity of Cibor within 2 hours.
For intravenous administration, the dose of protamine sulfate is calculated individually depending on the dose of bemiparin (1.4mg protamine sulfate per 100 ME of anti-Xa).
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
Cybor during pregnancy is prescribed after careful assessment of the risk/benefit ratio. In animal studies the drug Cibor had no teratogenic effect, there are no data on the penetration of bemiparin through the blood-placental barrier.
If it is necessary to use bemiparin during lactation, breastfeeding should be interrupted with prior consultation with the doctor.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Weight | 0.084 kg |
|---|---|
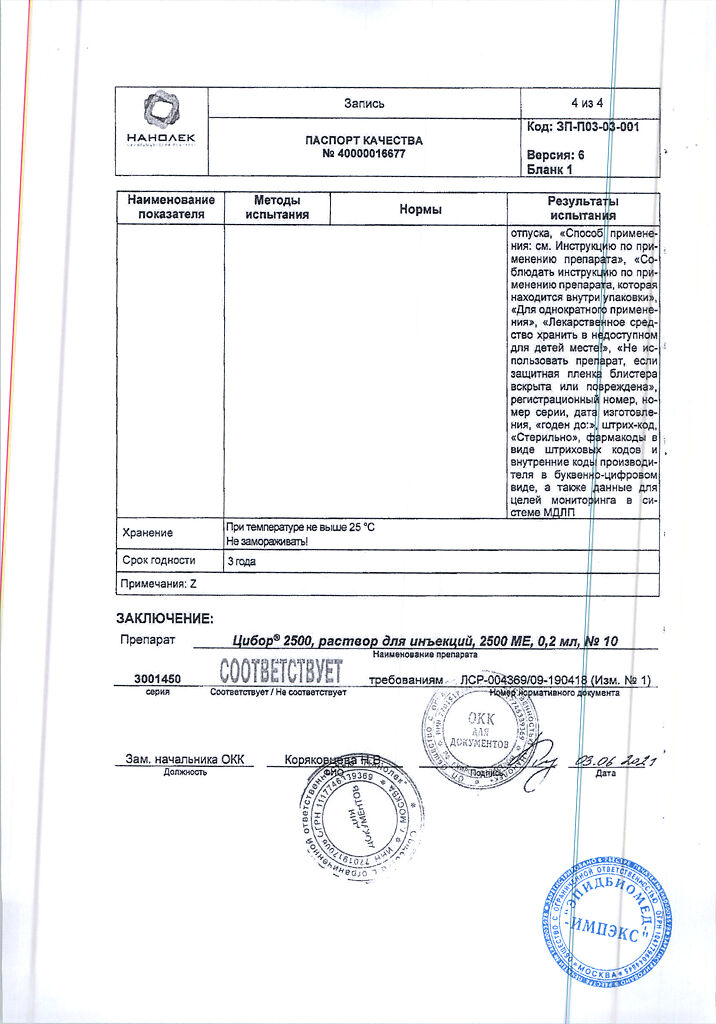
| Shelf life | 2 years |
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 30 °C (do not freeze) |
| Manufacturer | ROVI Contract Manufechering S.L., Spain |
| Medication form | solution for injection |
| Brand | ROVI Contract Manufechering S.L. |
Related products
Buy Cibor 2500,2500 me 0,2 ml syringes 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.