No products in the cart.
Aktiferrin, syrup 100 ml
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group: iron drug
ATC code: B03AE10
Pharmacological effect.
Pharmacodynamics. Iron is the body’s most important trace element. As a coenzyme of cytochrome oxidase, catalase and peroxidase and as a component of hemoglobin (Hb), myoglobin and cytochromes, it is involved in many metabolic processes and stimulates erythropoiesis.
The serine α-amino acid contained in the drug promotes more effective absorption of iron and its entry into the systemic bloodstream, resulting in rapid recovery of its normal content in the body. This provides better tolerability of the drug and reduces the amount of iron required.
The daily requirement for iron in adults is 1-2 mg, in pregnant women 2-5 mg, in children under 7 years of age 0.5-1.5 mg. On average, 10% is absorbed, so in order to meet the need for iron, the dose when taken orally must be 10 times the daily requirement.
Pharmacokinetics. After oral ingestion, about 10-15% of divalent iron is absorbed in the duodenum and jejunum. Absorption of iron is also possible through the mechanism of passive diffusion. Absorption of iron is significantly increased in iron deficiency and in increased erythropoiesis. In patients with low hemoglobin and depleted iron depot, absorption may increase up to 50-60% and decrease with normalization of these parameters. The maximum concentration of iron is reached 2-4 hours after intake.
In the blood, iron binds to transferrin and is transported in trivalent form to sites of hematopoiesis and to specific depots.
After iron binds to apoferritin, it is deposited in the liver, spleen and bone marrow in the form of ferritin. Iron penetrates the placental barrier and minimal amounts are excreted into breast milk.
Indications
Indications
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
If the physician has not prescribed a different dose, the instructions below should be strictly adhered to:
The daily dose for children over 2 years of age and adults is set at the rate of 5 ml per 12 kg of body weight.
Preschool children (over 2 years of age): the average dose is 5 ml 1 – 2 times a day.
School-age children: the average dose is 5 ml 2 to 3 times a day.
To open the bottle, press the cap down and at the same time turn in the direction of the arrow. After using the drug the cap should be tightly screwed on (preventing access for children).
The iron deficiency can be roughly calculated using the formula:
mg iron = kg body weight x 3.5 x (16 – Hb in g %)
Thresholds below or above which iron deficiency is taken as requiring treatment:
Children
School-age children, adults
Hb (g %)
< 11
< 12
Erythrocytes (million/mm 3)
< 3.5
< 4.0
Reticulocytes (%)
> 15
> 15
Serum iron (µg %)
< 60
< 80
Total iron content = transferrin (µg %)
> 380
> 400
Average red blood cell Hb (pg)
< 25
< 30
Average red blood cell volume
< 30
< 30
Interaction
Interaction
The specific antidote is deferoxamine (desferal).
When used concomitantly, iron salts reduce absorption of such drugs as tetracyclines, gyrase inhibitors (e.g., ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, norfloxoccin, ofloxacin), penicillamine, levodopa, carbidopa and methyldopa.
In patients receiving levothyroxine sodium replacement therapy, iron salts decrease its absorption.
High doses of iron preparations decrease renal absorption of zinc preparations (it is recommended to take these 2 hours after taking iron preparations).
The absorption of iron is reduced when colestyramine, antacids (containing aluminum, magnesium, calcium, bismuth), and calcium and magnesium supplements are taken at the same time.
The concomitant use of iron salts and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may increase the damaging effects of iron on the gastrointestinal mucosa.
In children, concomitant use of iron reduces the effectiveness of vitamin E.
Therefore, all of the above remedies are recommended to be taken 3-4 hours before or after taking Aktiferrin. Systematic clinical and laboratory monitoring should be carried out if concomitant administration of drugs is necessary.
Tea, coffee, plant foods containing iron-chelating agents (such as phosphates, phytates, oxalates), milk, eggs reduce iron absorption.
Ascorbic acid and citric acid increase iron absorption.
Ethanol increases iron absorption and the risk of toxic complications.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
The use of the drug may cause persistent darkening of the teeth. Hepatic or renal insufficiency increases the risk of iron cumulation. Use of the drug may aggravate ulcerative and inflammatory bowel diseases.
Influence on driving and operating machinery
Have not been identified.
Synopsis
Synopsis
Contraindications
Contraindications
– Hypersensitivity to the active or excipient components of the drug;
– disorders of iron absorption (sideroachrestic anemia, lead anemia, thalassemia);
– increased iron in the body (hemochromatosis, hemolytic anemia);
– anemia not related to iron deficiency.
Cautions
Caution should be exercised when concomitant use of iron preparations with dietary products and supplements containing iron salts (possible risk of overdose).
In patients with gastrointestinal inflammation and mucosal ulcers, the benefit ratio of treatment versus risk of gastroenterological exacerbations with therapy with iron should be assessed.
Patients with hereditary fructose or galactose intolerance, lack of lactase, glucose-galactose malabsorption or sucrose-isomaltose deficiency should not take the drug.
Side effects
Side effects
Immune system disorders: rare (> 1/10 000 and < 1/1000) skin allergic reactions.
Gastrointestinal tract: very rare (< 1/10 000) constipation, diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting.
When taking iron-containing drugs, dark (black) staining of the feces is possible, which is not clinically significant.
The gastrointestinal disturbances may be prevented by gradually increasing the dose at the beginning of treatment or by reducing the dose during treatment.
Overdose
Overdose
In children there is a high risk of intoxication with iron preparations, life-threatening conditions can occur when taking 1 g of iron sulfate. Therefore, iron preparations should be kept out of the reach of children.
Symptoms:the following symptoms may occur if very large doses of the drug are taken accidentally: weakness, fatigue, paresthesias, pale skin, cold clammy sweat, decreased blood pressure, palpitations, acrocyanosis, abdominal pain, diarrhea with blood mixed in, cyanosis, confusion, weak pulse, hyperthermia, lethargy, seizures, hyperventilation symptoms, coma.
The signs of peripheral circulatory collapse appear within 30 minutes after ingestion; metabolic acidosis, seizures, fever, leukocytosis, coma within 12-24 hours; acute renal and hepatic necrosis within 2-4 days.
Treatment:before specific therapy – take measures to remove from the stomach the drug has not yet been absorbed (gastric lavage), give milk, raw eggs. Specific therapy is carried out by prescribing deferoxamine (desferal) orally and parenterally. In acute poisoning to bind iron not yet absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, 5-10 g of the drug are given by dissolving the contents of 10-20 ampoules in drinking water.
In case of development of poisoning phenomena deferoxamine is administered slowly, in children – 15 mg/h, in adults – 5 mg/kg/h (up to 80 mg/kg/day); in mild poisoning – in children 1 g every 4-6 hours, in adults – 50 mg/kg (up to 4 g/day).
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
Additional information
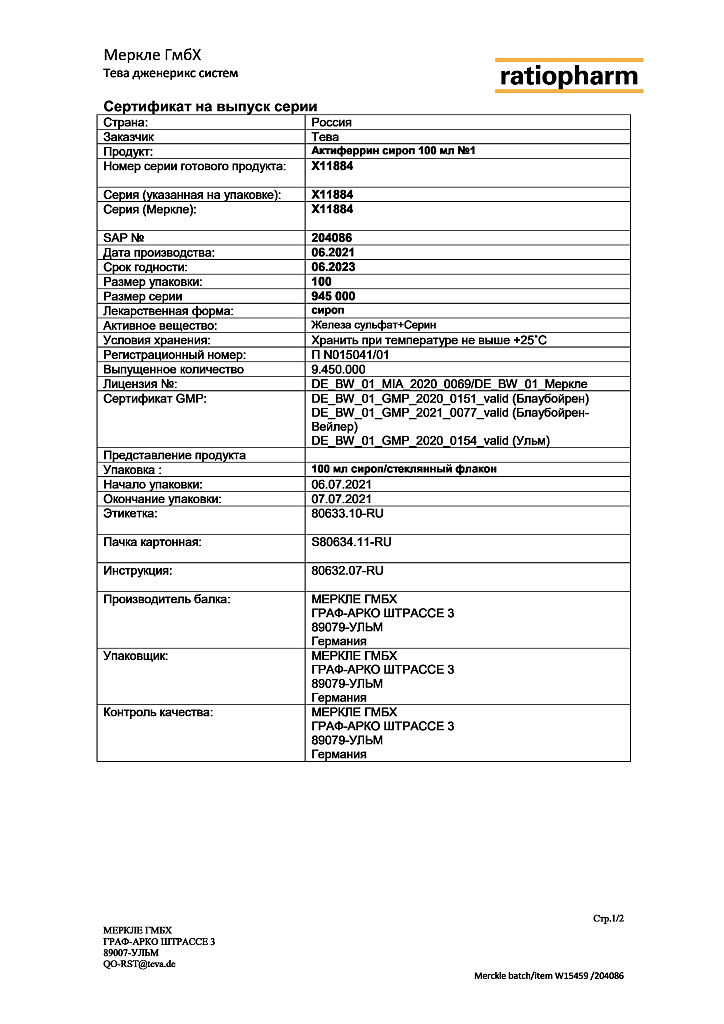
| Shelf life | 2 years. Do not use after the expiration date. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store in a moisture-proof place at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. |
| Manufacturer | Merkle GmbH, Germany |
| Medication form | syrup |
| Brand | Merkle GmbH |
Related products
Buy Aktiferrin, syrup 100 ml with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.