No products in the cart.
Vinpocetine, concentrate 5 mg/ml 5 ml 10 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description Psychostimulant and nootropic Pharmacokinetics:
ATC: N.06.B.X.18 Vinpocetine
Pharmacodynamics:
The mechanism of action of Vinpocetine is composed of several elements: it improves cerebral blood flow and metabolism and has beneficial effects on blood rheological properties.
The neuroprotective effect is realized by reducing the adverse cytotoxic effects of excitatory amino acids. It blocks Na- and Ca2+-channels and NMDA- and AMRA-receptors. Selectively inhibits Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent cGMP-phosphodiesterase. Increases serotonin and noradrenaline metabolism in the brain, stimulates noradrenergic neurotransmitter system and has antioxidant effect.
It improves microcirculation in the brain by inhibiting platelet aggregation, decreasing pathologically elevated blood viscosity, increasing erythrocyte deformability and inhibiting adenosine reuptake; it promotes oxygen transfer to cells by reducing the affinity of red blood cells for it.
It selectively increases cerebral blood flow by reducing cerebral vascular resistance without significant effect on systemic circulatory parameters (blood pressure (BP), cardiac output, heart rate, total peripheral vascular resistance); does not cause “stealing” effect.
Distribution
Distribution of radioactively labeled vinpocetine, when administered to rats, the greatest radioactivity was found in the liver and gastrointestinal tract. The maximum concentration in tissues was noted 2-4 h after administration. Concentrations in the brain did not exceed those found in blood.
In humans the binding to plasma proteins is 66%. Bioavailability is about 7%. The volume of distribution is 246.7±88.5 L, indicating high tissue binding. Total clearance (66.7 l/h) exceeds hepatic blood flow rate (50 l/h), indicating extrahepatic metabolism.
Metabolism
The main metabolite is apovincamic acid (AVC), which is 25-30% of the parent compound. The area under the “concentration-time” curve of AVC after oral administration is twice that of intravenous administration of vinpocetine. Thus, vinpocetine is subject to a pronounced “first pass” effect through the liver.
Other metabolites include: hydroxyvinpocetine, hydroxy-AVC, AVC-dioxyglycinate and their conjugates (sulfates and (or) glucuronides). Excretion of unchanged vinpocetine is low (a few percent).
In patients with hepatic or renal dysfunction, no dose adjustment is required because vinpocetine does not cumulate.
Excretion
When repeatedly administered in doses of 5 and 10 mg, vinpocetine exhibits linear pharmacokinetics, with equilibrium plasma concentrations of 1.2±0.27 and 2.1±0.33 ng/mL, respectively. The elimination half-life in humans is 4.83±1.29 h. In studies with radioactively labeled vinpocetine, renal and intestinal excretion was found to be 60:40%.
In rats and dogs a high concentration is found in bile, but significant enterohepatic recirculation was noted.
Pharmacokinetics in special patient groups
As vinpocetine is primarily intended to treat the elderly, the slower distribution and metabolism as well as excretion in this age group must be considered, especially with long-term use. According to the results of clinical studies it was found that the kinetics of vinpocetine in the elderly is not significantly different from the young, there is no cumulation.
With impaired liver and renal function no cumulation is noted, which allows for long-term therapy.
.
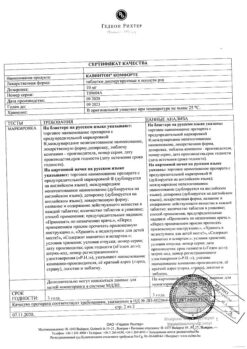
Indications
Indications
Neurology: transient ischemic attack, symptomatic treatment of the consequences of ischemic stroke, vascular vertebrobasilar insufficiency, vascular dementia, cerebral atherosclerosis, post-traumatic, hypertensive encephalopathy.
Ophthalmology: chronic vascular diseases of the retina and choroid.
Otology: perceptual hearing loss, Meniere’s disease, tinnitus, hearing impairment of vascular or toxic (including drug) origin.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Psychostimulant and nootropic agent
ATC: N.06.B.X.18 Vinpocetine
Pharmacodynamics:
The mechanism of action of vinpocetine consists of several elements: it improves cerebral blood flow and metabolism, and has a beneficial effect on the rheological properties of blood.
The neuroprotective effect is realized by reducing the adverse cytotoxic effect of excitatory amino acids. Blocks Na- and Ca2+ channels and NMDA and AMPA receptors. Selectively inhibits Ca2+-calmodulin-dependent cGMP phosphodiesterase. Increases the exchange of serotonin and norepinephrine in the brain, stimulates the noradrenergic neurotransmitter system and has an antioxidant effect.
Improves microcirculation in the brain by inhibiting platelet aggregation, reducing pathologically increased blood viscosity, increasing the deformability of erythrocytes and inhibiting the reuptake of adenosine; promotes the transition of oxygen into cells by reducing the affinity of red blood cells for it.
Selectively increases cerebral blood flow by reducing cerebral vascular resistance without significantly affecting systemic circulatory parameters (blood pressure (BP), cardiac output, heart rate, total peripheral vascular resistance); does not cause the effect of “stealing”.
Pharmacokinetics:
Distribution
Distribution of radioactively labeled vinpocetine, when administered to rats, the greatest radioactivity was found in the liver and gastrointestinal tract. The maximum concentration in tissues was observed 2-4 hours after administration. The concentration in the brain did not exceed the values found in the blood.
In humans, the binding to plasma proteins is 66%. Bioavailability is about 7%. The volume of distribution is 246.7±88.5 l, indicating high tissue binding. The total clearance (66.7 l/h) exceeds the hepatic blood flow rate (50 l/h), indicating extrahepatic metabolism.
Metabolism
The main metabolite is apovincamic acid (AVA), accounting for 25-30% of the parent compound. The area under the concentration-time curve of VKA after oral administration is twice that of intravenous vinpocetine. Thus, vinpocetine is subject to a pronounced first-pass effect through the liver.
Other metabolites include: hydroxyvinpocetine, hydroxy-AVK, ABC-dioxyglycinate and their conjugates (sulfates and (or) glucuronides). The excretion of unchanged vinpocetine is low (several percent).
If liver or kidney function is impaired, no dose adjustment is required, since vinpocetine does not accumulate.
Removal
With repeated administration in doses of 5 and 10 mg, vinpocetine exhibits linear pharmacokinetics, the equilibrium plasma concentration is 1.2 ± 0.27 and 2.1 ± 0.33 ng/ml, respectively. The half-life in humans is 4.83 ± 1.29 hours. In studies with radioactively labeled vinpocetine, it was found that excretion by the kidneys and intestines occurs in a ratio of 60:40%.
In rats and dogs, high concentrations are found in bile, but significant enterohepatic recirculation is noted.
Pharmacokinetics in special groups of patients
Since vinpocetine is intended primarily for the treatment of the elderly, slower distribution, metabolism, and elimination in this age group must be considered, especially with long-term use. Based on the results of clinical studies, it was established that the kinetics of vinpocetine in the elderly does not differ significantly from that in the young, and accumulation does not occur.
In cases of liver and kidney dysfunction, cumulation is not observed, which allows for long-term therapy.
Special instructions
Special instructions
The drug should be used with caution in cases of intracranial hypertension, when used concomitantly with antiarrhythmic drugs, as well as in long QT syndrome or concomitant use with drugs that prolong the QT interval. In case of long QT syndrome or concomitant use of drugs that prolong the QT interval, ECG monitoring should be performed.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles. Wed and fur.:
No studies have been conducted on the effect on the ability to drive vehicles. If undesirable reactions from the nervous system occur, care should be taken when driving vehicles and working with moving mechanisms.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Vinpocetine
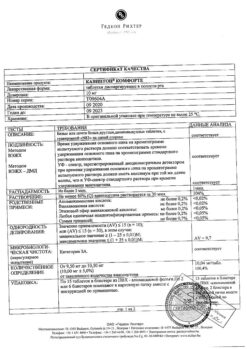
Composition
Composition
One ampoule contains:
active ingredient:
vinpocetine – 5 mg;
excipients:
ascorbic acid – 0.5 mg,
benzyl alcohol – 10 mg,
sodium disulfite (sodium metabisulfite) – 1 mg,
sorbitol (sorbitol) – 75 mg,
tartaric acid – 3 mg,
water for injection – up to 1 ml.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding is contraindicated.
Pregnancy
Vinpocetine crosses the placenta, but plasma concentrations in the placenta and fetus are lower than in the mother. Teratogenic and embryotoxic effects were not detected. In animal studies, placental hemorrhage and abortion have occurred with high doses (presumably due to increased placental blood flow).
Breastfeeding
Vinpocetine passes into breast milk. According to preclinical studies with radioactively labeled vinpocetine, its concentration in animal breast milk was 10 times higher than that in the mother’s blood. In 1 hour, 0.25% of the dose taken penetrates into milk.
Since vinpocetine passes into breast milk and there is no experience with its use in children, use during breastfeeding is contraindicated.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Acute phase of hemorrhagic stroke, severe form of coronary heart disease, severe cardiac arrhythmias.
Hypersensitivity to vinpocetine or other components of the drug.
Pregnancy, breastfeeding period.
Children under 18 years of age (due to lack of clinical trial data).
Side Effects
Side Effects
Adverse reactions are classified depending on the frequency of their occurrence: very often (≥1/10), often (≥1/100, <1/10), infrequently (≥1/1000, <1/100), rarely (≥1/10000, <1/1000), very rarely (<1/10000), frequency unknown (due to insufficient data).
Disorders of the blood and lymphatic system: rarely – thrombocytopenia, erythrocyte agglutination; very rarely – anemia.
Immune system disorders: very rarely – hypersensitivity.
Metabolic and nutritional disorders: rarely – hypercholesterolemia, diabetes mellitus, loss of appetite; very rarely – anorexia.
Mental disorders: infrequently – euphoria; rarely – anxiety; very rarely – depression, sleep disturbance.
Nervous system disorders: rarely – headache, dizziness, hemiparesis, drowsiness; very rarely – tremor, loss of consciousness, hypotension, presyncope.
Violations of the organ of vision: rarely – hemorrhage in the anterior chamber of the eye, hypermetropia, decreased visual acuity, myopia; very rarely – conjunctival hyperemia, papilledema, diplopia.
Disorders of the organ of hearing and labyrinth: rarely – hearing impairment, hyperacusis, hypoacusia, true dizziness; very rarely – tinnitus.
Cardiac disorders: rarely – myocardial ischemia/infarction, angina pectoris, bradycardia, tachycardia, extrasystole, palpitations; very rarely – heart failure, atrial fibrillation, arrhythmia.
Vascular disorders: rarely – hypotension, hypertension, hot flashes; very rarely – fluctuations in blood pressure, thrombophlebitis.
Gastrointestinal disorders: rarely – abdominal discomfort, epigastric pain, dry mouth, nausea; very rarely – hypersecretion of saliva, vomiting, dysphagia, stomatitis.
Pathology of the skin and subcutaneous tissue: rarely – erythema, hyperhidrosis, urticaria; very rarely – dermatitis, itching.
General disorders and reactions at the injection site: rarely – asthenia, malaise, burning sensation and inflammation at the injection site, thrombosis, chest discomfort.
Laboratory abnormalities: infrequently – decreased blood pressure; rarely – increased blood pressure; hypertriglyceridemia, ST segment depression, eosinopenia, abnormal liver function tests, QT segment prolongation; very rarely – increased LDH, abnormal EEG, PR prolongation.
Interaction
Interaction
According to the results of clinical studies, drug interactions with β-blockers (pindolol), clopamide, glibenclamide, digoxin, hydrochlorothiazide and acenocoumarol were not detected.
Methyldopa may enhance the hypotensive effect of vinpocetine, therefore, when used simultaneously, systematic monitoring of blood pressure is required.
Despite the lack of clinical data, simultaneous use with drugs that affect the central nervous system, anticoagulants and antiarrhythmics should be carried out with caution.
Vinpocetine solution is pharmaceutically incompatible with heparin and solutions containing amino acids.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years.
Do not use after expiration date.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Ozon, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years. Do not use after the expiration date. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In the dark place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °С. Store out of the reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Ozon, Russia |
| Medication form | concentrate for preparation of infusion solution |
| Brand | Ozon |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Vinpocetine, concentrate 5 mg/ml 5 ml 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.