No products in the cart.
Verapamil, tablets 80 mg 20 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Verapamil is one of the main drugs of the group of “slow” calcium channel blockers. It has antiarrhythmic, antianginal and antihypertensive activity.
Indications
Indications
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
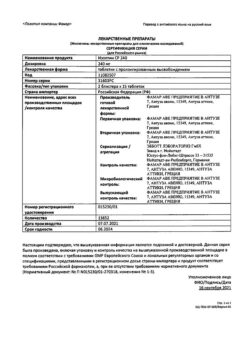
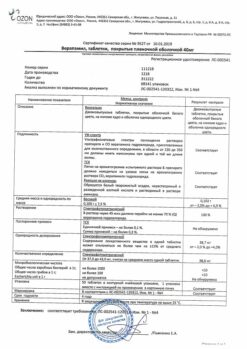
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
verapamil hydrochloride (in terms of 100% substance) – 40 mg or 80 mg;
Ancillary substances:
Lactose monohydrate – 26.12 mg/52.24 mg,
Potato starch – 9.5 mg/19.0 mg,
Talc – 0.375 mg/0.75 mg,
calcium stearate – 0.375 mg/0.75 mg,
povidone K 17 – 3.63 mg/7.26 mg;
Shell excipients:
polysorbate-80 (tween-80) – 0.2 mg/0.4 mg,titanium dioxide – 0.614 mg/1.228 mg, hypromellose (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose) – 1.06 mg/2.12 mg, beeswax yellow – 0.002 mg/0.004 mg, liquid paraffin -0.12 mg/0.24 mg, tropeoline O -0.004 mg/0.008 mg.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Interaction
Interaction
When used concomitantly with carbamazepine in patients with sustained partial epilepsy due to inhibition of carbamazepine metabolism in the liver, verapamil increases its effect (risk of side effects on the central nervous system, such as diplopia, headache, ataxia and dizziness).
When used concomitantly, verapamil inhibits the metabolism of cyclosporine in the liver, which leads to decreased excretion and increased plasma concentrations. This is accompanied by increased immunosuppressive effect.
Concomitant use of verapamil increases the concentration of theophylline (due to decreased clearance).
Concomitant use of verapamil with quinidine increases the plasma concentration of quinidine (risk of marked decrease in blood pressure especially in patients with hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy).
Concomitant use of verapamil increases the plasma concentration of ethanol and prolongs its effect.
Perhaps because verapamil inhibits isoenzyme surZ4, which is involved in metabolism of atorvastatin, lovastatin and simvastatin, there may be drug interaction caused by increased concentrations of statins in blood plasma (rhabdomyolysis).
Concomitant use of verapamil increases plasma concentrations of almotriptan, glibenclamide.
Concomitant use of verapamil increases the plasma concentrations of sirolimus and tacrolimus.
Concomitant use of verapamil increases the concentration of cardiac glycosides (requires close monitoring and reduction of the dose of glycosides). When used concomitantly, verapamil increases the concentration of metoprolol and propranololol in patients with angina pectoris.
Concomitant use of verapamil increases plasma concentrations of colchicine (substrate for surZ and p-glycoprotein isoenzyme).
Concomitant use of verapamil with doxorubicin increases plasma concentration of doxorubicin and increases its effectiveness.
Concomitant use of verapamil with imipramine increases imipramine plasma concentrations (risk of adverse changes due to the additive suppressive effect of verapamil and imipramine on AV conduction). Does not affect the concentration of the active metabolite, desipramine.
Verapamil increases the concentration of prazosin and terazosin when used concomitantly (risk of severe arterial hypotension).
Concomitant use of verapamil with buspirone or midazolam increases their plasma concentrations (risk of increased side effects). SurP4 inhibitors (including erythromycin, human immunodeficiency virus protease inhibitors), telithromycin increase plasma concentrations of verapamil.
Grapefruit juice increases plasma concentrations of r- and s-isomer verapamil.
Cimetidine either does not change or reduces the clearance of verapamil (possible increase in the effects of verapamil).
Rifampicin can significantly reduce bioavailability (up to 92%) as well as plasma concentrations of verapamil, which leads to a decrease in its clinical effectiveness.
Phenobarbital increases the clearance of verapamil by 5 times.
Sulfinpyrazone increases the clearance of verapamil by about 3 times and reduces the bioavailability by up to 60%.
The preparations of St. John’s wort reduce the plasma concentration of the r- and s-isomer of verapamil.
Concomitant use of verapamil with inhaled anesthetics increases the risk of bradycardia, atrioventricular block, and heart failure. Combination of verapamil with beta-adrenoblockers may increase the negative inotropic effect, increase the risk of atrioventricular conduction disorders, bradycardia (Verapamil and beta-adrenoblockers should be used several hours apart).
Prazosin and other alpha-adrenoblockers and other hypotensive drugs (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, vasodilators, diuretics, beta-adrenoblockers) enhance the antihypertensive effect of verapamil.
In concomitant use of verapamil with disopyramide and flecainide severe arterial hypotension and collapse, up to and including death, are possible. The risk of severe drug interaction is associated with increased negative inotropic effect. Disopyramide and flecainide should not be administered within 48 hours before or 24 hours after the use of verapamil, Verapamil increases the risk of neurotoxic effects of lithium preparations.
Verapamil increases the effect of peripheral myorelaxants (may require change in dosing regimen).
In concomitant use of verapamil with acetylsalicylic acid, increased bleeding time has been described.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Contraindications
Contraindications
Side effects
Side effects
Overdose
Overdose
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry place, protected from light and out of the reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. |
| Manufacturer | Avva Rus, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Avva Rus |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Verapamil, tablets 80 mg 20 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.