No products in the cart.
Verapamil, 40 mg 30 pcs
€1.92 €1.75
Description
Pharmacodynamics
Verapamil has antianginal, hypotensive, antiarrhythmic effects.
Blocks calcium channels and decreases transmembrane calcium current. It reduces contractility, sinus node rhythm driver frequency and conduction velocity in AV node, sinoatrial and AV conduction, relaxes smooth muscles (arterioles more than veins), causes peripheral vasodilation, reduces total peripheral vascular resistance, reduces afterload.
Enhances myocardial perfusion, reduces imbalance between cardiac oxygen demand and supply, promotes regression of left ventricular hypertrophy, lowers blood pressure. It prevents the development and eliminates coronary artery spasm in variant angina pectoris. In patients with uncomplicated hypertrophic cardiomyopathy it improves blood outflow from the ventricles. It reduces the frequency and severity of headaches of vascular genesis.
The antiarrhythmic effect develops 1-5 minutes after intravenous administration, hemodynamic effects within 3-5 minutes.
Pharmacokinetics
. During oral administration it is quickly absorbed in small intestine, absorption – 90-92 %, bioavailability after a single dose – 24-35 % due to intensive metabolism during “first passage” through the liver and increases 1.5-2 times during prolonged use. Bioavailability may increase with prolonged use in increasing doses.
The time of maximum drug concentration in plasma is 1-2 hours when administered orally. Maximum drug concentration in blood plasma (Cmax) is 80-400 ng/ml. Binding with blood plasma proteins is 90%. It penetrates through the blood-brain barrier, placental barrier (20-92% of concentrations in maternal blood plasma) and in breast milk (low concentrations).
The drug is rapidly metabolized in the liver by N-dealkylation and O-demethylation, with the formation of several metabolites (12 are identified in humans). Accumulation of the drug and its metabolites in the body explains the intensification of action during course of treatment. The main pharmacologically active metabolite is norverapamil (20% of the hypotensive activity of verapamil). CYP3A4, CYP3A5, CYP3A7 isoenzymes are involved in metabolism of the drug.
Half-life of the preparation is 3-7 hours with single use, 4-12 hours – with prolonged use (due to saturation of liver enzyme systems and increased plasma concentrations the half-life of the preparation is increased by almost 2 times). Bioavailability and half-life of the drug increases in hepatic insufficiency. Excreted 70% by kidneys (3-5% unchanged), 16-25% – in bile. It is not excreted in hemodialysis.
In intravenous administration the half-life is biphasic: early – about 4 minutes, final – 2 to 5 hours. It is 90% bound to plasma proteins. It is metabolized in liver to form norverapamil, which has 20% of verapamil hypotensive activity, and 11 other metabolites (determined in trace amounts).
Extracted mainly by the kidneys, partially – with the feces (16%). It penetrates into breast milk and passes through the placenta. In severe liver function disorders plasma clearance decreases by 70% and half-life increases to 14 – 16 hours.
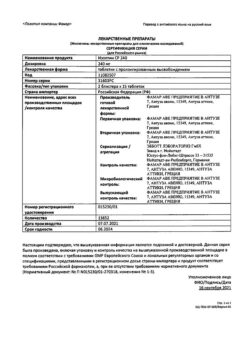
Indications
Indications
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
Active ingredient:
40 mg verapamil.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
The dosage regimen of Verapamil is determined individually.
Adults are prescribed in an initial dose of 40-80 mg 3 times daily. The maximum daily dose is 480 mg. Children aged 6-14 years are prescribed 80-360 mg daily, children under 6 years are prescribed 40-60 mg daily; the frequency of use is 3-4 times a day.
The tablets are taken with a meal or immediately after a meal with plenty of water.
Interaction
Interaction
Simultaneous use of Verapamil and beta-adrenoblockers, antiarrhythmic drugs, agents for inhalation anesthesia may lead to mutual enhancement of their cardiodepressant effects (AV blockade, bradycardia, hypotension, heart failure). Significant hypotension and pulmonary edema may develop in patients with hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy when concomitant use with quinidine.
In concomitant administration of Verapamil with other hypotensive drugs mutual potentiation of their effects is noted. Verapamil can significantly increase the concentration of digoxin in plasma, which requires reduction of the dose of cardiac glycoside when used together.
The neurotoxic effects of Verapamil are potentiated by carbamazepine and lithium salts, and the psychotropic effect of lithium is weakened when coadministered with verapamil. Plasma concentrations of cyclosporine or theophylline are increased when coadministered with Verapamil. Rifampicin, phenytoin, phenobarbital and cimetidine can decrease the plasma concentration of Verapamil and reduce its effectiveness. Verapamil potentiates the effects of muscle relaxants.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
With caution prescribe the drug in patients with hepatic impairment, in acute myocardial infarction. Administration of Verapamil during pregnancy is possible only when the estimated benefit to the mother exceeds the potential risk to the fetus.
If the drug is used during lactation, discontinuation of breastfeeding should be considered.
Verapamil is used with caution in patients engaged in potentially hazardous activities requiring increased attention and rapid motor and mental reactions.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Side effects
Side effects
Cardiovascular system: bradycardia (less than 50 bpm), marked BP decrease, development or worsening of heart failure, tachycardia; rarely – angina pectoris, up to and including myocardial infarction (especially in patients with severe obstructive coronary artery disease), arrhythmia (including ventricular fibrillation).including ventricular fibrillation and torsade de pointes); when rapidly injected intravenously – AV-blockade of degree III, asystole, collapse.
CNS and peripheral nervous system disorders: dizziness, headache, fainting, anxiety, lethargy, fatigue, asthenia, somnolence, depression, extrapyramidal disorders (ataxia, mask-like face, shuffling gait, stiff arms or legs, trembling hands and fingers, difficulty swallowing).
Digestive system disorders: nausea, constipation (rarely – diarrhea), gum hyperplasia (bleeding, soreness, swelling), increased appetite, increased liver transaminases and alkaline phosphatase activity.
Allergic reactions: skin itching, skin rash, facial hyperemia, erythema multiforme (including Stevens-Johnson syndrome).
Other: weight gain, very rarely – agranulocytosis, gynecomastia, hyperprolactinemia, galactorrhea, arthritis, transient vision loss with Cmax, pulmonary edema, asymptomatic thrombocytopenia, peripheral edema.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: bradycardia, AV block, marked BP decrease, CH, shock, asystole, SA block.
Treatment: in early detection – gastric lavage, activated charcoal; in violation of rhythm and conduction – IV isoprenaline, norepinephrine, atropine, 10-20 ml of 10% calcium gluconate solution, artificial pacemaker; IV infusion of plasma exchange solutions.
Alpha-adrenergic stimulants (phenylephrine) are prescribed to increase BP in CHD patients; isoprenaline and norepinephrine should not be used.
Hemodialysis is ineffective.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. |
| Manufacturer | Alkaloid AD Skopje, Republic of Northern Macedonia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Alkaloid AD Skopje |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Verapamil, 40 mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.