No products in the cart.
Trombopol, 75 mg 30 pcs
€1.72 €1.56
Description
Trombopol is an NSAID, anti-aggregant. The mechanism of action of acetylsalicylic acid is based on irreversible inhibition of COX-1, resulting in blockade of thromboxane A2 synthesis and suppression of platelet aggregation. The antiplatelet effect develops even after using the drug in low doses and lasts for 7 days after a single dose. Due to these properties, acetylsalicylic acid is used for the prevention and treatment of myocardial infarction, CHD, complications of varicose veins. Acetylsalicylic acid also has anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects.
Trombopol tablets have an enteric coating, due to which they dissolve and release the active substance in the more alkaline environment of the duodenum, reducing the irritating effect of acetylsalicylic acid on the gastric mucosa.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Absorption of acetylsalicylic acid from enteric-coated tablets begins 3-4 h from the time the drug is taken, confirming that the coating effectively blocks dissolution of the drug in the stomach. Cmax in plasma is reached after approximately 2-3 h and averages 12.7 µg/mL for 150 mg tablets and 6.72 µg/mL for 75 mg tablets. The presence of food in the gastrointestinal tract slows down absorption of the drug.
The AUC is 56.42 µg×h/ml for 75 mg tablets and 108.08 µg×h/ml for 150 mg tablets.
Distribution
Acetylsalicylic acid quickly and largely penetrates into most tissues and body fluids. The degree of binding of the drug to plasma proteins is concentration-dependent; in healthy individuals, it decreases simultaneously with a decrease in this concentration.
The relative distribution is about 0.15-0.2 L/kg and increases simultaneously with increasing serum concentration of the drug.
Unlike other salicylates, non-hydrolyzed acetylsalicylic acid does not accumulate in the blood serum when repeated administration of the drug.
Metabolism
Acetylsalicylic acid is partially metabolized during absorption. This process occurs under the influence of enzymes, mainly in the liver, with the formation of metabolites such as phenylsalicylate, salicylate glucuronide and salicyluric acid, found in many tissues and urine.
Elevation
The T1/2 of acetylsalicylic acid from blood plasma is about 15-20 minutes.
Only 1% of the oral dose of acetylsalicylic acid is excreted by the kidneys as unhydrolyzed acetylsalicylic acid, the rest is excreted as salicylates and their metabolites.
In patients with normal renal function, 80-100% of the single dose of the drug is excreted by the kidneys within 24-72 hours.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical cases
In renal insufficiency, in pregnancy, and in infants, salicylates may displace bilirubin from binding to albumin and contribute to bilirubin encephalopathy.
In women, the metabolic process is slower (lower serum enzyme activity).
Indications
Indications
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
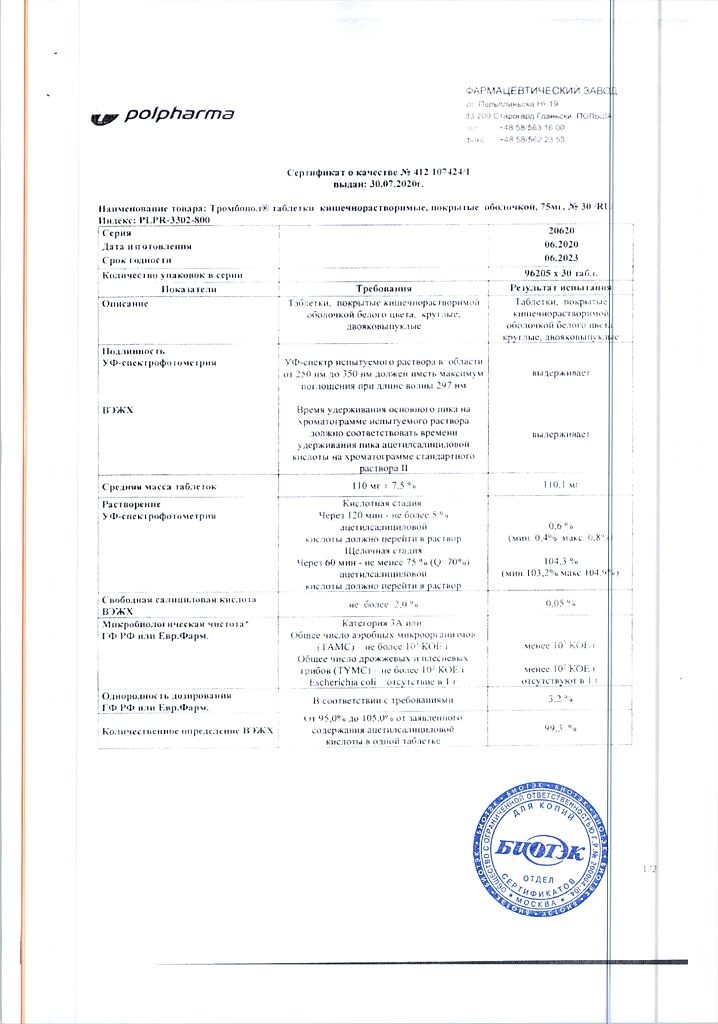
1 enteric-coated tablet contains:
acting substance:
acetylsalicylic acid 75 mg.
excipients:
Corn starch,
Microcrystalline cellulose,
sodium carboxymethyl starch.
coating composition:
Hypromellose, Acryl-Ice (mixture for coating tablets): methacrylic acid copolymer type C, talc, titanium dioxide, triethylcitrate, crimson dye (Ponceau 4R), colloidal silicon dioxide, sodium hydrocarbonate, sodium lauryl sulfate.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
The drug is intended for long-term use. The duration of therapy is determined by the doctor. Tablets are taken orally, regardless of meals, without chewing, with a small amount of water.
For the prevention of suspected acute myocardial infarction: 75 mg per day or 150 mg per day are prescribed.
In order to prevent first-time acute myocardial infarction in the presence of risk factors: 75 mg per day or 150 mg per day are prescribed.
In order to prevent recurrent myocardial infarction, in unstable angina pectoris, in order to prevent stroke and transient cerebral circulatory disorder, to prevent thromboembolic complications after surgical operations or invasive tests: 75 mg daily or 150 mg daily.
For prophylaxis of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary artery thromboembolism and its branches: 75 mg daily or 150 mg daily.
Interaction
Interaction
In concomitant use acetylsalicylic acid increases the effect of methotrexate by reducing renal clearance and displacing it from protein binding; heparin and indirect anticoagulants by impairing platelet function and displacing indirect anticoagulants from protein binding; thrombolytic agents and platelet aggregation inhibitors (ticlopidine); Digoxin, due to its reduced renal excretion; hypoglycemic agents (insulin and sulfonylurea derivatives) due to hypoglycemic properties of acetylsalicylic acid itself at high doses and displacement of sulfonylurea derivatives from protein binding; valproic acid due to displacement of its protein binding; NSAIDs; sulfonamides (incl.including co-trimoxazole); barbiturates; lithium salts.
Additive effect is observed with concomitant use of acetylsalicylic acid with alcohol.
Acetylsalicylic acid reduces the effect of antipodagric drugs that increase uric acid excretion (probenecid, sulfinpyrazone, benzbromaron), due to competitive tubular elimination of uric acid; antihypertensive agents, including ACE inhibitors; aldosterone antagonists (e.g., spironolactone); “loop” diuretics (e.g., furosemide).
By enhancing the elimination of salicylates, GCS for systemic use weaken their effects.
The combination of acetylsalicylic acid with anticoagulants, thrombolytics and platelet aggregation inhibitors is accompanied by an increased risk of bleeding.
The combination of acetylsalicylic acid with methotrexate is accompanied by an increased incidence of side effects from the hematopoietic organs.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Acetylsalicylic acid may provoke bronchospasm, as well as causing attacks of bronchial asthma and other hypersensitivity reactions. Risk factors include a history of bronchial asthma, hay fever, nasal polyposis, chronic respiratory diseases, and allergic reactions to other medications (e.g., skin reactions, itching, urticaria). Acetylsalicylic acid may cause bleeding of varying severity during and after surgical interventions. It is necessary to stop taking the drug 5-7 days before the intended surgery.
Acetylsalicylic acid in low doses may provoke the development of gout in predisposed persons (having reduced excretion of uric acid). Acetylsalicylic acid in high doses has a hypoglycemic effect, which should be kept in mind when prescribing it to patients with diabetes receiving hypoglycemic agents.
Please note that the combined use of GCS and salicylates leads to lower blood concentrations of salicylates, and after withdrawal of GCS, an overdose of salicylates is possible. It is not recommended to combine Trombopol with ibuprofen, because the latter reduces the effectiveness of acetylsalicylic acid. Excessive doses of acetylsalicylic acid are associated with the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding. When combining acetylsalicylic acid with ethanol there is an increased risk of damage to the gastrointestinal mucosa and prolongation of bleeding time.
Overdose is especially dangerous in the elderly. Patients over 65 years of age should be prescribed Trombopol in lower doses because of impaired renal function and more frequent adverse reactions from the digestive system.
Impact on the ability to drive and operate machinery.
There are no data on adverse effects of the drug Trombopol on the ability to drive or operate machinery.
Contraindications
Contraindications
. With caution, use the drug in patients with gout, hyperuricaemia, peptic ulcer or gastrointestinal bleeding (history), renal/liver failure, bronchial asthma, chronic respiratory diseases, hay fever, nasal polyposis, drug allergy, while taking methotrexate in dose less than 15 mg/week., concomitant therapy with anticoagulants, in the second trimester of pregnancy.
Side effects
Side effects
Digestive system disorders: nausea, vomiting, heartburn, abdominal pain, diarrhea, gastric and duodenal ulcers, including perforative, gastrointestinal bleeding, increased activity of liver enzymes.
Respiratory system: bronchospasm.
CNS disorders: dizziness, tinnitus.
Hematopoietic system: increased bleeding; rarely – anemia.
Allergic reactions: urticaria, Quincke’s edema.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: initial symptoms are nausea, vomiting, tinnitus, and rapid breathing. Hearing loss, visual disturbances, headaches, motor agitation, drowsiness, seizures, hyperthermia are also possible. In severe intoxication acid-base and water-electrolyte balance disorders may develop (metabolic acidosis and dehydration). Symptoms of mild to moderate intoxication develop after the use of acetylsalicylic acid at a dose of 150-300 mg/kg. Symptoms of severe overdose develop at a dose of 300-500 mg/kg. The potentially fatal dose of acetylsalicylic acid is more than 500 mg/kg.
Treatment: induce vomiting and gastric lavage (to reduce absorption of the drug). Such actions have an effect within 3-4 hours after taking the drug, and up to 10 hours if taken in an excessive dose. To reduce absorption of acetylsalicylic acid it is necessary to take activated carbon in the form of aqueous suspension (dose for adults – 50-100 g, for children – 30-60 g); the water-electrolyte balance should be closely monitored and replenished. In order to accelerate excretion of acetylsalicylic acid by the kidneys and to treat acidosis, sodium bicarbonate should be administered intravenously. The pH should be maintained within 7.0-7.5. Hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis should be performed if intoxication is very severe. Due to the possibility of respiratory acidosis, drugs that depress CNS, such as barbiturates, should not be taken. Patients with respiratory distress should be provided with airway patency and access to oxygen. If necessary, intratracheal intubation and ventilatory ventilation should be provided. There is no specific antidote.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
The use of the drug Trombopol is contraindicated in I and III trimesters of pregnancy and during lactation. The use of salicylates in the first trimester of pregnancy leads to the development of cleft palate, heart defects; in the third trimester it causes inhibition of labor activity, premature closure of the fetal arterial duct, increased bleeding in mother and fetus, and administration just before delivery may cause intracranial hemorrhages, especially in premature babies.
In the second trimester of pregnancy, salicylates may be prescribed only after a rigorous evaluation of the expected benefit of therapy to the mother and the potential risk to the fetus. Salicylates and their metabolites are excreted in small amounts with breast milk. Accidental administration of salicylates during lactation is not accompanied by the development of adverse reactions in the child and does not require discontinuation of breastfeeding. However, if the drug is used for a long time or if it is prescribed in a high dose, breastfeeding should be stopped immediately.
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
| Weight | 0.016 kg |
|---|---|
| Shelf life | 2 years |
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Polpharma S.A., Poland |
| Medication form | enteric soluble tablets |
| Brand | Polpharma S.A. |
Related products
Buy Trombopol, 75 mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.