No products in the cart.
Torasemide-SZ, tablets 5 mg 30 pcs
€4.11 €3.43
Description
Heart failure, Hypertension (high blood pressure), Oedema
- Oedematous syndrome of various genesis, including chronic heart failure, liver, lung and kidney disease
- arterial hypertension.
Indications
Indications
Edema syndrome of various origins, including with chronic heart failure, diseases of the liver, lungs and kidneys;
arterial hypertension.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group of the drug:
Special instructions
Special instructions
Use strictly as prescribed by your doctor. Patients with hypersensitivity to sulfonamides and sulfonylurea derivatives may have cross-sensitivity to Torasemide-SZ. For patients receiving high doses of Torasemide-SZ for a long period, in order to avoid the development of hyponatremia, metabolic alkalosis and hypokalemia, a diet with sufficient salt content and the use of potassium supplements are recommended. An increased risk of developing fluid and electrolyte imbalances is observed in patients with renal failure.
During the course of treatment, it is necessary to periodically monitor the concentration of blood plasma electrolytes (including sodium, calcium, potassium, magnesium), acid-base status, residual nitrogen, creatinine, uric acid and, if necessary, carry out appropriate corrective therapy (with a higher frequency in patients with frequent vomiting and against the background of parenterally administered fluids).
If azotemia and oliguria appear or worsen in patients with severe progressive kidney disease, it is recommended to suspend treatment.
The selection of a dosage regimen for patients with ascites against the background of liver cirrhosis should be carried out in a hospital setting (violations of water and electrolyte balance can lead to the development of hepatic coma). This category of patients requires regular monitoring of blood plasma electrolytes.
In patients with diabetes mellitus or with reduced glucose tolerance, periodic monitoring of glucose concentrations in the blood and urine is required.
In unconscious patients with prostatic hyperplasia and narrowing of the ureters, diuresis control is necessary due to the possibility of acute urinary retention.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
During the treatment period, patients should refrain from driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions (risk of dizziness and drowsiness).
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Torasemide
Composition
Composition
Active substance:
Contraindications
Contraindications
Renal failure with anuria;
hepatic coma and precoma;
refractory hypokalemia/refractory hyponatremia;
hypovolemia (with or without arterial hypotension) or dehydration;
pronounced disturbances in the outflow of urine of any etiology (including unilateral damage to the urinary tract);
glycoside intoxication;
acute glomerulonephritis;
decompensated aortic and mitral stenosis, hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy;
increased central venous pressure (over 10 mm Hg);
hyperuricemia;
simultaneous use of aminoglycosides and cephalosporins;
pregnancy;
breastfeeding period;
age under 18 years;
lactose intolerance, lactase deficiency or glucose-galactose malabsorption;
allergic reaction to sulfonamides (sulfonamide antimicrobials or sulfonylureas);
hypersensitivity to torsemide or to any of the components of the drug.
The drug should be prescribed with caution in case of arterial hypotension, stenosing atherosclerosis of the cerebral arteries, hypoproteinemia, predisposition to hyperuricemia, impaired outflow of urine (benign prostatic hyperplasia, narrowing of the urethra or hydronephrosis), history of ventricular arrhythmia, acute myocardial infarction (increased risk of developing cardiogenic shock), diarrhea, pancreatitis, diabetes mellitus (decreased glucose tolerance), hepatorenal syndrome, gout, anemia; simultaneous use of cardiac glycosides, corticosteroids and ACTH.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the senses: frequency unknown – visual impairment, hearing impairment, tinnitus and hearing loss (usually reversible), usually in patients with renal failure or hypoproteinemia (nephrotic syndrome).
From the cardiovascular system: infrequently – extrasystole, arrhythmia, tachycardia; frequency unknown – excessive decrease in blood pressure, orthostatic hypotension, collapse, deep vein thrombosis, thromboembolism, decrease in blood volume.
From the nervous system: often – headache, dizziness, drowsiness; infrequently – muscle cramps of the lower extremities; frequency unknown – confusion, fainting, paresthesia in the extremities (feeling of numbness, crawling and tingling).
From the respiratory system: infrequently – nosebleeds.
From the digestive system: often – diarrhea; infrequently – abdominal pain, flatulence, polydipsia; frequency unknown – dry mouth, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, pancreatitis, dyspeptic disorders, intrahepatic cholestasis.
From the urinary system: often – increased frequency of urination, polyuria, nocturia; infrequently – frequent urge to urinate; frequency unknown – oliguria, urinary retention (in patients with urinary tract obstruction), interstitial nephritis, hematuria.
From the reproductive system: frequency unknown – decreased potency.
From the skin and subcutaneous tissues: frequency unknown – skin itching, rash, urticaria, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, purpura, vasculitis, photosensitivity.
From the musculoskeletal system: frequency unknown – muscle weakness.
Metabolic: frequency unknown – hypokalemia, hyponatremia, hypomagnesemia, hypocalcemia, hypochloremia, metabolic alkalosis, hypovolemia, dehydration (more often in elderly patients).
From laboratory parameters: infrequently – hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia; frequency unknown – hyperuricemia, a slight increase in the activity of alkaline phosphatase in the blood plasma, an increase in the concentration of creatinine and urea in the blood plasma, an increase in the activity of some liver enzymes in the blood plasma (for example, GGT), thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, agranulocytosis, hyperglycemia, decreased glucose tolerance (possible manifestation of latent diabetes mellitus).
Other: frequency unknown – aplastic or hemolytic anemia.
Interaction
Interaction
Increases the concentration and risk of developing nephro- and ototoxic effects of cephalosporins, aminoglycosides, chloramphenicol, ethacrynic acid, cisplatin, amphotericin B (due to competitive renal excretion).
Increases the effectiveness of diazoxide and theophylline, reduces the effectiveness of hypoglycemic agents, allopurinol.
Pressor amines and torasemide mutually reduce each other’s effectiveness.
Drugs that block tubular secretion increase the concentration of torasemide in the blood serum.
With the simultaneous use of GCS, amphotericin B, the risk of developing hypokalemia increases, with cardiac glycosides – the risk of developing glycoside intoxication increases due to hypokalemia (for high- and low-polarity) and prolongation of T1/2 (for low-polarity).
Reduces the renal clearance of lithium drugs and increases the likelihood of intoxication.
NSAIDs and sucralfate reduce the diuretic effect due to inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis, disruption of renin activity in the blood plasma and excretion of aldosterone.
Strengthens the antihypertensive effect of antihypertensive drugs, neuromuscular blockade of depolarizing muscle relaxants (suxamethonium) and weakens the effect of non-depolarizing muscle relaxants (tubocurarine).
Concomitant use of salicylates in high doses during torsemide therapy increases the risk of their toxicity (due to competitive renal excretion).
Sequential or simultaneous use of torasemide with ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor antagonists can lead to a significant decrease in blood pressure. This can be avoided by reducing the dose of torasemide or temporarily stopping it.
Concomitant use of probenecid or methotrexate may reduce the effectiveness of torsemide (same secretion route). On the other hand, torasemide may lead to decreased renal elimination of these drugs.
With the simultaneous use of cyclosporine and torasemide, the risk of developing gouty arthritis increases due to the fact that cyclosporine can cause impaired urate excretion by the kidneys, and torasemide can cause hyperuricemia.
It has been reported that in patients at high risk of developing nephropathy taking torasemide orally, renal dysfunction was observed more frequently during the administration of radiocontrast agents than in patients at high risk of developing nephropathy who were given intravenous hydration before administration of radiocontrast agents.
The bioavailability and, as a result, the effectiveness of torasemide may be reduced when combined with cholestyramine.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: increased diuresis, accompanied by a decrease in blood volume and disturbance of the water-electrolyte balance of the blood, followed by an excessive decrease in blood pressure, drowsiness and confusion, collapse. Gastrointestinal disturbances may occur.
Treatment: there is no specific antidote. Provocation of vomiting, gastric lavage, activated charcoal.
Carrying out symptomatic therapy, reducing the dose or discontinuing the drug and simultaneous replenishment of blood volume and indicators of water-electrolyte balance and acid-base status under the control of serum concentrations of electrolytes, hematocrit. Hemodialysis is ineffective.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years. Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
North Star NAO, Russia
Additional information
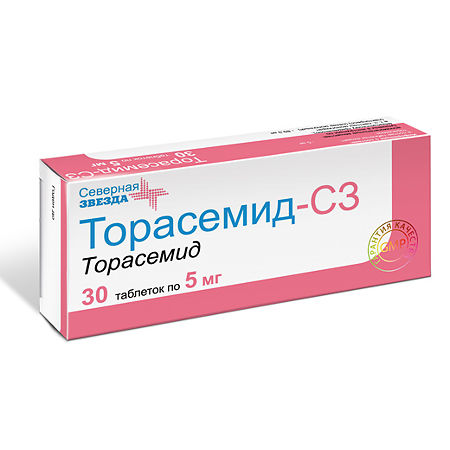
| Shelf life | 3 years. Do not use after the expiration date printed on the package. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 oC. Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | North Star NAO, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | North Star NAO |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Torasemide-SZ, tablets 5 mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.