No products in the cart.
Tenoric, 100 mg+25 mg 28 pcs
€10.15 €8.88
Description
Tenoric is a combined antihypertensive drug with a prolonged hypotensive effect. The effect is due to the action of two components: a beta1-adrenoblocker (atenolol) and a diuretic (chlorthalidone).
Atenolol is a cardioselective beta1-adrenoblocker. Selectivity decreases with increasing dose. Atenolol has no intrinsic sympathomimetic and membrane stabilizing effects. Like other beta-adrenoblockers, it has a negative inotropic effect and decreases HR.
Chlorthalidone is a nonthiazide sulfonamide diuretic, increases sodium and chlorine excretion. Increases the excretion of potassium, magnesium and bicarbonate.
The mechanism of antihypertensive action is probably related to sodium excretion. The combination of atenolol with diuretics is more effective than the use of each component alone.
The action of Tenoric lasts for 24 hours after a single oral daily dose.
Indications
Indications
Arterial hypertension.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Tenorik is a combined antihypertensive drug that has a long-lasting hypotensive effect. The effect is due to the action of two components: a beta1-blocker (atenolol) and a diuretic (chlorthalidone).
Atenolol is a cardioselective beta1-blocker. Selectivity decreases with increasing dose. Atenol does not have internal sympathomimetic and membrane-stabilizing effects. Like other beta-blockers, it has a negative inotropic effect and reduces heart rate.
Chlorthalidone is a non-thiazide sulfonamide diuretic that enhances the release of sodium and chlorine. Increases the release of potassium, magnesium and bicarbonate.
The mechanism of antihypertensive action is likely related to sodium excretion. The combination of atenolol with diuretics is more effective than using each component separately.
The effect of the drug Tenorik lasts for 24 hours after a single oral dose in a daily dose.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Caused by the beta-blocker atenolol, which is part of Tenorik
Prescribe with caution to patients with 1st degree AV block.
It should be taken into account that the use of the drug may mask the phenomena of thyrotoxicosis and hypoglycemia.
If bradycardia (heart rate up to 50 beats/min) with clinical symptoms develops while using the drug, the dose should be reduced or the drug should be discontinued.
Tenorik should not be abruptly discontinued in patients with coronary artery disease.
Smokers may experience a decrease in the therapeutic effect of the drug.
Particular attention should be paid in cases where surgery with general anesthesia is required. The drug should be discontinued 48 hours before surgery, and the anesthetic agent should be a drug with as little negative inotropic effect as possible.
While taking the drug, it is possible to increase sensitivity to allergens and develop severe anaphylactic reactions, and therefore patients receiving desensitization therapy should take the drug with great caution. These patients may not respond to moderate doses of epinephrine (adrenaline) used to treat allergic reactions.
It should be prescribed with caution to patients with broncho-obstructive syndrome, and in case of deterioration of bronchial conduction, therapy with beta-agonists should be carried out.
When using atenolol, it is possible to reduce the production of tear fluid, which is important for patients who use contact lenses.
Caused by the diuretic chlorthalidone, which is part of Tenorik
Hypokalemia may occur during the use of the drug. Serum potassium levels should be monitored, especially in patients receiving cardiac glycosides for the treatment of heart failure, in patients with an unbalanced diet (low potassium) or in patients with complaints of gastrointestinal disorders. The development of hypokalemia in patients receiving cardiac glycosides can lead to arrhythmia.
The drug should be used with caution in patients with impaired renal function.
While using the drug, impaired glucose tolerance may occur. The drug should be prescribed with caution to patients with a predisposition to diabetes mellitus.
While using the drug, it is possible to develop hyperuricemia, which is usually minor, but in some cases it may be necessary to use agents that promote the removal of uric acid.
Use in pediatrics
The effectiveness and safety of Tenorik in children and adolescents under 18 years of age have not been established, so the drug should not be prescribed to patients in this age group.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
The use of Tenorik, as a rule, does not affect the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery. However, the question of the ability to drive a vehicle should be decided after assessing the individual tolerability of the drug.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
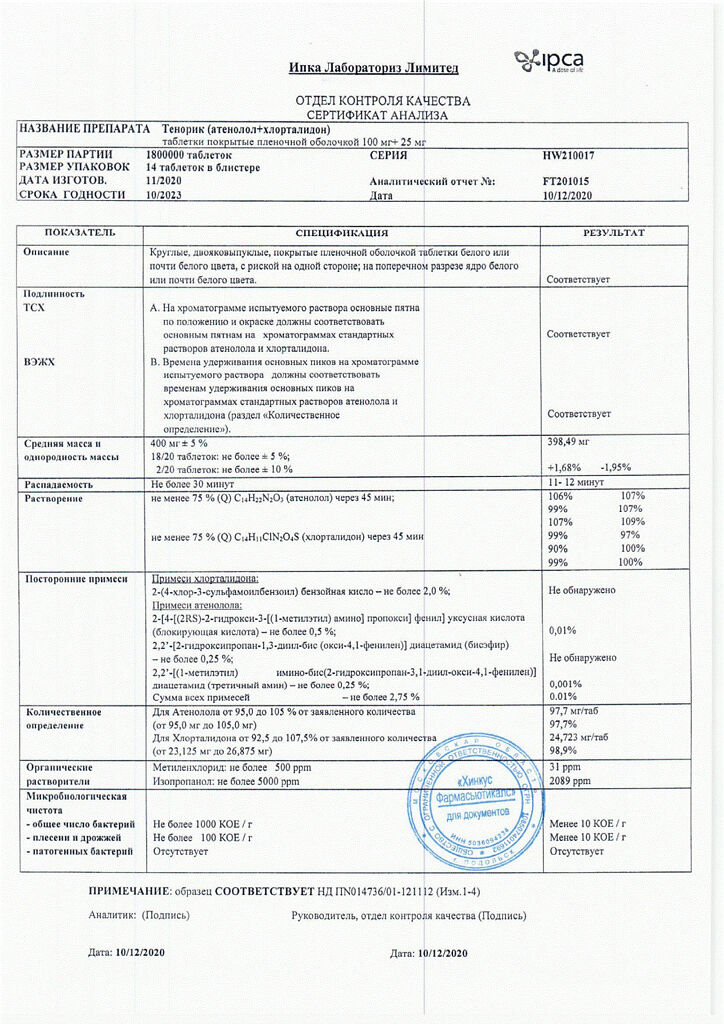
Atenolol, Chlorthalidone
Composition
Composition
1 tablet contains:
Active substances:
atenolol 100 mg;
chlorthalidone 25 mg.
Excipients:
corn starch,
lactose,
polyvinylpyrrolidone,
sodium lauryl sulfate,
talc,
isopropanol,
colloidal silicon dioxide,
magnesium stearate.
Film shell composition:
isopropanol, methylene chloride, hypromellose, talc, titanium dioxide, vaseline oil, macrogol.
Contraindications
Contraindications
heart rhythm disturbances
heart failure
renal dysfunction
pheochromocytoma
hypersensitivity to the components of the drug Tenorik.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Hyperuricemia, hypokalemia, impaired glucose tolerance, bradycardia, heart block, orthostatic hypotension, heart failure, cold extremities, intermittent claudication, Raynaud’s phenomenon, confusion, mood swings, hallucinations, insomnia, nightmares, dry eyes, dyspeptic and visual disorders, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, purpura, alopecia, psoriasis, paresthesia, bronchospasm.
Interaction
Interaction
The simultaneous use of Tenorik with dihydropyridine derivatives (nifedipine) may increase the risk of developing arterial hypotension; in patients with latent heart failure, signs of circulatory disorders may appear.
Cardiac glycosides in combination with beta-blockers may increase AV conduction time.
Beta blockers may exacerbate rebound hypertension that may occur after discontinuation of clonidine. If both drugs are prescribed, the beta blocker should be discontinued several days before stopping clonidine. If it is necessary to replace clonidine with a beta-blocker, the latter should be prescribed several days after stopping clonidine therapy.
It is necessary to prescribe a beta-blocker with caution in combination with class I antiarrhythmic drugs (disopyramide), because the cardiodepressive effects may be additive.
The concomitant use of sympathomimetic drugs, for example, epinephrine (adrenaline), norepinephrine (norepinephrine) can neutralize the effect of beta-blockers and lead to a significant increase in blood pressure.
Salicylates and NSAIDs (ibuprofen, indomethacin), estrogens can reduce the hypotensive effect of beta-blockers, and when salicylates are used in high doses, the toxic effect of salicylates on the central nervous system may be enhanced.
Preparations containing lithium should not be used with diuretics, because they may reduce the renal clearance of lithium.
The use of beta-blockers together with general anesthesia may lead to an increased risk of arterial hypotension and the additive negative inotropic effect of both drugs (an anesthetic with minimal negative inotropic effect should be used). It is also possible to enhance the effect of curare-like muscle relaxants.
When using the drug Tenorik with MAO inhibitors, an increase in blood pressure is possible (this combination should be avoided).
With the simultaneous use of Tenoric with ACE inhibitors (captopril, enalapril) at the beginning of therapy, a sharp increase in the antihypertensive effect is possible.
When Tenorik is used together with GCS, amphotericin B, and furosemide, potassium excretion may be increased.
When used together with Tenoric, the effect of insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents may decrease (blood glucose levels should be monitored).
Tricyclic antidepressants, barbiturates, phenothiazines, diuretics, vasodilators and other antihypertensive drugs may enhance the antihypertensive effect of Tenorik.
The use of beta-blockers in combination with calcium channel blockers that have a negative inotropic effect, for example verapamil, diltiazem, can lead to an increase in this effect, especially in patients with reduced myocardial contractility and/or impaired sinoatrial or AV conduction, which can cause severe arterial hypotension, severe bradycardia and heart failure (a calcium channel blocker should not be used IV within 48 hours after stopping the beta blocker).
When Tenorik is prescribed simultaneously with reserpine, clonidine, and guanfacine, severe bradycardia may occur.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: severe bradycardia, arterial hypotension, acute heart failure, bronchospasm, convulsions, increased drowsiness.
Treatment: careful monitoring of the patient’s condition, if necessary, hospitalization in the ICU, gastric lavage, use of activated charcoal and laxatives; for arterial hypotension and shock – administration of plasma or plasma substitutes; for brochospasm – use of bronchodilators; for significant diuresis – administration of fluids and electrolytes. Hemodialysis or hemoperfusion may be performed.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Ipka Laboratories Limited, India
Additional information
| Conditions of storage | In a light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Ipka Laboratories Limited, India |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Ipka Laboratories Limited |
Related products
Buy Tenoric, 100 mg+25 mg 28 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.