No products in the cart.
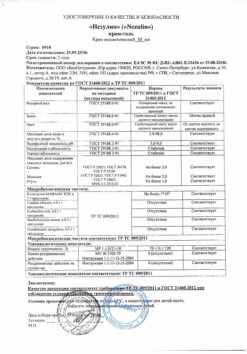
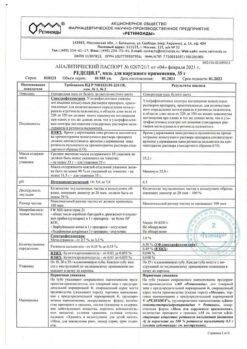
Supirocin, ointment 15 g
€21.75 €19.42
Description
Mechanism of action
Mupirocin is a new antibiotic produced by fermentation of Pseudomonas fluorescens. Mupirocin inhibits isoleucine transfer RNA synthetase, blocking protein synthesis in the bacterial cell.
Mupirocin has no cross-resistance with other antibiotics used in clinical practice due to its specific mechanism of action and unique chemical structure.
Mupirocin has bacteriostatic properties at minimal suppressive concentrations (MPC) when applied topically and bactericidal properties at higher concentrations.
Pharmacodynamic Effects
Activity
Mupirocin is a topical antibacterial agent that demonstrates in vivo activity against Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-resistant strains), S. epidermidis and beta-haemolytic strains of Streptococcus species.
The spectrum of in vitro activity includes the following bacteria:
Sensitive species:
– Staphylococcus aureus1,2;
– Staphylococcus epidermidis1,2;
– Coagulazonegative staphylococci1,2;
– Streptococcus species1;
– Haemophilus influenzae;
– Neisseria gonorrhoeae;
– Neisseria meningitidis;
– Moraxella catarrhalis;
– Pasteurella multocida.
1 Clinical efficacy has been demonstrated for isolates of susceptible bacteria for registered clinical indications.
2 Including beta-lactamase-producing strains and methicillin-resistant strains.
Resistant species
– Corynebacterium species;
– Enterobacteriaceae;
– Gram-negative non-fermenting bacilli;
– Micrococcus species;
– Anaerobes.
Sensitivity limit concentrations to mupirocin (MPC) for Staphylococcus spp.
Sensitive: less than or equal to 1 µg/mL.
Intermediate sensitivity: 2 to 256 µg/mL.
Resistant: above 256 µg/mL.
Betamethasone is a glucocorticosteroid for external use.
It has local anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, anti-edema and antiproliferative effects. It has stronger vasoconstrictor action than other fluorine derivatives of glucocorticosteroids; the systemic effects are expressed insignificantly due to limited absorption through the skin. When exposed to the skin, there is prevention of marginal accumulation of neutrophils, which leads to decrease of exudation, cytokines production, inhibition of macrophages migration, resulting in final reduction of infiltration and granulation processes.
Mupirocin is poorly absorbed through intact human skin.
If absorbed through damaged skin, mupirocin is rapidly metabolized to inactive monic acid.
Mupirocin is rapidly eliminated from the body by metabolic conversion to the inactive metabolite monic acid, which is rapidly excreted by the kidneys.
Betamethasone dipropionate is a lipophilic substance and is easily absorbed through the stratum corneum without biotransformation. Absorption is increased when applied to the skin in body folds, on skin with damaged epidermis or on the area of inflammation, when using the drug frequently or after application over a large area of skin. Absorption of betamethasone dipropionate through the skin in children is faster than in adults.
Indications
Indications
Treatment of primary and secondary infectious skin lesions caused by mupirocin-sensitive microorganisms including:
primary skin infections: impetigo, folliculitis, furunculosis (including boils of the external auditory canal and auricle) and ecthyma;
secondary infections: infected eczema; infected injuries (abrasions, insect bites), minor wounds and burns (not requiring hospitalization).
Prevention of bacterial infections in small wounds, cuts, abrasions and other uncontaminated skin lesions.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Mechanism of action
Mupirocin is a new antibiotic produced by fermentation of Pseudomonas fluorescens. Mupirocin inhibits isoleucine transfer RNA synthetase, blocking protein synthesis in the bacterial cell.
Due to its specific mechanism of action and unique chemical structure, mupirocin is not characterized by cross-resistance with other antibiotics used in clinical practice.
When applied topically in minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs), mupirocin has bacteriostatic properties, and in higher concentrations, bactericidal properties.
Pharmacodynamic effects
Activity
Mupirocin is a topical antibacterial agent with in vivo activity against Staphylococcus aureus (including methicillin-resistant strains), S. epidermidis and beta-hemolytic strains of Streptococcus species.
The spectrum of in vitro activity includes the following bacteria:
Sensitive species:
– Staphylococcus aureus1,2;
– Staphylococcus epidermidis1,2;
– Coagulase-negative staphylococci1,2;
– Streptococcus species1;
– Haemophilus influenzae;
– Neisseria gonorrhoeae;
– Neisseria meningitidis;
– Moraxella catarrhalis;
– Pasteurella multocida.
1 Clinical efficacy has been demonstrated for isolates of susceptible bacteria for registered clinical indications.
2 Including beta-lactamase-producing and methicillin-resistant strains.
Resistant species
– Corynebacterium species;
– Enterobacteriaceae;
– Gram-negative non-fermenting rods;
– Micrococcus species;
– Anaerobes.
Mupirocin susceptibility breakpoints (MIC) for Staphylococcus spp.
Sensitive: less than or equal to 1 µg/ml.
Intermediate sensitivity: 2 to 256 μg/ml.
Resistant: above 256 µg/ml.
Betamethasone is a glucocorticosteroid for external use.
Has local anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, anti-edematous and anti-proliferative effects. Has a stronger vasoconstrictor effect than other fluorinated glucocorticosteroids; systemic effects are insignificant due to limited absorption through the skin. When exposed to the skin, the marginal accumulation of neutrophils is prevented, which leads to a decrease in exudation, cytokine production, inhibition of macrophage migration, ultimately leading to a decrease in the processes of infiltration and granulation.
Mupirocin is poorly absorbed through intact human skin.
If absorbed through damaged skin, mupirocin is rapidly metabolized to inactive monic acid.
Mupirocin is rapidly eliminated from the body by metabolic transformation into an inactive metabolite – monic acid, which is quickly excreted by the kidneys.
Betamethasone dipropionate is a lipophilic substance and is easily absorbed through the stratum corneum of the skin without undergoing biotransformation. Absorption increases when applied to skin in the area of body folds, to skin with damaged epidermis or to areas of inflammation, with frequent use of the drug or after application to a large surface of the skin. Absorption of betamethasone dipropionate through the skin in children occurs faster than in adults.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Avoid getting the ointment in your eyes. In case of contact with eyes, rinse with plenty of water until the remaining ointment is completely removed.
In rare cases, when using the drug, a hypersensitivity reaction or severe local irritation may occur. In this case, it is necessary to stop treatment, remove the drug from the treated surface if possible, and prescribe alternative therapy for the infection.
As with other antibacterial drugs, there is a risk of overgrowth of non-susceptible microorganisms with long-term use of mupirocin.
Pseudomembranous colitis has been described with the use of antibiotics, the severity of which can vary from mild to life-threatening. Thus, it is important to consider this diagnosis in patients who develop diarrhea during or after antibiotic use. Despite the fact that the likelihood of this phenomenon developing with topical use of mupirocin is less, if prolonged or severe diarrhea or abdominal cramps develop, treatment should be stopped immediately and additional examination of the patient should be performed.
The drug should not be used in ophthalmology, intranasally, in combination with the use of catheters, or at the site of insertion of a central venous catheter.
Polyethylene glycol (macrogol) can be absorbed through an open wound surface or other damage to the skin and be excreted by the kidneys.
Like other ointments based on macrogol, Supirocin ointment should not be used in conditions where absorption of large quantities of macrogol is possible. especially in moderate or severe renal impairment.
Do not mix the drug with other medicinal products to avoid diluting the ointment and, therefore, reducing the antibacterial activity or possibly changing the stability of mupirocin.
The ointment remaining in the tube at the end of treatment should not be used for the next course of treatment
Special patient groups
Elderly patients
No restrictions (in the absence of symptoms of moderate or severe renal disease insufficiency).
Effect on the ability to drive vehicles and other machinery:
Not studied.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Mupirocin
Composition
Composition
100 g of ointment for local and external use contains:
active ingredients:
mupirocin – 2.0 g.
excipients:
macrogol 400 (polyethylene glycol 400),
macrogol 4000 (polyethylene glycol 4000).
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Currently, there is insufficient data on the use of mupirocin during pregnancy, so the use of the drug is possible if the expected benefit outweighs the possible risk of complications.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to any component of the drug Supirocin. With caution: moderate to severe renal failure, old age.
Side Effects
Side Effects
The undesirable reactions presented below are listed in accordance with the damage to organs and organ systems and the frequency of occurrence.
The frequency of occurrence is determined as follows: very often (> 1/10) often (> 1/100 1/1000 1/10000 < 1/1000) very rarely (< 1/10000) including isolated cases.
Frequency of occurrence of adverse reactions
Immune system disorders
Very rare: systemic allergic reactions (including anaphylaxis, generalized rash, urticaria and angioedema).
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
Common: burning at the site of application.
Uncommon: itching, erythema, tingling, dryness at the application site. Allergic skin reactions to mupirocin or ointment base.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms
There are currently limited data on overdose with mupirocin.
Treatment
There is no specific treatment for mupirocin overdose. In case of overdose, maintenance therapy and appropriate monitoring of the patient are indicated if necessary.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd, India
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. |
| Manufacturer | Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd, India |
| Medication form | topical ointment |
| Brand | Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd |
Related products
Buy Supirocin, ointment 15 g with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.