No products in the cart.
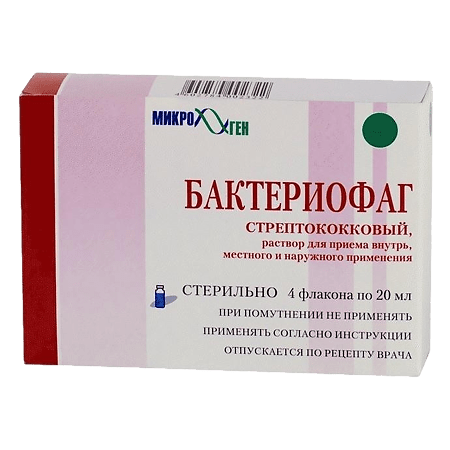
Streptococcus bacteriophage, 20 ml 4 pcs
€30.41 €29.34
Description
Streptococcus bacteriophage is an immunobiological drug, phage.
Streptococcal bacteriophage has the ability to specifically lyse streptococcal bacteria (streptococci, enterococci) isolated in purulent infections.
Indications
Indications
Streptococcal bacteriophage is used for the treatment and prevention of purulent infections of the skin, mucous membranes, visceral organs (purulent-inflammatory and enteral diseases) caused by streptococci, as well as for dysbiosis:
diseases of the ear, throat, nose, respiratory tract and lungs (inflammation of the sinuses and middle ear, sore throat, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, tracheitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, pleurisy);
surgical infections (wound suppuration, purulent burns, abscess, phlegmon, boil, carbuncle, hidradenitis, panaritium, paraproctitis, mastitis, bursitis, tendovaginitis, osteomyelitis);
urogenital infectious pathologies (urethritis, cystitis, pyelitis, pyelonephritis, colpitis, endometrigus, salpingoophoritis);
enteral infections (gastroenterocolitis, cholecystitis, dysbacteriosis);
generalized septic diseases;
purulent-inflammatory diseases of newborns (omphalitis, gastroenterocolitis, pyoderma, conjunctivitis, sepsis);
other diseases caused by streptococci, incl. enterococci;
for prophylactic purposes in case of freshly infected wounds (in case of street and industrial injuries, etc.); for the treatment of postoperative wounds, irrigation of the vagina and uterine cavity in the postpartum period; for the prevention of nosocomial infections for epidemic indications.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Streptococcal bacteriophage is an immunobiological preparation, phage.
Streptococcal bacteriophage has the ability to specifically lyse streptococcal bacteria (streptococci, enterococci) isolated during purulent infections.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Liquid streptococcal bacteriophage is not suitable for use if it is cloudy or has flakes.
Use during pregnancy is possible as prescribed by a doctor, subject to dosage.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Bacteriophage of streptococcus bacteria, monocomponent
Composition
Composition
The drug is a sterile filtrate of phagolysate, active against streptococcal bacteria, the most significant in the etiology of purulent-inflammatory diseases.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Individual intolerance.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Reactions to the introduction of streptococcal bacteriophage have not been established.
Interaction
Interaction
The use of streptococcal bacteriophage does not exclude the use of other drugs, incl. antibiotics.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store in a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature of 2–8°C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Microgen NPO, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store in a dry, light-protected place at 2-8°C. |
| Manufacturer | Microgen NPO, Russia |
| Medication form | oral solution and topical solution |
| Brand | Microgen NPO |
Related products
Buy Streptococcus bacteriophage, 20 ml 4 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.