No products in the cart.
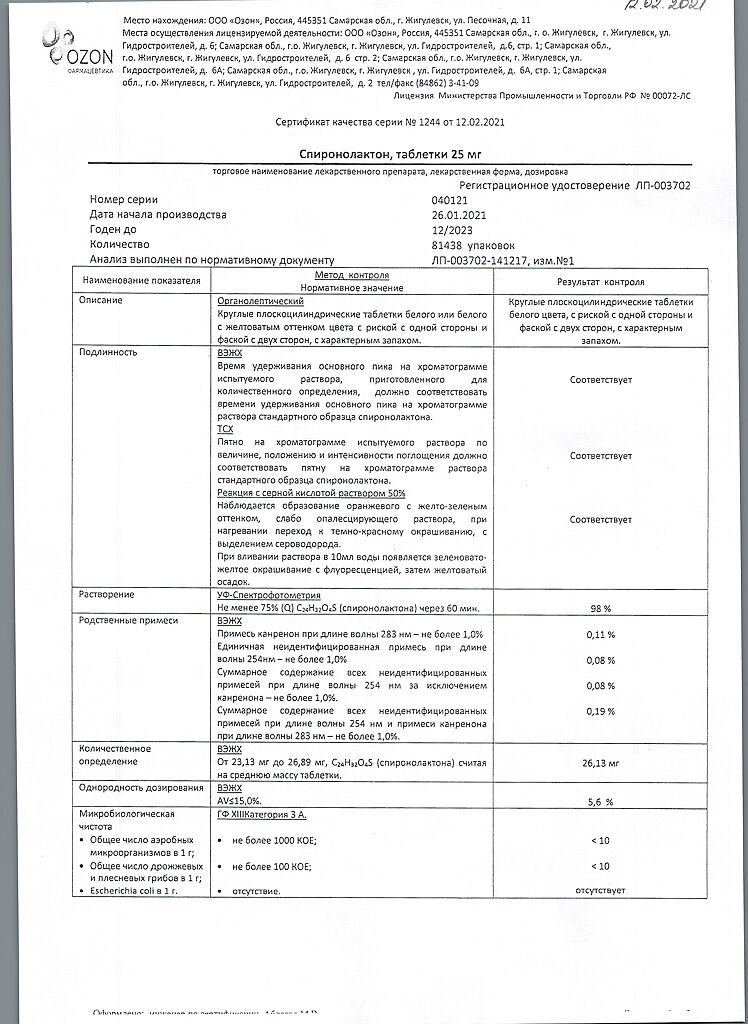
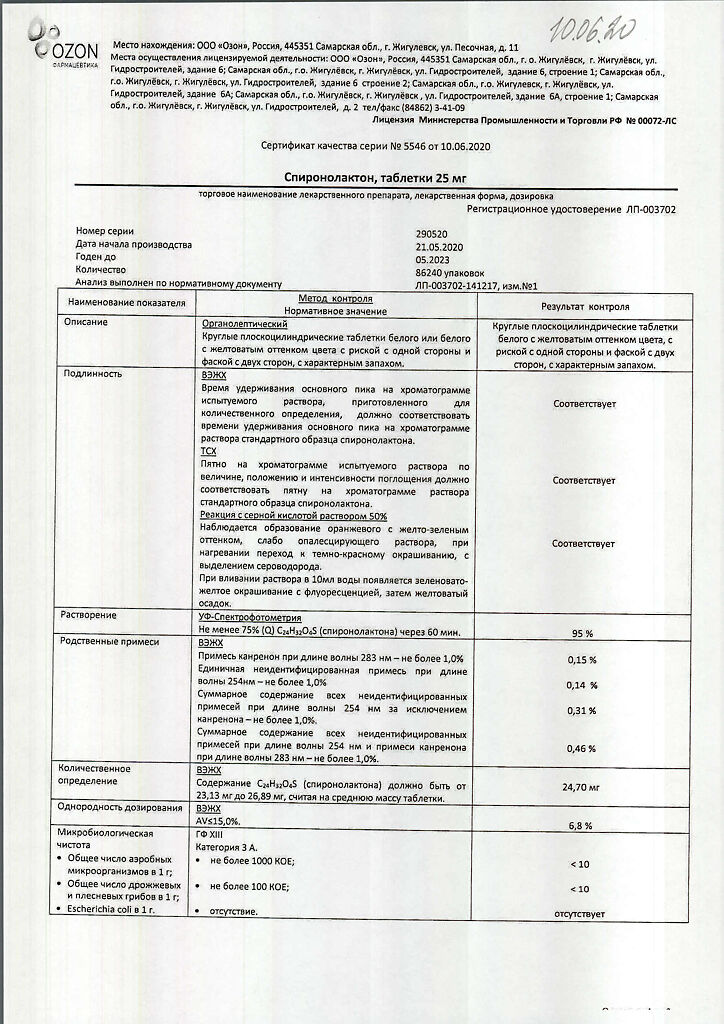
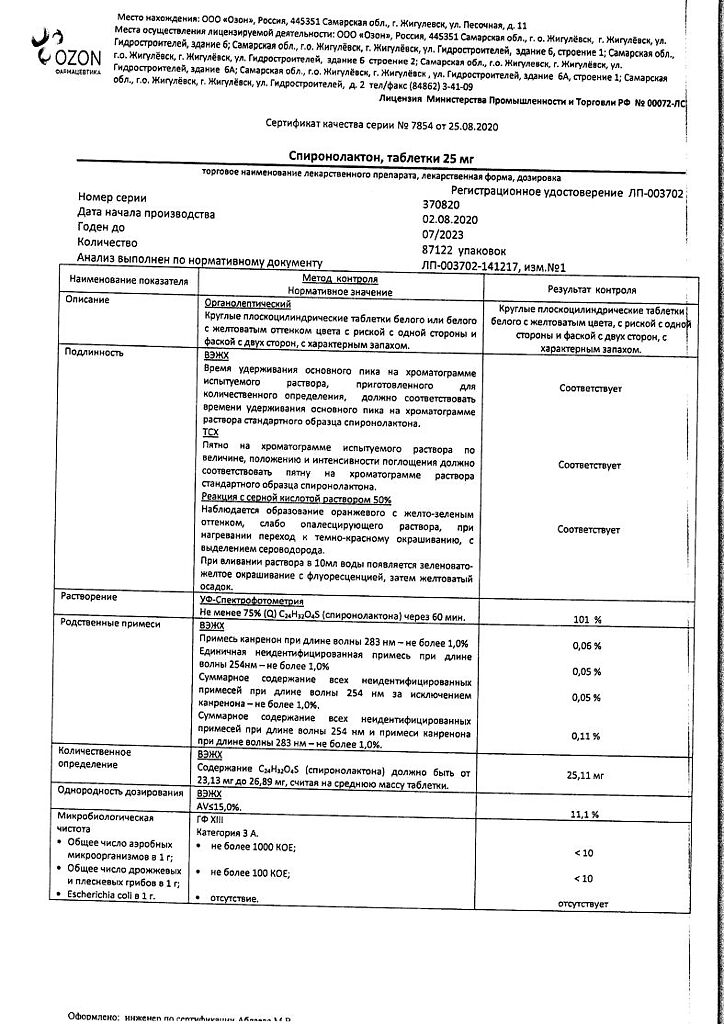
Spironolactone, tablets 25 mg 20 pcs
€2.52 €2.29
Description
Potassium-, magnesium-saving diuretic. It is a competitive aldosterone antagonist in its effect on the distal nephron (competes for binding sites at cytoplasmic protein receptors, reduces permease synthesis in the aldosterone-dependent site of the collecting tubes and distal tubules), increases Na+, Cl– and water and decreases K+ and urea excretion and decreases urine titratable acidity.
The increased diuresis causes a hypotensive effect that is intermittent.
The hypotensive effect is independent of plasma renin levels and is not seen with normal BP.
The diuretic effect is seen on days 2-5 of treatment.
Indications
Indications
Edema in chronic heart failure, liver cirrhosis (especially with the simultaneous presence of hypokalemia and hyperaldosteronism), in nephrotic syndrome.
Edema in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy.
Arterial hypertension, incl. for aldosterone-producing adrenal adenoma (as part of combination therapy).
Primary hyperaldosteronism. Aldosterone-producing adrenal adenoma (long-term maintenance therapy if surgical treatment is contraindicated or in case of refusal). Diagnosis of hyperaldosteronism.
Hypokalemia and its prevention during treatment with saluretics.
Polycystic ovary syndrome, premenstrual syndrome.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Potassium-, magnesium-sparing diuretic. It is a competitive antagonist of aldosterone in its effect on the distal nephron (competes for binding sites on cytoplasmic protein receptors, reduces the synthesis of permeases in the aldosterone-dependent area of the collecting ducts and distal tubules), increases the excretion of Na+, Cl- and water and reduces the excretion of K+ and urea, reduces the titratable acidity of urine.
Increased diuresis causes a hypotensive effect, which is not permanent.
The hypotensive effect does not depend on the level of renin in the blood plasma and does not occur at normal blood pressure.
The diuretic effect appears on days 2-5 of treatment.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Use with caution in case of AV blockade (possibility of intensification due to the development of hyperkalemia), decompensated liver cirrhosis, surgical interventions, taking drugs that cause gynecomastia, when taking local and general anesthetics, in elderly patients.
While using spironolactone, you should not prescribe drugs containing potassium, as well as other diuretics that cause potassium retention in the body. The use of spironolactone with carbenoxolone, which causes sodium retention, should be avoided.
During the treatment period, periodic determination of the content of electrolytes and urea in the blood should be carried out.
When using spironolactone in combination with other diuretic or antihypertensive drugs, it is recommended to reduce the dose of the latter. When spironolactone is used concomitantly with digoxin, it may be necessary to reduce both the saturating and maintenance doses of the latter.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Spironolactone
Composition
Composition
Pills
1 tab.
spironolactone
25 mg
Contraindications
Contraindications
Addison’s disease, hyperkalemia, hypercalcemia, hyponatremia, chronic renal failure, anuria, liver failure, diabetes mellitus with confirmed or suspected chronic renal failure, diabetic nephropathy, first trimester of pregnancy, metabolic acidosis, menstrual irregularities or breast enlargement, hypersensitivity to spironolactone.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, gastritis, ulceration and bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, intestinal colic, diarrhea or constipation.
From the side of the central nervous system: dizziness, drowsiness, lethargy, headache, lethargy, ataxia.
Metabolism: increased urea concentration, hypercreatininemia, hyperuricemia, impaired water-salt metabolism and acid-chain reaction (metabolic hypochloremic acidosis or alkalosis).
From the hematopoietic system: megaloblastosis, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia.
From the endocrine system: with long-term use – gynecomastia, erectile dysfunction in men; in women – dysmenorrhea, amenorrhea, metrorrhagia during menopause, hirsutism, deepening of the voice, breast tenderness, breast carcinoma.
Allergic reactions: urticaria, maculopapular and erythematous rashes, drug fever, itching.
Other: muscle spasms, decreased potency.
Interaction
Interaction
When used simultaneously with antihypertensive drugs, the hypotensive effect of spironolactone is potentiated.
When used simultaneously with ACE inhibitors, hyperkalemia may develop (especially in patients with impaired renal function), because ACE inhibitors reduce aldosterone levels, which leads to potassium retention in the body while limiting potassium excretion.
When used simultaneously with potassium supplements, other potassium-sparing diuretics, table salt substitutes and dietary supplements containing potassium, hyperkalemia may develop.
When used simultaneously with salicylates, the diuretic effect of spironolactone is reduced due to blockade of canrenone excretion by the kidneys.
Indomethacin and mefenamic acid inhibit renal excretion of canrenone.
With simultaneous use, the hypoprothrombinemic effect of oral anticoagulants is reduced.
When used simultaneously with digitoxin, it is possible to either enhance or reduce the effects of digitoxin.
When used concomitantly, spironolactone inhibits the renal excretion of digoxin and likely reduces its volume of distribution. This may cause an increase in plasma digoxin concentrations.
When used simultaneously with candesartan, losartan, eprosartan, there is a risk of developing hyperkalemia.
When used simultaneously with cholestyramine, cases of hypochloremic alkalosis have been described.
When used simultaneously with lithium carbonate, it is possible to increase the concentration of lithium in the blood plasma.
When used simultaneously with norepinephrine, it is possible to reduce the sensitivity of blood vessels to norepinephrine.
With simultaneous use, the effect of triptorelin, buserelin, and gonadorelin is enhanced.
Recommendations for use
Recommendations for use
The method of administration and dosage regimen of a particular drug depend on its release form and other factors. The optimal dosage regimen is determined by the doctor. It is necessary to strictly observe the compliance of the dosage form of a particular drug with the indications for use and dosage regimen.
They are set individually depending on the severity of disturbances in water-electrolyte metabolism and hormonal status.
For edematous syndrome – 100-200 mg/day (less often – 300 mg/day) in 2-3 doses (usually in combination with a loop and/or thiazide diuretic) daily for 14-21 days. Dose adjustments should be made taking into account plasma potassium concentrations. If necessary, courses are repeated every 10-14 days. With severe hyperaldosteronism and reduced potassium content in plasma – 300 mg/day in 2-3 doses.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Ozon, Russia
Additional information
| Manufacturer | Ozon, Russia |
|---|---|
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Ozon |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Spironolactone, tablets 25 mg 20 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.