No products in the cart.
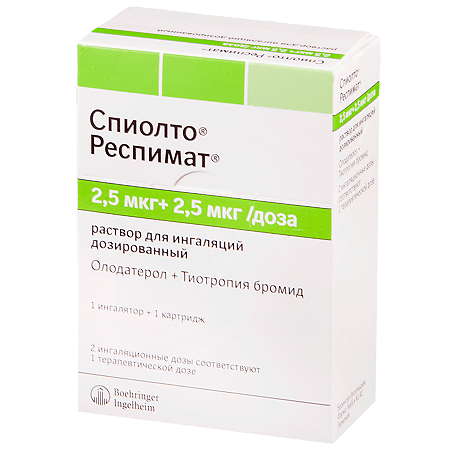
Spiolto Respimat, 2.5 mcg+2, 5 mcg/dose 4 ml cartridges, complete with respimat inhaler
€80.98 €67.48
EAN: 9006968012537
SKU: 261666
Categories: Bronchial asthma, Corticosteroid hormones, Medicine, Pain and fever
Description
Bronchodilator.
Olodaterol – a long-acting beta2-adrenomimetic – and tiotropium bromide – an m-cholinoblocker – provide complementary bronchodilation as a result of the different mechanism of action of the active substances and the different localization of the target receptors in the lungs.
Olodaterol has high affinity and selectivity for beta2-adrenoreceptors. Activation of beta2-adrenoceptors in the respiratory tract leads to stimulation of intracellular adenylate cyclase, which is involved in the synthesis of cAMP. Increased levels of cAMP cause bronchodilation, relaxing the smooth muscle cells of the airways.
Olodaterol is a selective long-acting beta2-adrenoceptor agonist with rapid onset of action and long (at least 24 hours) retention of effect. Beta2-adrenoceptors are present not only in smooth muscle cells, but also in many other cells, including epithelial and endothelial cells of the lungs and heart. The exact function of beta2-receptors in the heart is not fully understood, but their presence indicates that even highly selective beta2-adrenergic agonists can affect the heart.
Tiotropium bromide is a long-acting muscarinic receptor antagonist, often referred to in clinical practice as an m-cholin blocker. It has the same affinity for m1-m5-subtypes of muscarinic receptors. The result of inhibition of m3-receptors in the respiratory tract is relaxation of smooth muscles.
The bronchodilator effect is dose-dependent and persists for at least 24 hours. The considerable duration of action is probably due to the very slow dissociation of tiotropium bromide from m3-receptors: the half-dissociation period is significantly longer than that of ipratropium bromide.
When administered by inhalation, tiotropium bromide, as an N-quaternary ammonium derivative, has a local selective effect (on the bronchi), while not causing systemic m-cholinoblocking side effects at therapeutic doses. Dissociation from m2-receptors is faster than from m3-receptors, indicating the predominance of selectivity for m3-subtype receptors over m2-receptors. High affinity for receptors and slow dissociation of tiotropium bromide from bonding to receptors cause a pronounced and prolonged bronchodilator effect in patients with COPD.
The bronchodilation that develops after inhalation of tiotropium bromide is due primarily to local action (on the airways) rather than systemic action.
Indications
Indications
The drug SPIOLTO RESPIMAT, taken once a day, is indicated for long-term maintenance therapy in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), chronic bronchitis, emphysema, to reduce airway obstruction and concomitant shortness of breath; reducing the frequency of exacerbations; improving exercise tolerance and quality of life.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Bronchodilator.
Olodaterol, a long-acting beta2-adrenergic agonist, and tiotropium bromide, an m-anticholinergic blocker, provide complementary bronchodilation as a result of different mechanisms of action of the active substances and different localization of target receptors in the lungs.
Olodaterol has high affinity and selectivity for beta2-adrenergic receptors. Activation of beta2-adrenergic receptors in the respiratory tract leads to stimulation of intracellular adenylate cyclase, which is involved in the synthesis of cAMP. An increase in cAMP levels causes bronchodilation, relaxing the smooth muscle cells of the airways.
Olodaterol is a selective, long-acting beta2-adrenergic receptor agonist with a rapid onset of action and long-lasting (at least 24 hours) effect. Beta2-adrenergic receptors are present not only in smooth muscle cells, but also in many other cells, incl. epithelial and endothelial cells of the lungs and heart. The precise function of beta2 receptors in the heart is not fully understood, but their presence suggests that even highly selective beta2-adrenergic agonists may have effects on the heart.
Tiotropium bromide is a long-acting muscarinic receptor antagonist, often called an m-anticholinergic agent in clinical practice. It has the same affinity for the m1–m5 subtypes of muscarinic receptors. The result of inhibition of m3 receptors in the airways is the relaxation of smooth muscles.
The bronchodilator effect is dose dependent and lasts for at least 24 hours. The significant duration of action is probably due to the very slow dissociation of tiotropium bromide from m3 receptors: the half-life of dissociation is significantly longer than that of ipratropium bromide.
When administered by inhalation, tiotropium bromide, as an N-quaternary ammonium derivative, has a local selective effect (on the bronchi), while in therapeutic doses without causing systemic m-anticholinergic side effects. Dissociation from m2 receptors occurs faster than from m3 receptors, which indicates the predominance of selectivity for the m3 receptor subtype over m2 receptors. The high affinity for receptors and the slow dissociation of tiotropium bromide from binding to receptors determine a pronounced and long-lasting bronchodilator effect in patients with COPD.
Bronchodilation that develops after inhalation of tiotropium bromide is primarily due to a local effect (on the respiratory tract) rather than a systemic one.
Special instructions
Special instructions
The drug Spiolto Respimat should not be used for bronchial asthma. The effectiveness and safety of Spiolto Respimat in bronchial asthma have not been studied.
Hypersensitivity
After using the drug Spiolto Respimat, immediate hypersensitivity reactions may develop.
Acute bronchospasm
Spiolto Respimat is not indicated for the treatment of acute episodes of bronchospasm, i.e. as an ambulance.
Paradoxical bronchospasm
The use of Spiolto Respimat, like other inhaled drugs, can lead to paradoxical bronchospasm, sometimes life-threatening. If paradoxical bronchospasm develops, the use of Spiolto Respimat should be immediately discontinued and alternative therapy should be prescribed.
Patients with impaired renal function
Because Tiotropium bromide is excreted primarily by the kidneys; patients with moderate to severe renal failure (creatinine clearance <50 ml/min) using Spiolto Respimat should be closely monitored by a physician.
Visual disorders
Patients should be informed about the correct use of Spiolto Respimat. Do not allow the solution or aerosol to get into your eyes. Eye pain or discomfort, blurred vision, visual halos around light sources, combined with redness of the eyes caused by swelling of the conjunctiva and cornea can be symptoms of acute angle-closure glaucoma. If any combination of these symptoms develops, you should immediately consult a specialist. Miotic eye drops are not considered an effective treatment.
Cardiovascular effects
Olodaterol, like other beta-agonists, may have clinically significant effects on the cardiovascular system in some patients (increased heart rate, increased blood pressure and/or the appearance of related symptoms). If such symptoms occur, treatment may need to be discontinued. In addition, beta2-agonists have been reported to cause ECG changes such as T-wave flattening and ST-segment depression, although the clinical significance of these changes is unknown.
Hypokalemia
Beta2-agonists in some patients can lead to the development of hypokalemia, which creates the preconditions for the occurrence of undesirable effects on the cardiovascular system. The decrease in serum potassium concentration is usually short-term and does not require replenishment. In patients with severe COPD, hypokalemia may be exacerbated by hypoxia and concomitant medications and increase the risk of developing arrhythmias.
Hyperglycemia
Inhaled use of large doses of beta2-agonists may lead to an increase in plasma glucose concentrations.
Spiolto Respimat should not be used in combination with any other medicinal product containing long-acting beta2-agonists.
Patients frequently using short-acting inhaled beta2-agonists (eg, 4 times daily) should be instructed that these drugs are used only to relieve acute symptoms of bronchospasm.
The drug Spiolto Respimat is intended for the maintenance treatment of patients with COPD. Due to the fact that in the general COPD population there is a significant predominance of patients over the age of 40 years. When prescribing the drug to patients under 40 years of age, spirometric confirmation of the diagnosis of COPD is required.
The effect of the drug on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
No studies have been conducted to study the effect on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery. Caution should be exercised when performing these activities as… Dizziness or blurred vision may develop.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Olodaterol, Tiotropium bromide
Composition
Composition
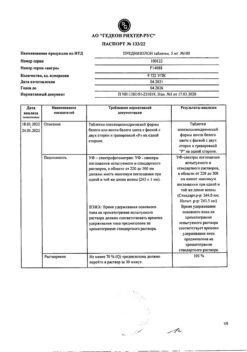
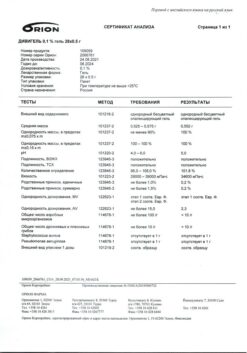
1 dose contains:
olodaterol hydrochloride – 2.736 mcg, which corresponds to the content of olodaterol – 2.5 mcg
tiotropium bromide monohydrate – 3.124 mg, which corresponds to the content of tiotropium – 2.5 mg
Excipients:
benzalkonium chloride solution – 0.0022 mg (respectively benzalkonium chloride – 0.0011 mg),
disodium edetate – 0.0011 mg,
anhydrous citric acid 1M – up to pH 2.9,
purified water – up to 11.05 mg.
Contraindications
Contraindications
SPIOLTO RESPIMAT is contraindicated in patients with hypersensitivity to olodaterol, tiotropium bromide or any component of the drug;
patients who have previously had hypersensitivity to atropine or its derivatives, for example ipratropium and oxitropium;
not recommended for use in children under 18 years of age (due to lack of data on effectiveness and safety).
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the nervous system: dizziness, insomnia.
Metabolism and nutrition: dehydration.
From the organ of vision: increased intraocular pressure, glaucoma; blurred vision.
From the cardiovascular system: atrial fibrillation, palpitations, tachycardia, supraventricular tachycardia, increased blood pressure.
From the respiratory organs, chest and mediastinum: cough, nosebleeds, pharyngitis, dysphonia, bronchospasm, laryngitis, sinusitis.
From the gastrointestinal tract: slight dry mouth, constipation, oral candidiasis, dysphagia, gastroesophageal reflux, gingivitis, glossitis, stomatitis; intestinal obstruction, including paralytic ileus.
From the skin: skin infections and skin ulcers, dry skin.
Allergic reactions: rash, itching, angioedema, urticaria, hypersensitivity, including immediate reactions.
Musculoskeletal system and related connective tissue diseases: arthralgia, swelling in the joints, back pain.
From the kidneys and urinary system: dysuria, urinary retention (more often in men with predisposing factors), urinary tract infection.
Infections and infestations: nasopharyngitis.
Interaction
Interaction
Although specific drug interaction studies have not been conducted, tiotropium bromide has been used in conjunction with other drugs for the treatment of COPD, including methylxanthines, oral and inhaled steroids, with no clinical evidence of drug interactions observed.
Long-term combined use of tiotropium bromide with other m-anticholinergic drugs has not been studied. Therefore, long-term combined use of Spiolto Respimat with other m-anticholinergic drugs is not recommended.
Concomitant use of other adrenergic drugs may enhance the undesirable effects of Spiolto Respimat.
The simultaneous use of xanthine derivatives, steroids or diuretics (not classified as potassium-sparing) may enhance the hypokalemic effect of adrenergic agonists.
Beta blockers may reduce or antagonize the effect of olodaterol. In this case, the use of running 1-blockers is preferable, although they should be used with caution.
MAO inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants or other drugs that can prolong the QTc interval may increase the effect of Spiolto Respimat on the cardiovascular system.
Concomitant use of olodaterol with ketoconazole resulted in a 1.7-fold increase in systemic exposure to olodaterol. However, this did not affect safety. No dose change is required.
Overdose
Overdose
An overdose of olodaterol can lead to pronounced effects typical of beta2-agonists, for example, myocardial ischemia, increased or decreased blood pressure, tachycardia, arrhythmias, palpitations, dizziness, nervousness, insomnia, anxiety, headache, tremor, dry mouth, muscle spasms, nausea, fatigue, malaise, hypokalemia, hyperglycemia and metabolic acidosis.
When using high doses of tiotropium bromide, manifestations of m-anticholinergic action are possible. After 14 days of inhaled use of tiotropium bromide in doses reaching 40 mcg, no significant adverse events were observed in healthy individuals, except for a feeling of dryness of the mucous membranes of the nose and oropharynx, the frequency of which depended on the dose (10-40 mcg/day). The exception was a clear decrease in salivation starting from the 7th day of drug use.
Treatment
Spiolto Respimat should be discontinued. Supportive and symptomatic treatment is indicated. In severe cases, hospitalization is necessary. The use of beta1-blockers may be recommended, but only with extreme caution, because use of these drugs may cause bronchospasm.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. Keep out of the reach of children!
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years
Use within 3 months after the first inhalation.
Do not use after the expiration date stated on the packaging.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co.KG, Germany
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years Usage within 3 months of first inhalation. Do not use after the expiration date printed on the package. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Keep out of reach of children! |
| Manufacturer | Boehringer Ingelheim Pharma GmbH & Co. |
| Medication form | metered solution for inhalation |
| Brand | #Н/Д |
Related products
Buy Spiolto Respimat, 2.5 mcg+2, 5 mcg/dose 4 ml cartridges, complete with respimat inhaler with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.