No products in the cart.
Sinflorix, 1 dose 0.5 ml suspension
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Sinflorix vaccine contains antigens of 10 Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes (1, 4, 5, 6B, 7F, 14, 18C, 19F and 23F) causing the most cases of invasive pneumococcal infection (50-96%) and pneumonia in children under 5 years old worldwide.
Also, in 60-70% of clinical cases, acute otitis media (AMI) has a bacterial cause and is most commonly caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae and untypable Haemophilus influenzae.
Immunological efficacy
In clinical trials, Sinflorix induced an immune response to all 10 serotypes included in the vaccine, but the magnitude of the response varied by serotype. The immune response against serotypes 1 and 5 was slightly lower compared to the other serotypes. The effect of this phenomenon on the clinical efficacy of the vaccine to prevent diseases caused specifically by these serotypes is not known.
The efficacy of the vaccine to prevent invasive pneumococcal infection
. In accordance with WHO requirements, the efficacy evaluation of the Sinflorix vaccine was based on a comparison of the immune response for the 7 pneumococcal serotypes included in both Sinflorix and the 7-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine with known protective efficacy. The decision on efficacy was based on the results of immunogenicity evaluation by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and their average geometric titers by opsonophagocytic activity assessment (OPA).
In a direct comparative immunogenicity study, the immune response against the 7 common antigens in Sinflorix vaccine was comparable to the comparison product, with the exception of serotypes 6B and 23F (the clinical significance of this phenomenon is unknown). In addition, the immune response to additional serotypes 1, 5, and 7F included in the Sinflorix vaccine was evaluated. Seroconversion against these antigens reached 97.3%, 99%, and 99.5%, respectively.
Sinflorix has also been shown to induce an immune response against Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes 6A and 19A, which are not part of the vaccine. One month after revaccination, there was a 5.5-fold and 6.1-fold increase in SCC antibodies to these serotypes and a 6.7-fold and 6.1-fold increase in SCC antibodies to these serotypes, respectively.
In clinical trials the high immunogenicity of the Sinflorix vaccine has been confirmed with the use of two-dose and three-dose regimens of primary immunization in children under 2 and 2-5 years of age.
The effectiveness of the vaccine for the prevention of acute otitis media
The presence of D-protein in the vaccine was the cause of the effectiveness of Sinflorix vaccine for the prevention of acute otitis media caused not only by Streptococcus pneumoniae, but also by Haemophilus influenzae with a high degree of confidence. The administration of Sinflorix vaccine induces an immune response to D-protein after the initial course of vaccination with three doses in the first year of life.
The effectiveness of the vaccine for the prevention of acute otitis media of any etiology was 336%; 35.3% for acute otitis media caused by nontypical Haemophilus influenzae; 35.6% for acute otitis media caused by Haemophilus influenzae (including nontypical Haemophilus influenzae); 51.5% in the case of acute otitis media caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae of any serotype; 65.5% in the case of acute otitis media caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes related to the serotypes included in the Sinflorix vaccine (6A and 19A); 67.9% in cases of acute otitis media caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes whose antigens are part of the Sinflorix vaccine.
After completion of vaccination with Sinflorix, the incidence of recurrent acute middle ear otitis (≥3 exacerbations after 6 months or ≥4 after 12 months) was reduced by 56% and episodes of auditory tube catheterization by 60.3%.
The efficacy of the Sinflorix vaccine in the 2-dose primary immunization regimen
. Although the 2-dose primary immunization regimen for children under 6 months of age had a slightly lower SGT antibody value for serotypes 6B and 23F compared with the same value for the 3-dose regimen, no significant difference was found between the two vaccination regimens. The secondary immune response to the revaccination dose in the second year of life was comparable for all serotypes, regardless of the initial primary vaccination regimen, although the 2-dose regimen had a slightly lower antibody titer for serotypes 5 and 23F. The clinical significance of the lower immune response to individual serotypes in the 2-dose regimen is not known. Thus, immune memory formation with respect to the antigens included in Sinflorix was demonstrated for both primary vaccination regimens.
The immunogenicity of the Sinflorix vaccine in children born prematurely
Sinflorix demonstrated high immunogenicity when vaccinating preterm infants (27-36 weeks gestation) with 3 doses according to the 2-4-6 month schedule followed by revaccination. In 97.6% of the infants 97.6% achieved threshold antibody concentrations (SBC ≥ 0.2 μg/ml), measured by ELISA, and 91.9% of the children had opsonizing antibody titers (OSA) ≥ 8 for all Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes in the vaccine. No fundamental differences were found in the formation of the immune response and immune memory in children born prematurely and those born at term.
Indications
Indications
Active immunization of children from 6 weeks to 5 years of age to prevent invasive diseases (including sepsis, meningitis, pneumonia, bacteremia) and acute otitis media caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae serotypes 1, 4, 5, 6B, 7F, 9V, 14, 18C, 1,9F and 23F.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
1 dose of suspension for intramuscular administration contains:
acting ingredients:
vaccine for the prevention of pneumococcal infections 0.5 ml,
The polysaccharides of Streptococcus pneumoniae,
conjugated with carrier proteins:
Polysaccharide serotype 1 1 µg/PD,
Polysaccharide serotype 4 3 µg/PD,
serotype 5 polysaccharide 1 µg/PD,
serotype 6B polysaccharide 1 µg/PD,
serotype 7F polysaccharide 1 µg/PD,
serotype 9V polysaccharide 1 µg/PD,
serotype 14 polysaccharide 1 µg/PD,
serotype 18C polysaccharide 3 µg/PD,
p> serotype 19F polysaccharide 3 µg/PD,
Polysaccharide serotype 23F 1 µg/PD,
Carrier proteins (total amount):
PD: Haemophilus influenzae D-protein 9-16 µg*
TT: tetanus toxoid 5-10 µg*
DT: Diphtheria anatoxin 3-6 µg*
* the composition of the drug is based on the polysaccharide content, and the individual carrier protein content depends on the polysaccharide/protein ratio
excipients:
aluminum phosphate (in terms of aluminum) 0.5 mg,
sodium chloride 4.4 mg,
water d / i to 0.5 ml.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
A single dose of the vaccine is 0.5 ml.
Children aged 6 weeks to 6 months (inclusive)
Initial immunization with 3 doses of vaccine
The recommended immunization schedule, providing an optimal level of protection, consists of 3 vaccinations followed by revaccination. The optimum age (start of vaccination is 2 months of life, and subsequent vaccinations at least 1 month apart. Vaccinations can be started earlier but not earlier than at 6 weeks of life.
Revaccinations are recommended not earlier than 6 months after the last primary vaccination, preferably at the age of 12-15 months.
Initial immunization with 2 doses of vaccine
When Sinflorix is administered as part of mass immunization, the vaccination schedule may consist of 2 vaccinations followed by revaccination. The first vaccination is given at 2 months of life, and the second two months after the first. The revaccination dose is recommended no earlier than 6 months from the date of the last vaccination.
Infants born prematurely (at least 27 weeks of gestation)
The recommended immunization regimen consists of 3 vaccinations followed by revaccination. The first shot will be given at two months of life and the subsequent shots at least one month apart.
It is recommended to give the booster dose not earlier than six months after the last shot.
Children who have not been immunized during the first 6 months of life
Children aged 7-11 months
The immunization schedule consists of two vaccinations with an interval of at least 1 month between doses.
The revaccinating dose is recommended for the second year of life no earlier than 2 months from the date of the last vaccination.
Children aged 12-23 months
The vaccination regimen consists of two doses with at least 2 months between doses.
The need for a revaccinating dose with this regimen has not been determined.
Children between the ages of 24 months and 5 years
The vaccine schedule consists of two doses at least two months apart.
If the vaccination was initiated with the Sinflorix vaccine it is recommended that the full course of vaccination also be given with the same vaccine.
Interaction
Interaction
Do not mix the vaccine with other products in the same syringe!
Performance with other vaccines
Sinflorix vaccine can be given at the same time as any of the following monovalent or combination vaccines (including combination vaccines (AACDS-HepV-IPV/Hib and AACDS-HepV/Hib) diphtheria-tetanus cell-free pertussis vaccine (DTPV), diphtheria-tetanus all-cell pertussis vaccine (DTPV), vaccine to prevent infection caused by Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib), hepatitis B vaccine, inactivated polio vaccine (IPV), vaccine against measles, mumps and rubella, varicella vaccine, meningococcal serogroup C conjugate vaccine (CRM197 and TT conjugates), oral polio vaccine (OPV), rotavirus vaccine.
Injections with different vaccines should always be given in different parts of the body!
The immune response and safety profile of co-injected vaccines remain unchanged, with the exception of the immune response to inactivated polio vaccine (inactivated polio virus type 2), for which inconsistent results were observed (seroprotection values ranged from 78% to 100%). The clinical significance of this phenomenon is not known. The type of carrier protein (CRM197 or TT) in the meningococcal conjugate vaccines had no adverse effect when the vaccines were used together.
The immune response to Haemophilus influenzae capsular polysaccharide type b conjugated with tetanus toxoid as well as diphtheria and tetanus antigens was enhanced.
The use with systemic immunosuppressive drugs
In patients receiving immunosuppressive therapy, Sinflorix (like other vaccines in a similar case) may not cause an adequate immune response.
The use with antipyretics
The prophylactic use of paracetamol as an antipyretic may decrease the immune response to pneumococcal vaccine administration. The clinical significance of this observation remains unknown.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Before vaccination, the medical history should be ascertained, paying particular attention to previous vaccinations and the occurrence of possible adverse events.
Given the possibility of extremely rare development of anaphylactic reactions, the patient should be under medical supervision for at least 30 minutes, and the place of vaccination should be provided with antishock therapy.
During or before vaccination fainting may occur as a psychogenic reaction of the patient to the injection. In order to avoid injury, the possibility of fainting should be considered when choosing where to administer the injection.
As with other intramuscularly administered vaccines, Sinflorix should be administered with caution to patients with thrombocytopenia or other clotting disorders because of the risk of bleeding during intramuscular administration.
Sinflorix does not prevent disease caused by pneumococci of other serogroups whose antigens are not in this vaccine. Although an immune response to diphtheria toxoid, tetanus toxoid, and Haemophilus influenzae D-protein is observed after administration of Sinflorix vaccine, immunization with Sinflorix vaccine is not a replacement for routine immunization against diphtheria, tetanus, or Haemophilus influenzae type b. Official immunization requirements for these infections must be followed.
As with any vaccination, not all people who receive the Sinflorix vaccine may have a protective immune response.
Children with compromised immune status, possibly due to immunosuppressive therapy, genetic defect, HIV infection or other causes, may have reduced antibody production after immunization.
There are currently no data on the safety and immunogenicity of the Sinflorix vaccine in children at increased risk for pneumococcal infections (sickle cell anemia, congenital and acquired spleen dysfunction, HIV infection, malignancies, nephrotic syndrome).
The decision to vaccinate must be made on a case-by-case basis and it must be kept in mind that in children 12-23 months of age, a two-dose vaccination regimen may not be sufficient to provide protection and revaccination may be recommended. However, for children at increased risk for pneumococcal infection (e.g., those with sickle cell anemia, asplenia (absent spleen), HIV infection, chronic disease, or immune disorders) under 2 years of age, immunization with the Sinflorix vaccine according to age guidelines is recommended; at the age of 2 years and older a 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine may be used (the minimum interval after administration of Sinflorix vaccine is 8 weeks).
The potential risk of apnea and the need to monitor respiratory function for 48-72 hours during the initial vaccination of children born prematurely (⤠28 weeks gestation) and especially those with respiratory distress syndrome should be considered. Because of the need to vaccinate this group of children, the primary vaccination should not be delayed or refused.
The prophylactic use of antipyretics before or immediately after vaccine administration may reduce the frequency and intensity of postvaccination febrile reactions and may be recommended for children receiving Sinflorix concomitantly with whole-cell pertussis vaccine and for children with a history of febrile reactions. For more information on co-administration with paracetamol, see “Interaction with other medicinal products”.
The efficacy and safety of Sinflorix vaccine in children over 5 years of age has not been studied.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Side effects
Side effects
In a clinical trial, about 1,800 doses of Sinflorix vaccine were used to initially immunize approximately 4,500 healthy children and 137 children born prematurely. About 3,800 healthy children and 116 children born prematurely were revaccinated with Sinflorix vaccine in the second year of life.
The safety of use has also been confirmed with data from about 200 children between the ages of 2 and 5 years. In all studies, Sinflorix was administered concomitantly with other recommended vaccines for this age range. No increase in frequency or severity of adverse events was noted with each subsequent vaccination in the primary vaccination series.
It was noted that the incidence of local reactions during the primary immunization series was higher in children older than 12 months compared with younger children.
Higher reactogenicity was noted in children when all-cell pertussis vaccines were used concomitantly.
The most frequent, but mostly transient, adverse events were injection site redness and irritability, with a frequency of 38.3% and 52.3%, respectively. At the revaccination stage these events increased slightly compared to the initial vaccination series, reaching 52.6% and 55.4%, respectively.
The adverse events listed below are listed by body system and according to frequency of occurrence for all age groups.
The frequency of occurrence is defined as follows: very common (⥠1/10), common (⥠1/100 and < 1/10), infrequent (⥠1/1,000 and < 1/100), rare (⥠1/10,000 and < 1/1,000).
Nervous system disorders
Very common: somnolence
Rare: febrile and afebrile seizures
Respiratory system, thorax and mediastinum disorders
Infrequent: apnea in severely premature (â¤28 weeks gestation) infants (see “Special Indications.
Metabolism and nutrition
Very common: loss of appetite
Gastrointestinal tract
Infrequent: diarrhea, vomiting
Immune system disorders
Rarely: Allergic reactions (such as allergic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, eczema)
Mental health
Very common: irritability
Infrequent: pathological crying
Skin and subcutaneous fatty tissue
Rare: rash, urticaria
General and local reactions
Very common: pain, redness, swelling at the injection site, fever (rectally ⥠38°C, age < 2 years)
Frequent: injection site thickening, fever (rectally > 39°C, age < 2 years; ⥠38°C, age 2-5 years)
Infrequently: Hematoma at injection site, hemorrhage and thickening at injection site, fever (rectally > 40°C*, age < 2 years; > 39°C, age 2-5 years)
* noted at revaccination.
Overdose
Overdose
Incidents of overdose have not been described.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
Because Sinflorix vaccine is not intended for use in adults, there have been no studies of vaccine use during pregnancy or while breastfeeding.
Additional information
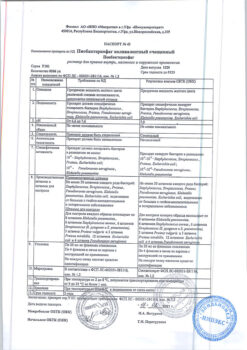
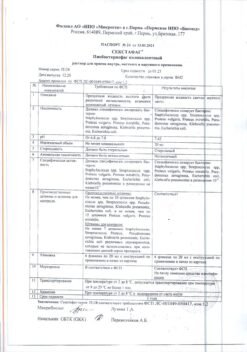
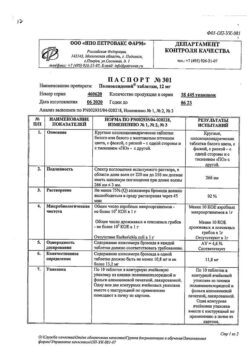
| Shelf life | 3 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store at 2 to 8°C in a light-protected place. Do not freeze. |
| Manufacturer | De Mizlen a.s., Slovakia |
| Medication form | suspension for injection |
| Brand | De Mizlen a.s. |
Related products
Buy Sinflorix, 1 dose 0.5 ml suspension with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.