No products in the cart.
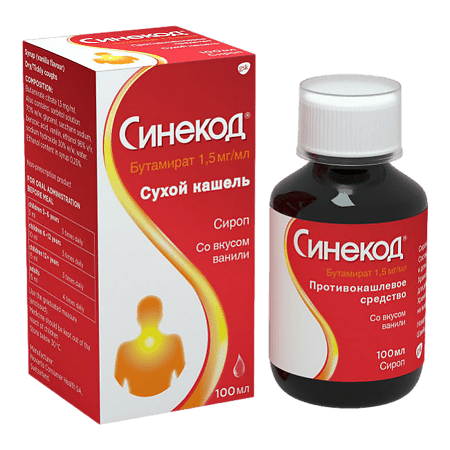
Sinekod, syrup 1.5 mg/ml 100 ml
€11.05 €9.67
Description
Anti-cough drug of central action, does not relate to opium alkaloids neither chemically nor pharmacologically.
Indications
Indications
Symptomatic treatment of dry cough of various etiologies.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Butamirate is a centrally acting antitussive. However, the exact mechanism of action of the drug is not known. Butamirate citrate has nonspecific anticholinergic and bronchospasmolytic effects. Suppresses cough, having a direct effect on the cough center. Has a bronchodilator effect (expands the bronchi). Helps make breathing easier by improving spirometry (reduces airway resistance) and blood oxygenation (saturates the blood with oxygen). In therapeutic doses, the drug is well tolerated. Butamirate in the form of an oral solution has a soothing effect on an irritated throat due to the moisturizing properties of glycerol.
Special instructions
Special instructions
The drug contains saccharinate and sorbitol (248 mg in each ml) as sweeteners, so it can be prescribed to patients with diabetes.
Sorbitol is a source of fructose.
Patients with hereditary fructose intolerance should not take this drug.
Sorbitol may cause gastrointestinal discomfort and have a mild laxative effect.
The drug contains a small amount of ethyl alcohol, less than 100 mg per dose.
Due to the presence of ethyl alcohol in the drug, use with caution in patients with a tendency to develop drug dependence, with liver diseases, alcoholism, epilepsy, brain diseases, in pregnant women and children.
The drug contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) sodium per dose, i.e. Virtually “sodium-free.”
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Butamirat
Composition
Composition
(mass-volume percentage):
Active substance – butamirate citrate – 0.150 (1.5 mg/ml).
Excipients: sorbitol solution 70% m/m 40.50, glycerol 29.00, sodium saccharinate 0.06, benzoic acid 0.115, vanillin 0.06, ethanol 96% v/v. 0.25, sodium hydroxide 30% m/m 0.031, water up to 100 ml.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
In animal studies, no adverse effects on the fetus were observed. There have been no controlled studies in pregnant women. The use of the drug during pregnancy is contraindicated.
Breastfeeding period
The use of the drug during breastfeeding is contraindicated
Contraindications
Contraindications
• Pregnancy;
• breastfeeding period;
• children under 3 years of age (for this dosage form);
• simultaneous use with expectorants;
• sucrase/isomaltase deficiency, fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption.
Side Effects
Side Effects
The adverse reactions presented below are listed according to the damage to organs and organ systems and the frequency of occurrence. The frequency of occurrence is defined as follows: very common (≥ 1/10), common (≥ 1/100 and < 1/10), uncommon (≥ 1/1,000 and < 1/100), rare (≥ 1/10,000 and < 1/1,000), very rare (< 1/10,000, including isolated cases), frequency unknown (frequency cannot be determined) estimated based on available data).
Nervous system disorders
Rarely: drowsiness.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Rarely: nausea, diarrhea.
Disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissues
Rarely: urticaria, possible development of allergic reactions
Interaction
Interaction
No drug interactions have been reported for butamirate.
Due to the fact that butamirate suppresses the cough reflex, the simultaneous use of expectorants should be avoided to avoid the accumulation of sputum in the respiratory tract with the risk of developing bronchospasm and respiratory tract infection.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms
Drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dizziness and decreased blood pressure.
Treatment
There is no special antidote. In case of overdose, you should do a gastric lavage, take activated charcoal and support the vital functions of the body.
Clinical pharmacology
Clinical pharmacology
Suction
Butamirate is quickly and completely absorbed when taken orally and is hydrolyzed into 2-phenylbutyric acid and diethylaminoethoxyethanol. The effect of simultaneous food intake on the processes has not been studied. The plasma levels of 2-phenylbutyric acid and diethylaminoethoxyethanol are fully proportional over the dose range of 22.5–90 mg. Measurable concentrations of butamirate are detected in the blood 5–10 minutes after administration of doses of 22.5 mg, 45 mg, 67.5 mg and 90 mg. Peak plasma concentrations are achieved 1 hour after all 4 doses, and the mean peak plasma concentration is 16.1 ng/mL at the 90 mg dose. The average maximum concentration of 2-phenylbutyric acid is achieved within 1.5 hours, and maximum exposure is observed after application of 90 mg (3052 ng/ml). The average maximum concentration of diethylaminoethoxyethanol is reached after 0.67 hours, the maximum exposure is also observed after taking 90 mg (160 ng/ml).
Distribution
Butamirate has a volume of distribution between 81 and 112 l (taking into account body weight in kg), as well as a high degree of binding to plasma proteins. 2-phenylbutyric acid is highly bound to plasma proteins in the dose range of 22.5–90 mg, with an average value of 89.3–91.6%. Diethylaminoethoxyethanol binds to plasma proteins to some extent, with average values ranging from 28.8 to 45.7%. There is no data on the penetration of butamirate through the placental barrier and its excretion in breast milk.
Metabolism
Hydrolysis of butamirate occurs quickly, the concentrations of metabolites are detected after 5 minutes. Based on these studies, these metabolites are also believed to have antitussive activity, but there are no clinical data on the metabolism of diethylaminoethoxyethanol. 2-phenylbutyric acid undergoes further partial metabolism by hydroxylation at the para position.
Removal
24 hours after taking the drug, the main metabolites (77%) consist of conjugated 2-phenylbutyric acid and parahydroxy-2-phenylbutyric acid. Excretion of 2-phenylbutyric acid, diethylaminoethoxyethanol and p-hydroxy?2-phenylbutyric acid occurs primarily in the urine. The level of 2-phenylbutyric acid conjugate in urine is significantly higher than its level in plasma. Butamirate is detected in urine within 48 hours after taking the drug orally. The amount of butamirate excreted in the urine over 96 hours corresponds to 0.02%, 0.02%, 0.03% and 0.03% at drug doses of 22.5 mg, 45 mg, 67.5 mg and 90 mg. Butamirate metabolites are excreted in greater quantities. The half-life of butamirate is 1.48–1.93 hours, 2-phenylacetic acid is 23.26–24.42 hours, diethylaminoethoxyethanol is 2.72–2.90 hours.
Recommendations for use
Recommendations for use
For oral administration.
Do not exceed the recommended dose! Maximum duration of use of the drug without consulting a doctor: 7 days. The drug is taken before meals. Use the measuring cap (supplied). The measuring cap should be washed and dried after each use. If the product is used by multiple patients, the measuring cap should be washed and dried between uses on different patients.
Adults:
15 ml (22.5 mg) 4 times a day. The maximum daily dose is 60 ml (90 mg).
Children over 12 years old:
15 ml (22.5 mg) 3 times a day. The maximum daily dose is 45 ml (67.5 mg).
Children aged 6 to 12 years:
10 ml (15 mg) 3 times a day. The maximum daily dose is 30 ml (45 mg).
Children aged 3 to 6 years:
5 ml (7.5 mg) 3 times a day. The maximum daily dose is 15 ml (22.5 mg).
If symptoms worsen or do not improve after 7 days of treatment, as well as fever, rash or persistent headache, you should consult a doctor for further examination.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 30 °C.
Keep out of reach of children
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years. Do not use after expiration date
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
GSK Consumer Healthcare S.A., Switzerland
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | The drug should be kept out of reach of children at a temperature not exceeding 30°C. |
| Manufacturer | GSC Consumer Healthcare S.A., Switzerland |
| Medication form | syrup |
| Brand | GSC Consumer Healthcare S.A. |
Related products
Buy Sinekod, syrup 1.5 mg/ml 100 ml with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.