No products in the cart.
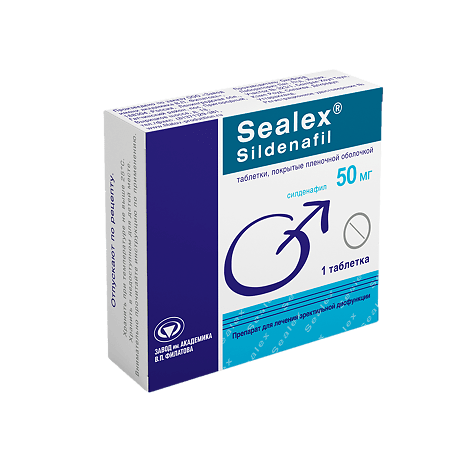
Sealex Sildenafil, 50 mg
€12.54 €10.97
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Description
Sildenafil is a powerful selective inhibitor of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP)-specific phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5).
Mechanism of action.
The realization of the physiological mechanism of erection is associated with the release of nitric oxide (NO) in the cavernous body during sexual stimulation. This, in turn, leads to an increase in cGMP levels, a subsequent relaxation of the smooth muscle tissue of the cavernous body, and an increase in blood flow.
Sildenafil has no direct relaxant effect on the isolated human cavernous body, but it enhances the effect of nitric oxide (NO) through
Inhibition of FDE5, which is responsible for the breakdown of cGMP.
Sildenafil is selective against FDE5 shuigo, its activity against FDE5 is greater than that against other known phosphodiesterase isoenzymes: FDE6, 10 times; FDE1, more than 80 times; FDE2, FDE4, FDE7-FDE11, more than 700 times. Sildenafil is 4,000 times more selective against FDE5 compared to FDEZ, which is of critical importance because FDEZ is one of the key enzymes
Regulation of myocardial contractility.
The mandatory condition for the effectiveness of sildenafil is sexual stimulation. Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of sildenafil in the recommended dose range is linear. Absorption
After oral administration, sildenafil is rapidly absorbed. Absolute bioavailability averages about 40 % (25 % to 63 %). sildenafil at a concentration of about 1.7 ng/ml (3.5 nM) inhibits human FDE5 activity by 50 %. After a single dose of sildenafil at a dose of 100 mg, the average maximum plasma concentration of free sildenafil (Stah) in men is about 18 ng/ml (38 nM). The average absorption rate when sildenafil is taken orally on an empty stomach is reached within 90 minutes:
The rate of absorption decreases by 29% and the time to reach the maximum concentration (Ttach) increases by 60 min, but the degree of absorption does not change significantly (the area under the pharmacokinetic curve of concentration-time (ATC) decreases by 11%).
Metabolism
Sildenafil is metabolized primarily in the liver by the cytochrome isoenzyme SURSA4 (major pathway) and the cytochrome isoenzyme SUR2C9 (minor pathway). The main circulating active metabolite formed as a result of
Ms-demethylation of sildenafil undergoes further – metabolism.
The selectivity of this metabolite against FDE is comparable with that of sildenafil, and its activity against FDE5 {t uigo is about 50% of the activity of sildenafil. Concentration of the metabolite in plasma of healthy volunteers was about 40% of sildenafil concentration. M-demethyl metabolite undergoes further metabolism; its half-life (T1/2) is about 4 hours.
Elevation
The total clearance of sildenafil is 41 L/hour, and the final T!/? – 3 to 5 hours. After oral administration as well as after intravenous administration sildenafil is excreted as metabolites mainly by the intestine (about 80% of the oral dose) and, to a lesser extent, by the kidneys (about 13% of the oral dose).
Pharmacokinetics in special groups of patients:
Elderly patients
In the elderly (65 years and older), sildenafil clearance is decreased and free sildenafil plasma concentrations are about 40% higher than in younger patients (18-45 years). Age has no clinically significant effect on the incidence of side effects. Renal dysfunction
In mild (creatinine clearance 50-80 ml/min) and moderate (creatinine clearance 30-49 ml/min) renal impairment, the pharmacokinetics of sildenafil after
Single oral administration of 50 mg does not change. In severe renal impairment
The area under the pharmacokinetic, concentration-time curve (APS by 100%) and Csache (88%) is approximately doubled compared to that of normal renal function in patients of the same age group.
Liver function disorders
In patients with cirrhosis (Child-Pugh stages A and B), sildenafil clearance is reduced, resulting in increased APS (84%) and Csache (47%) compared
with those of normal hepatic function in patients of the same age group. The pharmacokinetics of sildenafil in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh stage C) have not been studied.
Indications
Indications
Treatment of erectile dysfunction, characterized by the inability to achieve or maintain a penile erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual intercourse.
Sildenafil is effective only in the presence of sexual stimulation.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Sildenafil is a powerful selective inhibitor of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) – specific phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5).
Mechanism of action.
The implementation of the physiological mechanism of erection is associated with the release of nitric oxide (NO) in the corpus cavernosum during sexual stimulation. This, in turn, leads to an increase in cGMP levels, subsequent relaxation of smooth muscle tissue
Corpus cavernosum and increased blood flow.
Sildenafil does not have a direct relaxing effect on the isolated human corpus cavernosum, but enhances the effect of nitric oxide (NO) through
Inhibition of PDE5, which is responsible for the breakdown of cGMP.
Sildenafil is selective against PDE5 and its activity against PDE5 exceeds that against other known phosphodiesterase isoenzymes: PDE6 – 10 times; PDE1 – more than 80 times; PDE2, PDE4, PDE7-PDE11 – more than 700 times. Sildenafil is 4000 times more selective for PDE5 compared to PDEZ, which is critical since PDEZ is one of the key enzymes
Regulation of myocardial contractility.
A prerequisite for the effectiveness of sildenafil is sexual stimulation. Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of sildenafil in the recommended dose range is linear. Suction
After oral administration, sildenafil is rapidly absorbed. Absolute bioavailability averages about 40% (from 25% to 63%). sildenafil at a concentration of about 1.7 ng/ml (3.5 nM) inhibits human PDE5 activity by 50%. After a single dose of sildenafil 100 mg, the average maximum concentration of free
sildenafil in the blood plasma (Cmax) of men is about 18 ng/ml (38 nM). Us when taking sildenafil orally on an empty stomach is achieved on average within 90 Nri AEk B
combination with fatty foods, the rate of absorption decreases: Stach decreases 66-8 ENTER on
29%, and the time to reach maximum concentration (Tmax) increases by 60 minutes, but the degree of absorption does not change significantly (the area under the pharmacokinetic concentration-time curve (AOC) decreases by 11%).
Metabolism
Sildenafil is metabolized mainly in the liver under the influence of the cytochrome CYP3A4 isoenzyme (major pathway) and the cytochrome CYP2C9 isoenzyme (minor pathway). The main circulating active metabolite resulting from
MN-demethylation of sildenafil undergoes further metabolism.
The selectivity of this metabolite for PDE is comparable to that of sildenafil, and its activity for PDE5 is about 50% of the activity of sildenafil. The concentration of the metabolite in the blood plasma of healthy volunteers was about 40% of the concentration of sildenafil. The M-demethyl metabolite undergoes further metabolism; its half-life (T1/2) is about 4 hours.
Removal
The total clearance of sildenafil is 41 l/hour, and the final T!/? — 3-5 hours. After oral administration, as after intravenous administration, sildenafil is excreted in the form of metabolites, mainly by the intestines (about 80% of the oral dose) and, to a lesser extent, by the kidneys (about 13% of the oral dose).
Pharmacokinetics in special groups of patients:
Elderly patients
In the elderly (65 years and older), the clearance of sildenafil is reduced, and the concentration of free sildenafil in plasma is approximately 40% higher than in young people (18-45 years). Age does not have a clinically significant effect on the incidence of side effects. Renal dysfunction
With mild (creatinine clearance 50-80 ml/min) and moderate (creatinine clearance 30-49 ml/min) renal failure, the pharmacokinetics of sildenafil after
A single oral dose of 50 mg does not change. For severe renal failure
Approximately twofold increase in the area under the pharmacokinetic curve
Concentration-time (APS at 100%) and Cmax (88%) compared with those in normal renal function in patients of the same age group.
Liver dysfunction
In patients with liver cirrhosis (stages A and B according to the Child-Pugh classification), the clearance of sildenafil is reduced, which leads to an increase in APS (84%) and Cmax (47%) compared
with those indicators for normal liver function in patients of the same age group. Pharmacokinetics of sildenafil in patients with severe dysfunction
liver (Child-Pugh stage C) has not been studied.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Sildenafil
Composition
Composition
Tablets 50 mg
Active ingredient:
sildenafil citrate – 70.2 mg (in terms of sildenafil – 50.0 mg).
Excipients:
corn starch – 156.0 mg,
cellulose
Microcrystalline — 74.0 mg,
magnesium stearate – 5.0 mg,
talc – 5.0 mg,
silicon dioxide
Colloidal – 3.0 mg,
sodium carboxymethyl starch – 10.0 mg.
Film coating tyasoa! pink – 10.0 mg:
titanium dioxide – 1.1 mg,
red iron oxide dye – 1.6 mg,
hypromellose – 3.2 mg,
macrogol – 3.7 mg,
talc – 0.4 mg.
Contraindications
Contraindications
1. Hypersensitivity to sildenafil or any other component of the drug. Use in patients receiving continuous or intermittent nitric oxide donors, organic nitrates or nitrites in any form, since sildenafil enhances the hypotensive effect of nitrates (see section “Interaction with other drugs”).
2. Use in patients for whom sexual activity is undesirable (for example, with severe cardiovascular diseases such as severe heart failure, unstable angina).
3. Arterial hypotension (blood pressure less than 90/50 mm Hg).
4. Chronic renal failure of severe severity.
5. A history of cerebrovascular accident or myocardial infarction within the last six months.
6. Severe liver dysfunction.
7. Hereditary degenerative diseases of the retina, including retinitis pigmentosa. Concomitant use of ritonavir.
The safety and effectiveness of sildenafil when used in combination with other drugs for the treatment of erectile dysfunction have not been studied, therefore the use of such
combinations are not recommended (see section “Special instructions”).
According to its registered indication, sildenafil is not intended for use in children
up to 18 years old. According to the registered indication, sildenafil is not intended for
use in women.
With caution
1. Arterial hypertension (BP > 170/100 mm Hg).
2. Heart failure.
3. Life-threatening arrhythmias.
4. Anatomical deformation of the penis (angulation, cavernous fibrosis or Peyronie’s disease) (see section “Special instructions”).
5. Diseases predisposing to the development of priapism (sickle cell anemia, multiple myeloma, leukemia, thrombocythemia) (see section “Special instructions”). Patients with a history of episodes of anterior non-arteritic ischemic optic neuropathy.
6. Diseases accompanied by bleeding.
7. Exacerbation of peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum.
8. Simultaneous use of alpha-blockers.
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
According to its registered indication, the drug is not intended for use in women.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Usually the side effects of sildenafil are mild or moderate
Fixed dose studies have shown that the incidence of some
adverse events increase with increasing dose.
General condition disorders: chest pain, general weakness, irritability,
feeling hot, feeling tired. Allergic reactions: hypersensitivity reactions (including skin rash), Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell’s syndrome). Disorders of the central and peripheral nervous system: drowsiness, stroke, fainting, hypoesthesia, transient ischemic attack, convulsions, incl. recurrent.
Cardiovascular system disorders: tachycardia, increased or decreased blood pressure, myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation, ventricular arrhythmia, unstable angina, hot flashes and palpitations, sudden death. Respiratory disorders: nosebleeds, sinus congestion, tightness in the throat, dry nasal mucosa, swelling of the nasal mucosa.
Digestive system disorders: vomiting, nausea, dry oral mucosa, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, gastroesophageal reflux disease, hypoesthesia of the oral mucosa.
Visual disorders: eye pain, eye redness/scleral injections, conjunctival damage, lacrimal dysfunction, anterior ischemic optic neuropathy, retinal vascular occlusion, visual field defects, photophobia, photopsia, diplopia, glaucoma, decreased visual acuity, myopia, asthenopia, retinal edema, retinal vascular disease, discomfort in eyes, mydriasis, blurred vision, blurred vision, retinal hemorrhage, atherosclerotic retinopathy, eye irritation, eyelid swelling, scleral discoloration.
Hearing disorders: vertigo, tinnitus, deafness, ringing in the ears. Musculoskeletal disorders: myalgia, pain in the extremities.
Reproductive system disorders: prolonged erection and/or priapism, hematospermia and bleeding from the penis.
Disorders of the genitourinary system: hematuria.
Overdose
Overdose
With a single dose of the drug up to 800 mg, adverse events were
comparable to those when taking the drug in lower doses, but were more common.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years.
Do not use after expiration date.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Oxford Laboratories Pvt. Ltd., India
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years. Do not use after the expiration date. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Store out of the reach of children. . |
| Manufacturer | Oxford Laboratories Pvt. Ltd. |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | #Н/Д |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Sealex Sildenafil, 50 mg with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.