No products in the cart.
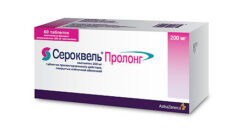
Quetiapine, 300 mg 60 pcs
€82.09 €68.41
Description
Quetiapine is an atypical antipsychotic that has a higher affinity for serotonin (hydroxytryptamine) receptors (5NT2) than for brain dopamine D1 and D2 receptors. Quetiapine also has greater affinity for histamine and alpha1 adrenoreceptors and less affinity for alpha2 adrenoreceptors. No significant affinity of quetiapine for muscarinic and benzodiazepine receptors was found. In standard tests, quetiapine exhibits antipsychotic activity.
Pharmacokinetics
Quetiapine is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is actively metabolized in the liver when administered orally. The major plasma metabolites have no pronounced pharmacological activity.
The bioavailability of quetiapine is not significantly affected by food intake. The T1/2 is about 7 hours. About 83% of quetiapine is bound to plasma proteins.
The pharmacokinetics of vetiapine are linear; there are no differences in pharmacokinetics between men and women.
The average clearance of quetiapine in elderly patients is 30-50% less than in patients aged 18 to 65 years.
The mean plasma clearance of quetiapine is about 25% lower in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m2) and in patients with liver damage, but interindividual clearance rates are within limits consistent with healthy volunteers. Approximately 73% of quetiapine is excreted in the urine and 21% in the feces. Less than 5% of quetiapine is not metabolized and is excreted unchanged by the kidneys or in the feces. CYP3A4 has been found to be a key isoenzyme of cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism of quetiapine.
In a study of the pharmacokinetics of quetiapine at various doses, administration of quetiapine prior to or concomitantly with ketoconazole resulted in an average increase in Cmax and area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) of quetiapine of 235% and 522%, respectively, and a decrease in quetiapine clearance of 84%, on average. The T1/2 of quetiapine increased, but the Tmax was unchanged.
Quetiapine and some of its metabolites have weak inhibitory activity against cytochrome P450 isoenzymes 1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6 and ZA4, but only at concentrations 10-50 times greater than those observed at the commonly used effective dose of 300-450 mg/day.
Based on in vitro results, concomitant use of quetiapine with other drugs should not be expected to result in clinically significant inhibition of cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism of other drugs.
Indications
Indications
Acute and chronic psychoses, including schizophrenia.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Quetiapine is an atypical antipsychotic drug that exhibits a higher affinity for serotonin (hydroxytryptamine) receptors (5HT2) than for dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in the brain. Quetiapine also has a more pronounced affinity for histamine and alpha1-adrenergic receptors and less affinity for alpha2-adrenergic receptors. No significant affinity of quetiapine for muscarinic and benzodiazepine receptors was found. In standard tests, quetiapine exhibits antipsychotic activity.
Pharmacokinetics
When administered orally, quetiapine is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is actively metabolized in the liver. The main metabolites found in plasma do not have pronounced pharmacological activity.
Food intake does not significantly affect the bioavailability of quetiapine. T1/2 is about 7 hours. Approximately 83% of quetiapine is bound to plasma proteins.
The pharmacokinetics of quetiapine is linear; there are no differences in pharmacokinetic parameters between men and women.
The average clearance of quetiapine in elderly patients is 30-50% less than in patients aged 18 to 65 years.
The average plasma clearance of quetiapine is approximately 25% less in patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min/1.73 m2) and in patients with liver damage, but interindividual clearance rates are within the range corresponding to healthy volunteers. Approximately 73% of quetiapine is excreted in urine and 21% in feces. Less than 5% of quetiapine is not metabolized and is excreted unchanged by the kidneys or in feces. It has been established that CYP3A4 is a key isoenzyme in the metabolism of quetiapine, mediated by cytochrome P450.
In a study of the pharmacokinetics of quetiapine at various doses, the use of quetiapine before taking ketoconazole or concomitantly with ketoconazole led to an average increase in Cmax and area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) of quetiapine by 235% and 522%, respectively, and also to a decrease in quetiapine clearance by an average of 84%. T1/2 of quetiapine increased, but Tmax did not change.
Quetiapine and some of its metabolites have weak inhibitory activity against cytochrome P450 isoenzymes 1A2, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6 and 3A4, but only at concentrations 10-50 times higher than those observed at the commonly used effective dose of 300-450 mg/day.
Based on in vitro results, concomitant use of quetiapine with other drugs should not be expected to result in clinically significant inhibition of cytochrome P450-mediated metabolism of other drugs.
Special instructions
Special instructions
There was no relationship between taking quetiapine and an increase in the QTc interval. However, when using quetiapine simultaneously with drugs that prolong the QTc interval, caution must be exercised.
In children, adolescents and young people (under 24 years of age) with depression and other mental disorders, antidepressants, compared with placebo, increase the risk of suicidal thoughts and suicidal behavior. Therefore, when prescribing antidepressants in children, adolescents and young adults (under 24 years of age), the risk of suicide should be weighed against the benefits of their use.
In short-term studies, the risk of suicide did not increase in people over 24 years of age, but it decreased slightly in people over 65 years of age. Any depressive disorder itself increases the risk of suicide. Therefore, during treatment with antidepressants, all patients should be monitored for early detection of disturbances or changes in behavior, as well as suicidality.
During the treatment period, care must be taken when driving vehicles and engaging in other potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Quetiapine
Composition
Composition
Active ingredients:
quetiapine fumarate (quetiapine hemifumarate), in terms of quetiapine 300 mg;
Excipients:
hyprolose (hydroxypropylcellulose Klucel LF),
calcium hydrogen phosphate dihydrate,
pregelatinized starch,
magnesium stearate,
sodium carboxymethyl starch (sodium starch glycolate; Primogel),
microcrystalline cellulose;
Film shell composition:
AquaPolish D 8107 [hypromellose (hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose), glycerol (glycerin), microcrystalline cellulose, talc, kandurin silver luster dye ([potassium aluminum silicate E555, titanium dioxide E171]), aluminum varnish based on indigo carmine dye].
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
The safety and effectiveness of quetiapine in pregnant women have not been established.
Therefore, quetiapine should only be used during pregnancy if the expected benefit justifies the potential risk.
The extent of quetiapine excretion in human milk is not known.
Women should be advised to avoid breastfeeding while taking quetiapine.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the nervous system: drowsiness, dizziness, headache, anxiety, asthenia, hostility, agitation, insomnia, akathisia, tremor, convulsions, depression, paresthesia, neuroleptic malignant syndrome (hyperthermia, muscle rigidity, altered mental status, lability of the autonomic nervous system, increased creatine phosphokinase activity).
From the cardiovascular system: orthostatic hypotension (accompanied by dizziness), tachycardia, fainting, prolongation of the QT interval (no relationship between the use of quetiapine and a constant increase in QTc has been identified).
From the digestive system: dryness of the oral mucosa, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea or constipation, increased activity of liver transaminases.
From the respiratory system: pharyngitis, rhinitis.
Allergic reactions: skin rash, eosinophilia.
Laboratory indicators: leukopenia, hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, decreased thyroxine concentration (first 4 weeks).
Other: lower back pain, chest pain, low-grade fever, weight gain (mainly in the first weeks of treatment), myalgia, dry skin, blurred vision.
Interaction
Interaction
With simultaneous administration of drugs that have a strong inhibitory effect on CYP3A4 (such as azole antifungals and macrolide antibiotics), the plasma concentration of quetiapine may increase.
In such cases, lower doses of quetiapine should be used. Particular attention should be paid to elderly and debilitated patients. It is necessary to assess the risk-benefit ratio individually for each patient.
Inducers of liver microsomal systems (phenytoin, etc.), thioridazine increase the clearance of quetiapine, inhibitors of liver microsomal systems reduce it; at the same time, the simultaneous administration of quetiapine and antidepressants – imipramine (inhibitor of CYP2D6) or fluoxetine (inhibitor of CYP3A4 and CYP2D6) does not have a significant effect on its pharmacokinetics.
The pharmacokinetics of quetiapine does not change significantly when administered concomitantly with the antipsychotic drugs risperidone or haloperidol.
Does not cause induction of liver enzyme systems involved in the metabolism of antipyrine.
The pharmacokinetics of lithium preparations does not change with simultaneous administration of quetiapine.
There were no clinically significant changes in the pharmacokinetics of valproic acid and quetiapine when divalproex sodium (sodium valproate and valproic acid in a 1:1 molar ratio) and Quetiapine were co-administered.
Medicines that depress the central nervous system and ethanol increase the risk of side effects.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
In a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Kanonpharma production CJSC, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Kanonfarma Production ZAO, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Kanonfarma Production ZAO |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Quetiapine, 300 mg 60 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.