No products in the cart.
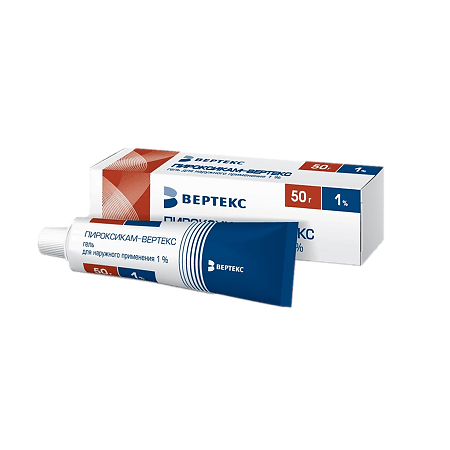
Pyroxicam-Vertex, gel 1% 50 g
€9.92 €8.68
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).
ATX code
M02AA07
Pharmacological properties Pharmacodynamics
Pyroxicam has analgesic, anti-inflammatory and local cooling effects. It inhibits cyclooxygenase type 1 and 2 (COX-1 and COX-2) nonselectively, thus reducing the content of prostaglandins in tissues, which are mediators of inflammation. Pyroxicam reduces pain in joints, muscles, increases range of motion and reduces swelling associated with inflammation.
Pharmacokinetics
Assimilation
When applied externally, piroxicam penetrates through the surface of the skin into the underlying muscles and joint tissues.
Distribution
. When the gel is applied at a daily dose equivalent to 20 mg of oral piroxicam for 14 days, the plasma concentration of the active substance slowly increases and reaches 200 ng/ml on day 4. The equilibrium plasma concentration of piroxicam (Css) is 300-400 ng/ml, which is about 5% of the concentration achieved with piroxicam in appropriate oral dosage forms.
Elimination
The plasma elimination half-life is approximately 50 hours.
Indications
Indications
– sports injuries (bruises, dislocations, sprains, damage to ligaments and muscles);
– osteoarthritis;
– tendonitis;
– tendovaginitis;
– glenohumeral syndrome.
The drug is intended for symptomatic therapy, reducing pain and inflammation at the time of use, and does not affect the progression of the disease.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID).
ATX code
M02AA07
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Piroxicam has analgesic, anti-inflammatory and local cooling effects. Non-selectively inhibits cyclooxygenase types 1 and 2 (COX-1 and COX-2), thereby reducing the content of prostaglandins in tissues, which are mediators of inflammation. Piroxicam reduces joint and muscle pain, increases range of motion and reduces swelling associated with inflammation.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
When applied externally, piroxicam penetrates through the surface of the skin into the underlying muscles and joint tissues.
Distribution
When the gel is applied in a daily dose equivalent to 20 mg of piroxicam for oral administration for 14 days, the concentration of the active substance in the blood plasma slowly increases and reaches 200 ng/ml on day 4. The equilibrium concentration of piroxicam in blood plasma (Css) is 300-400 ng/ml, which is about 5% of the concentration achieved when using piroxicam preparations in appropriate dosage forms orally.
Removal
The half-life from plasma is approximately 50 hours.
Special instructions
Special instructions
Hypersensitivity
Patients with bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or chronic lung infections are more sensitive to the use of NSAIDs. In these patients, attacks of bronchial asthma may become more frequent, Quincke’s edema or urticaria may appear.
Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR)
TCPRs have been reported with systemic administration of piroxicam. These reactions were not associated with topical use of piroxicam, but the possibility of TCPR with topical use of piroxicam cannot be excluded.
Patients should note that in the event of manifestations of TCPR after topical use of piroxicam (such as, for example, a progressive skin rash, often accompanied by vesicles or mucosal lesions), treatment should be discontinued and immediate medical attention should be sought. If a patient develops TCPR after use of piroxicam, treatment with piroxicam for that patient should not be restarted.
Kidney diseases
NSAIDs, including piroxicam, can lead to the development of interstitial nephritis, nephrotic syndrome and renal failure. The development of interstitial nephritis, nephrotic syndrome and renal failure has also been reported after topical use of piroxicam. A cause-and-effect relationship with topical use of piroxicam has not been established, but the possibility of side effects due to topical use of piroxicam cannot be excluded.
Local irritation
If local irritation develops during use of the drug, use of the drug should be discontinued, and appropriate therapy should be prescribed as necessary.
Avoid contact with eyes and mucous surfaces. The gel should not be applied to damaged skin, including open wounds. After application, do not apply an occlusive dressing.
Effect on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery When applied externally, no effect of piroxicam on the ability to perform potentially dangerous activities that require increased concentration of attention and speed of psychomotor reactions (driving vehicles, working with moving mechanisms) was detected.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Piroxicam
Composition
Composition
1 g of gel contains:
Dosage 0.5%
active ingredient: piroxicam – 5.0 mg;
excipients: ethyl alcohol 95% (ethanol 95%) – 200.0 mg; propylene glycol – 150.0 mg; trolamine (triethanolamine) – 16.0 mg; carbomer – 8.4 mg; purified water – up to 1.0 g.
Dosage 1%
active ingredient: piroxicam – 10.0 mg;
excipients: ethyl alcohol 95% (ethanol 95%) – 200.0 mg; propylene glycol – 150.0 mg; trolamine (triethanolamine) – 22.0 mg; carbomer – 8.4 mg; purified water – up to 1.0 g.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
The drug is contraindicated for use during pregnancy. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis may adversely affect pregnancy. Epidemiological studies indicate an increased risk of spontaneous
miscarriage after using prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors in early pregnancy.
In animals, administration of prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors led to an increase in pre- and post-implantation fetal losses.
Breastfeeding period
The drug is contraindicated for use during breastfeeding, as clinical safety has not been established.
Fertility
Based on their mechanism of action, use of NSAIDs, including piroxicam, may delay or prevent ovarian ovulation, which may result in decreased fertility. Women planning pregnancy or undergoing treatment for infertility are not recommended to use the drug.
Contraindications
Contraindications
– hypersensitivity to piroxicam, acetylsalicylic acid, other NSAIDs or other components of the drug;
– complete or incomplete combination of bronchial asthma, recurrent polyposis of the nose and paranasal sinuses and intolerance to acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs (including a history);
– severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min);
– violation of the integrity of the skin at the site of intended application;
– pregnancy;
– period of breastfeeding;
– age under 18 years (due to insufficient data on effectiveness and safety for this group of patients).
With caution
– hepatic porphyria (exacerbation);
– severe dysfunction of the liver and kidneys;
– erosive and ulcerative diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in the acute phase (including peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease);
– bronchial asthma;
– allergic rhinitis;
– chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases or chronic pulmonary infections;
– chronic heart failure;
– blood clotting disorders (including hemophilia, prolongation of bleeding time, bleeding tendency, hemorrhagic diathesis);
– old age.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Immune system disorders:
In predisposed patients, hypersensitivity reactions and angioedema may occur. If hypersensitivity reactions occur (may take the form of skin reactions), use of the drug should be discontinued and appropriate treatment prescribed (see section “Special Instructions”).
Disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissues:
Skin reactions may occur at the application site with symptoms such as skin irritation, erythema, rash, vesicles, peeling and itching at the application site. Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR), such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Contact dermatitis, eczema, and skin photosensitivity have been identified during long-term experience with piroxicam.
Renal and urinary tract disorders:
Isolated cases of tubulointerstitial nephritis, renal failure and nephrotic syndrome have been observed (see section “Special Instructions”).
When piroxicam is applied to large areas of skin, systemic effects are possible. The following side effects have been reported:
Disorders of the respiratory system, chest and mediastinal organs:
Bronchospasm and shortness of breath.
Gastrointestinal disorders:
Nausea, dyspepsia, abdominal pain and gastritis.
Interaction
Interaction
Clinically significant interactions of piroxicam in forms for external use with other drugs have not been described. However, the possibility of enhancing the effect of drugs that cause photosensitivity cannot be ruled out.
Overdose
Overdose
The low systemic absorption of piroxicam when applied topically makes overdose unlikely.
Symptoms
Only if the gel is accidentally ingested or the drug is used in doses higher than recommended, overdose symptoms may develop: burning in the mouth, salivation, nausea, vomiting and the appearance of systemic side effects (headache, nausea, epigastric pain, shortness of breath), interstitial nephritis, renal failure and nephrotic syndrome.
Treatment
It is necessary to rinse the mouth and stomach; if necessary, symptomatic treatment is prescribed. Hemodialysis is ineffective.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years.
Do not use after expiration date.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Vertex, Russia
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years. Do not use after the expiration date. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store at a temperature not higher than 25 ° C. Keep out of the reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Vertex, Russia |
| Medication form | gel for external use |
| Brand | Vertex |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Pyroxicam-Vertex, gel 1% 50 g with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.