No products in the cart.
Proflosin, 0.4 mg 30 pcs
€11.15 €9.29
Description
Pharmacodynamics
Tamsulosin selectively and competitively blocks postsynaptic α1A-adrenoreceptors located in the smooth muscles of the prostate, bladder neck and prostatic urethra. This results in reduction of the tone of the smooth muscles of the prostate, bladder neck and prostatic part of the urethra and improvement of the outflow of urine.
The α-adrenoreceptor blockers can lower blood pressure (BP) by reducing peripheral vascular resistance. However, in clinical trials of tamsulosin, no clinically significant BP reduction has been observed in patients with normal BP levels.
Pharmacokinetics
Intake
After oral administration, tamsulosin is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the GI tract. Absorption of tamsulosin slows down slightly after meals. After a single oral dose of 0.4 mg, maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) of tamsulosin is reached after about 6 hours.
Distribution
The binding to plasma proteins is about 99%, the volume of distribution is small – 0.2 l/kg.
Metabolism
Tamsulosin is not subject to the “first pass” effect and is slowly metabolized in the liver to form less active metabolites. Most of tamsulosin is present in the blood in the unchanged form. The ability of tamsulosin to slightly induce activity of liver microsomal enzymes was revealed in the experiment.
Tamsulosin and its metabolites are excreted mainly in the urine, 9% of the drug is excreted unchanged. The half-life (T1/2) of tamsulosin is approximately 10 hours (when taken once after a meal), with regular use – 13 hours.
Indications
Indications
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (treatment of dysuric disorders).
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacodynamics
Tamsulosin selectively and competitively blocks postsynaptic α1A-adrenergic receptors located in the smooth muscles of the prostate gland, bladder neck and prostatic urethra. This leads to a decrease in the tone of the smooth muscles of the prostate gland, bladder neck, prostatic urethra and improved urine outflow.
α-adrenergic blockers may reduce blood pressure (BP) by reducing peripheral vascular resistance. However, during clinical trials of tamsulosin, in patients with normal blood pressure levels, no clinically significant decrease in blood pressure was observed.
Pharmacokinetics
Suction
After oral administration, tamsulosin is quickly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The absorption of tamsulosin slows down somewhat after eating. After a single oral dose of 0.4 mg, the maximum concentration (Cmax) of tamsulosin in the blood plasma is reached after approximately 6 hours.
Distribution
The connection with blood plasma proteins is about 99%, the volume of distribution is small – 0.2 l/kg.
Metabolism
Tamsulosin does not undergo a first-pass effect and is slowly metabolized in the liver to form less active metabolites. Most tamsulosin is present in the blood in unchanged form. The experiment revealed the ability of tamsulosin to slightly induce the activity of microsomal liver enzymes.
Removal
Tamsulosin and its metabolites are excreted mainly in the urine, 9% of the drug is excreted unchanged. The half-life (T1/2) of tamsulosin is approximately 10 hours (with a single dose after a meal), with regular use – 13 hours.
Special instructions
Special instructions
At the first signs of orthostatic hypotension (dizziness, weakness), the patient should be seated or laid down.
Before starting therapy with Proflosin®, the patient should exclude the presence of diseases and conditions that could cause symptoms similar to those of benign prostatic hyperplasia.
Before starting treatment and regularly during therapy, a digital rectal examination and, if necessary, determination of the concentration of prostate specific antigen (PSA) should be performed.
If angioedema develops, therapy with Proflosin should be stopped immediately. Repeated administration of the drug is contraindicated. During surgery for cataracts while taking the drug, the development of atonic iris syndrome is possible, which must be taken into account by the surgeon for the preoperative preparation of the patient and during the operation.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and other mechanisms that require increased concentration
Care must be taken when driving vehicles and engaging in potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions, due to the fact that dizziness may develop.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Tamsulosin
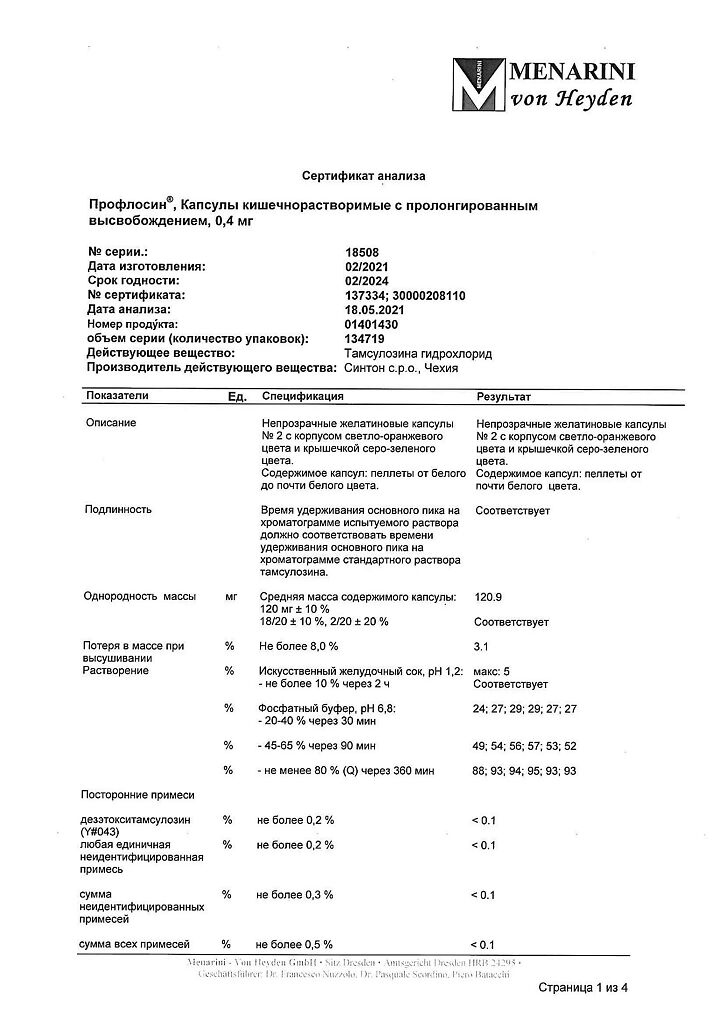
Composition
Composition
Active ingredients:
tamsulosin hydrochloride 400 mcg.
Excipients:
microcrystalline cellulose – 276.9 mg,
copolymer of methacrylic acid and ethyl acrylate (1:1) – 16.5 mg,
triethyl citrate – 1.65 mg, talc – 16.5 mg.
Pellet shell composition:
copolymer of methacrylic acid and ethyl acrylate (1:1) – 21.63 mg,
talc – 8.65 mg,
triethyl citrate – 2.16 mg.
Composition of the capsule body:
red iron oxide dye – 0.0239 mg,
titanium dioxide – 0.53 mg,
iron oxide yellow dye – 0.258 mg,
gelatin – 38.938 mg.
Composition of the capsule cap:
indigo carmine – 0.00152 mg,
iron dye black oxide – 0.0107 mg,
titanium dioxide – 0.356 mg,
iron oxide yellow dye – 0.114 mg,
gelatin – 23.889 mg.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
The drug is prescribed only to men.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to tamsulosin or other components of the drug;
orthostatic hypotension (including history);
severe liver failure.
With caution: chronic renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 10 ml/min); arterial hypotension.
Side Effects
Side Effects
Possible side effects when using the drug are listed below in descending frequency of occurrence:
often (1/100);
uncommon (1/1000);
rarely (1/10000);
very rare (<1/10000), including isolated reports.
Nervous system disorders: often – dizziness; infrequently – headache; rarely – fainting.
Cardiovascular disorders: infrequently – tachycardia, orthostatic hypotension.
Gastrointestinal disorders: uncommon – constipation, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting.
Reproductive system disorders: infrequently – ejaculation disorders; very rarely – priapism.
Disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissues: infrequently – rash, itching, urticaria; rarely – angioedema.
Other: in some cases – development of atonic iris syndrome (narrow pupil syndrome) during cataract surgery, asthenia, rhinitis.
Interaction
Interaction
Tamsulosin does not interact with atenolol, enalapril, nifedipine and theophylline.
When used simultaneously with cimetidine, a slight increase in the concentration of tamsulosin in the blood plasma was observed; with furosemide – a decrease in concentration, but this does not require adjustment of the dose of the drug Proflosin®, since the concentration of the drug remains within the normal range.
Diclofenac and warfarin may increase the elimination rate of tamsulosin.
Concomitant administration of tamsulosin with other α1-adrenergic receptor blockers may lead to a decrease in blood pressure.
Overdose
Overdose
There have been no cases of overdose while taking the drug to date. However, theoretically, there is a possibility of a sharp decrease in blood pressure and tachycardia, which may require appropriate measures.
To restore blood pressure (including orthostatic hypotension) and heart rate to normal values, the patient must be laid down. Hemodialysis is not advisable because tamsulosin has a high affinity for plasma proteins.
To prevent further absorption of tamsulosin, it is advisable to lavage the stomach, take activated charcoal or an osmotic laxative (for example, sodium sulfate).
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C
Shelf life
Shelf life
3 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Sinton Spain S.L., Spain
Additional information
| Shelf life | 3 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C |
| Manufacturer | Sinton Spain S.L., Spain |
| Medication form | enteric capsules |
| Brand | Sinton Spain S.L. |
Related products
Buy Proflosin, 0.4 mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.