No products in the cart.
Pentalgin Neo, 50 mg+220 mg+325 mg 10 pcs.
€7.00 €6.21
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group: combined analgesic (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent + analgesic non-narcotic agent + psychostimulant).
ATX code: N02BE71
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics:
Indications
Indications
Pain syndrome of different genesis:
Pentalgin® NEO is used for symptomatic therapy (decrease in pain and inflammation) and has no effect on the progression of the underlying disease.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Interaction
Interaction
Other NSAIDs, including selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors, corticosteroids: increased risk of gastrointestinal side effects of naproxen.
Propranololol and other beta-adrenoblockers: naproxen may decrease the antihypertensive effect of the drugs. Caffeine may inhibit the therapeutic effects of beta-adrenoblockers.
Heart glycosides: caffeine accelerates absorption and enhances the effect of cardiac glycosides, increases their toxicity.
Diuretics: naproxen may decrease the diuretic effect of diuretics, inhibit the natriuretic effect of furosemide. Diuretics may increase the risk of nephrotoxicity of NSAIDs.
Lithium: naproxen decreases lithium excretion, which leads to increased plasma lithium concentrations.
Myelotoxic drugs: increase hematoxicity of naproxen.
Cyclosporine: increased risk of renal failure.
Probenecid: increases the plasma concentration of naproxen.
Methotrexate, phenethiones, sulfonamides: naproxen slows down their excretion, which increases the risk of their toxic effects.
Antacids containing magnesium and aluminum: decreased absorption of naproxen.
Anticoagulants: naproxen may increase the effect of anticoagulants, paracetamol with long-term use increases the effect of indirect anticoagulants.
Antiplatelet drugs, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors: increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Mifepristone: concomitant administration of NSAIDs for 8-12 days after mifepristone administration is not recommended.
Tacrolimus: concomitant use of NSAIDs increases the risk of nephrotoxicity.
Diflunisal: increased plasma concentrations of paracetamol, which increases the risk of hepatotoxicity.
Hepatic microsomal enzyme inducers: increased hepatotoxic effects of paracetamol may occur.
Hepatic microsomal enzyme inhibitors: decrease the risk of hepatotoxic effects of paracetamol.
Chloramphenicol: paracetamol increases the elimination time of chloramphenicol.
Methoclopramide, domperidone: increase the rate of absorption of paracetamol.
Colestyramine: decrease the rate of absorption of paracetamol.
Theophylline: caffeine decreases the excretion of theophylline.
Barbiturates, primidone, anticonvulsants: may increase metabolism and increase caffeine clearance.
Cimetidine, oral contraceptives, disulfiram, ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin: possible decrease in metabolism of caffeine in the liver (delayed excretion and increased blood concentrations).
Calcium preparations: caffeine decreases their absorption in the gastrointestinal tract.
Drugs and sleeping pills: caffeine decreases their effectiveness.
Alcohol: increased risk of liver damage and acute pancreatitis.
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
General
Do not exceed the doses given in the instructions. To reduce the risk of adverse events, use the lowest effective dose for the shortest possible course.
If pain persists or worsens with therapy, see a physician.
Long-term use of the drug requires monitoring of peripheral blood and liver function.
The drug should not be taken together with other anti-inflammatory and pain medications except when prescribed by a physician.
The drug should be avoided for 48 hours before surgery. If 17-corticosteroid determination is necessary, the drug should be withdrawn 48 hours before the study. Similarly, naproxen may affect the determination of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in urine.
The use of naproxen, as well as other drugs that block the synthesis of prostaglandins, may affect fertility, so it is not recommended for women who plan to become pregnant.
At the time of treatment it is necessary to refrain from drinking alcohol-containing drinks (see section “Drug Interactions”).
When using the drug, consumption of caffeine containing products should be limited, as an excessive intake of caffeine can lead to nervousness, irritability, insomnia, and in some cases, palpitations.
Influence on laboratory values
The use of paracetamol can affect the results of uric acid determination by the phosphoric acid method and glucose oxidase/peroxidase glycemia method.
Caffeine may interfere with the dipyridamole assay; refrain from taking caffeine for 8-12 hours.
Each tablet contains approximately 20 mg of sodium. When restricting salt intake, this should be considered.
Naproxen and caffeine in the drug may affect psychomotor reaction time, therefore caution should be exercised when driving a vehicle and performing tasks requiring increased attention during treatment.
Synopsis
Synopsis
Pentalgin Neo is a new combined analgesic for modern and active people, which has a faster (due to naroxen salt compared to naproxen containing drugs) analgesic effect. Compared to naproxen monodrug and a combination of paracetamol and caffeine and a dual mechanism of pain control.
Pentalgin Neo has an anti-inflammatory effect directly at the site of pain and activates a person’s own analgesic system in the brain. Due to naproxen salt contained in it Pentalgin Neo enters the bloodstream more quickly. Due to its combined composition Pentalgin Neo has a pronounced analgesic effect.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Side effects
Side effects
Unwanted effects that may develop during treatment with Pentalgin® NEO are classified according to the following frequency of occurrence:
Very common (> 1/10), common (â¥1/100 to < 1/10), infrequent (â¥1/1,000 to < 1/100), rare (â¥1/10,000 to < 1/1,000), very rare (< 1/10,000), frequency unknown (cannot be determined based on available data).
Blood and lymphatic system disorders:
infrequent: eosinophilia, granulocytopenia, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia; very rare: methemoglobinemia, hemolytic anemia.
Nervous system disorders:
often: headache, vertigo, dizziness, somnolence; infrequent: tremor, paresthesias, headache, depression, sleep disorders, attention deficit, insomnia, malaise.
Mental disorders:
often: nervousness; infrequently: insomnia; rarely: anxiety, euphoric mood, inner tension.
Visual disorders:
often: visual disturbances.
Hearing and labyrinth disorders:
often: tinnitus, hearing impairment; infrequent: decreased hearing.
Heart disorders:
often: swelling, palpitations; infrequent: congestive heart failure, tachycardia, arrhythmia; frequency unknown – increase in blood pressure.
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders:
often: dyspnea; infrequent: eosinophilic pneumonia; very rare: bronchospasm (in patients with hypersensitivity to acetylsalicylic acid and other NSAIDs).
Gastrointestinal disorders:
often: constipation, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, nausea, diarrhea, stomatitis, flatulence; infrequent: gastrointestinal bleeding and/or gastric perforation, bloody vomiting, melena, vomiting; dry mouth; very rare: recurrence or exacerbation of ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease; frequency unknown: gastritis.
Liver and biliary tract disorders:
infrequent: increased activity of “liver” enzymes, jaundice; very rare: impaired liver function.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders:
often: skin itching, skin rash, ecchymoses, purpura; infrequent: alopecia, photodermatosis; very rare: bullous reactions, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Muscular and connective tissue disorders:
infrequent: myalgia and muscle weakness.
Renal and urinary tract disorders:
infrequent: glomerulonephritis, hematuria, interstitial nephritis, nephrotic syndrome, renal failure, renal papillary necrosis.
General disorders and disorders at the site of administration:
often: thirst, increased sweating; infrequently: hypersensitivity reactions, menstrual disorders, hyperthermia (chills and fever).
There are no data about intensification or expansion of the spectrum of adverse effects of the individual components when using them in combination in accordance with the instructions for medical use.
In case of side effects, consult a physician.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms: Drowsiness, dyspeptic disorders (heartburn, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain), headache, tinnitus, weakness, sweating, pale skin, anxiety, agitation, motor anxiety, anorexia, confusion, tachycardia, arrhythmia, hyperthermia, tremor or muscle twitching; in severe cases – bloody vomiting, melena, impaired consciousness, seizures, renal and/or liver failure.
If overdose of the drug is suspected, it is necessary to seek medical attention immediately.
Treatment. The sufferer should perform gastric lavage and prescribe enterosorbents (activated charcoal). The need for additional therapeutic measures is determined according to the severity of the condition and the severity of intoxication symptoms.
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
Additional information
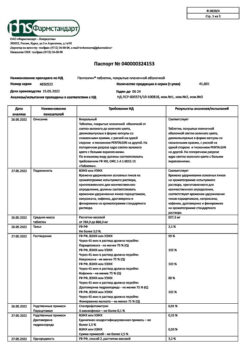
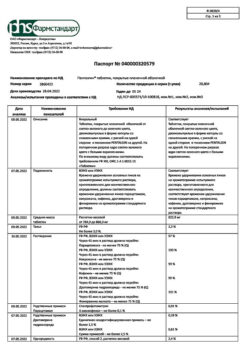
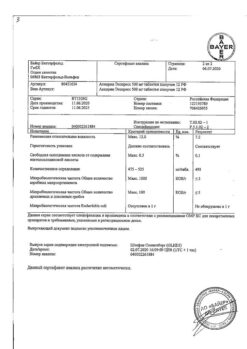
| Shelf life | 2 years. Do not use after the expiration date stated on the package. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | Store in a dry place at a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C in the original package (blister in the package). Keep out of reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Pharmstandard-Leksredstva, Russia |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | Pharmstandard-Leksredstva |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Pentalgin Neo, 50 mg+220 mg+325 mg 10 pcs. with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.