No products in the cart.
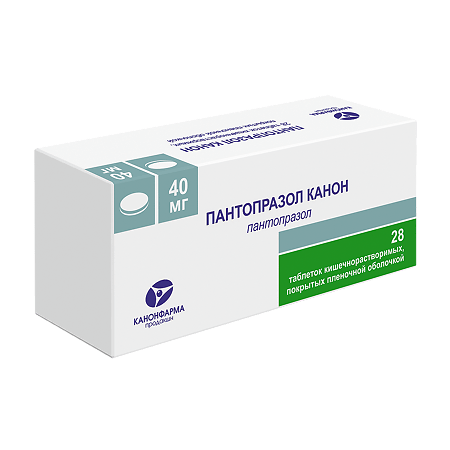
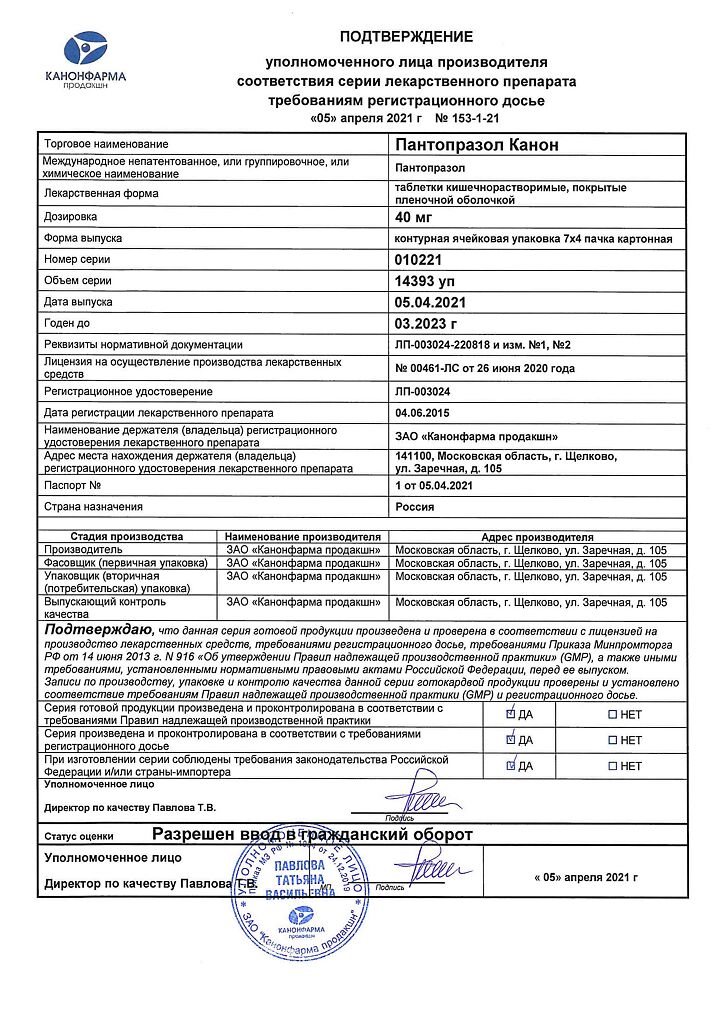
Pantoprazole Canon, 40 mg 28 pcs
€1.00
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
EAN: 4606486023616
SKU: 251865
Categories: Medicine, Stomach, intestines, liver, Ulcer and gastritis
Description
Pharmacotherapeutic group:
A gastric gland secretion reducing agent – proton pump inhibitor.
ATC code: A02BC02
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Proton pump inhibitor (H+/K+-ATPase). Blocks the final stage of hydrochloric acid secretion, reducing basal and stimulated secretion regardless of the nature of the stimulus.
Antisecretory activity
After oral administration of Pantoprazole Canon, the antisecretory effect occurs in 1 hour and reaches a maximum in 2-4 hours. In duodenal ulcer associated with Helicobacter pylori, decreased gastric secretion increases the sensitivity of microorganisms to antibiotics. It does not affect the motility of the gastrointestinal tract. The secretory activity is normalized in 3-4 days after the end of intake.
In comparison with other proton pump inhibitors, pantoprazole has greater chemical stability at neutral pH and less potential for interaction with the cytochrome P450-dependent liver oxidase system. Therefore, pantoprazole does not interact with many other common drugs.
Pharmacokinetics
Intake
Pantoprazole is rapidly absorbed after oral administration. The maximum plasma concentration (Cmax) with oral administration is reached after the first dose of 20 mg or 40 mg. On average, Cmax equal to 1.0 – 1.5 mcg/ml is reached after 2-2.5 hours for 20 mg dose, and 2.0 – 3.0 mcg/ml – after 2.5 hours for 40 mg dose. This indicator remains constant after repeated administration of the drug. Absolute bioavailability is 77 %. Concomitant use of pantoprazole with food does not affect the area under the pharmacokinetic curve “concentration-time” (AUC) and Cmax.
Distribution
The binding to plasma proteins is 98%. The volume of distribution is 0.15 l/kg, clearance – 0.1 l/h/kg.
Metabolism
Metabolized in the liver. The main metabolite in blood plasma and urine is desmethylpantoprazole, which conjugates with sulfate.
The elimination half-life (T½) of pantoprazole is 1 h, the metabolite 1.5 h. The main route of excretion is through the kidneys (about 80%) as pantoprazole metabolites, a small amount is excreted through the intestine.
Pharmacokinetics in different groups of patients
Age: Slight increase in AUC and Cmax in the elderly is not clinically significant.
Renal impairment: No dose reduction is required when using pantoprazole in patients with impaired renal function (including patients on hemodialysis). As in healthy patients, the drug is excreted rather quickly and there is no cumulation.
Hepatic failure: In patients with cirrhosis (Child-Pugh grades A and B) the T½ is increased to 3-6 h with pantoprazole 20 mg and to 7-9 h with pantoprazole 40 mg. AUC increases 3-5-fold (for 20 mg dosage) and 5-7-fold (for 40 mg dosage). Cmax is increased 1.3-fold (for 20 mg dose) and 1.5-fold (for 40 mg dose) compared to healthy patients.
Indications
Indications
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Composition
Composition
1 film-coated, enteric-soluble tablet, 40 mg contains:
the active ingredient:
pantoprazole sodium sesquihydrate 45.14 mg, in terms of pantoprazole 40 mg;
excipients:
magnesium hydroxycarbonate heavy 15.06 mg,
macrogol (polyethylene glycol) 2.4 mg,
mannitol 126 mg,
calcium stearate 2.4 mg,
colloidal silicon dioxide 2 mg,
crospovidone 40 mg,
povidone K-30 7 mg;
film coating composition: Opadray clear 4.8 mg (including: Hypromellose (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose) 3.84 mg, macrogol (polyethylene glycol) 0.96 mg), Acryl-Iz green 17.2 mg (including: methacrylic acid and ethyl acrylate copolymer [1:1] 11.352 mg, colloidal silica 0.172 mg, sodium hydrocarbonate 0.172 mg, sodium lauryl sulfate 0.086 mg, iron oxide yellow 0.12 mg, indigo carmine dye 0.138 mg, diamond blue dye 0.052 mg, talc 2.838 mg, titanium dioxide 2.27 mg). Triethylcitrate 2 mg.
.
How to take, the dosage
How to take, the dosage
Ingestion. The tablet should be swallowed whole without chewing or breaking, washed down with a small amount of liquid, before meals, usually before breakfast. If taken twice, a second dose should be taken before dinner.
Peptic ulcer disease of the stomach and duodenum, erosive gastritis (including those associated with taking NSAIDs)
The recommended dose is 40-80 mg per day. The course of treatment is 2 weeks in case of exacerbation of duodenal ulcer and 4-8 weeks in case of exacerbation of peptic ulcer.
Antiretroviral treatment of peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum – 20 mg/day.
Eradication of Helicobacter pylori
The following combinations are used as triple therapy:
1. Pantoprazole Canon 20-40 mg 2 times a day + amoxicillin 1000 mg 2 times a day + clarithromycin 500 mg 2 times a day. The course of treatment is 7-14 days.
2. Pantoprazole Canon 20-40 mg 2 times a day + metronidazole 500 mg 2 times a day + clarithromycin 500 mg 2 times a day. The course of treatment is 7-14 days.
3. pantoprazole Canon 20-40 mg 2 times a day + amoxicillin 1000 mg 2 times a day + metronidazole 500 mg 2 times a day. The course of treatment is 7-14 days.
After the end of combined therapy, Pantoprazole Canon may be continued for ulcer healing. In duodenal ulcer the use of Pantoprazole Canon may be prolonged from 1 to 3 weeks.
Patients with severe renal dysfunction (creatinine Cl<20 ml/min) or those undergoing hemodialysis should not be prescribed eradication therapy for Helicobacter pylori.
Treatment of mild symptoms of GERD (such as heartburn, nausea, acid reflux)
The recommended dose of the drug is 20 mg/day. It may be necessary to take the drug for 2-3 days to achieve positive dynamics in elimination of symptoms; however, it may be necessary to take the drug for 7 days for complete elimination of symptoms. If the condition worsens during the first 3 days of treatment, it is recommended to consult a specialist. The drug should be discontinued as soon as the symptoms disappear.
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
The recommended dose is 40-80 mg per day. In patients with significant liver dysfunction the dose should be reduced to 40 mg once every 2 days. In this case it is necessary to monitor the biochemical blood parameters. In case of increased liver enzymes activity the drug should be discontinued.
Elderly patients
Dose adjustment is not required. However, elderly patients should not exceed the daily dose of 40 mg. The exception is the use of combined antimicrobial therapy against Helicobacter pylori, when also elderly patients should use Pantoprazole Canon 40 mg 2 times daily.
Patients with renal impairment
Patients with severe renal impairment (Cl creatinine <20 ml/min) or those on hemodialysis should not exceed the daily dose of 40 mg. For this reason, eradication therapy of Helicobacter pylori is not indicated in these patients.
Pantoprazole Canon should not be taken for prophylaxis.
Interaction
Interaction
Simultaneous use of pantoprazole may reduce absorption of drugs whose bioavailability depends on the pH of the stomach (e.g., iron salts, ketoconazole, atazanavir).
The absorption of ritonavir is also known to be pH dependent. Therefore, pantoprazole should be used with ritonavir with caution because of the possible decrease in bioavailability of ritonavir.
Pantoprazole, unlike other proton pump inhibitors, can be prescribed without risk of drug interaction:
Special Instructions
Special Instructions
Pantoprazole Canon should be regularly monitored in patients with severe hepatic impairment, especially with long-term use. In case of increased plasma transaminase activity, treatment with the drug should be discontinued.
In patients with increased risk of gastrointestinal tract complications and who receive nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for a long time, the preparation Pantoprazole Canon in dose of 20 mg for prophylaxis of gastric and duodenal ulcer must be used with caution.
Pantoprazole Canon should be used with caution in elderly patients (over 65 years) with a history of gastric or duodenal ulcer or bleeding from the upper gastrointestinal tract.
Before and after treatment, endoscopic control is mandatory to rule out the possibility of malignant diseases of the stomach and esophagus, since treatment with the drug.
Pantoprazole Canon may mask symptoms and make correct diagnosis difficult.
Lowering gastric acidity increases the number of bacteria in the stomach, leading to gastrointestinal tract infections caused by Salmonella spp, and Campylobacter spp. Pantoprazole decreases vitamin B12 absorption due to hypo- and achlorhydria. This should be considered during long-term therapy in patients with low body weight or with an increased risk of reduced absorption of vitamin B12. Patients in whom treatment has had no effect within 4 weeks should be evaluated.
Patients on long-term use of Pantoprazole Canon require regular medical monitoring.
Impact on ability to drive vehicles and engage in other potentially dangerous activities
Patient should note that during treatment dizziness may occur, therefore caution should be exercised when driving motor vehicles and engaging in other potentially dangerous activities requiring increased concentration and quick psychomotor reactions.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Side effects
Side effects
Overdose
Overdose
Pregnancy use
Pregnancy use
Similarities
Similarities
Additional information
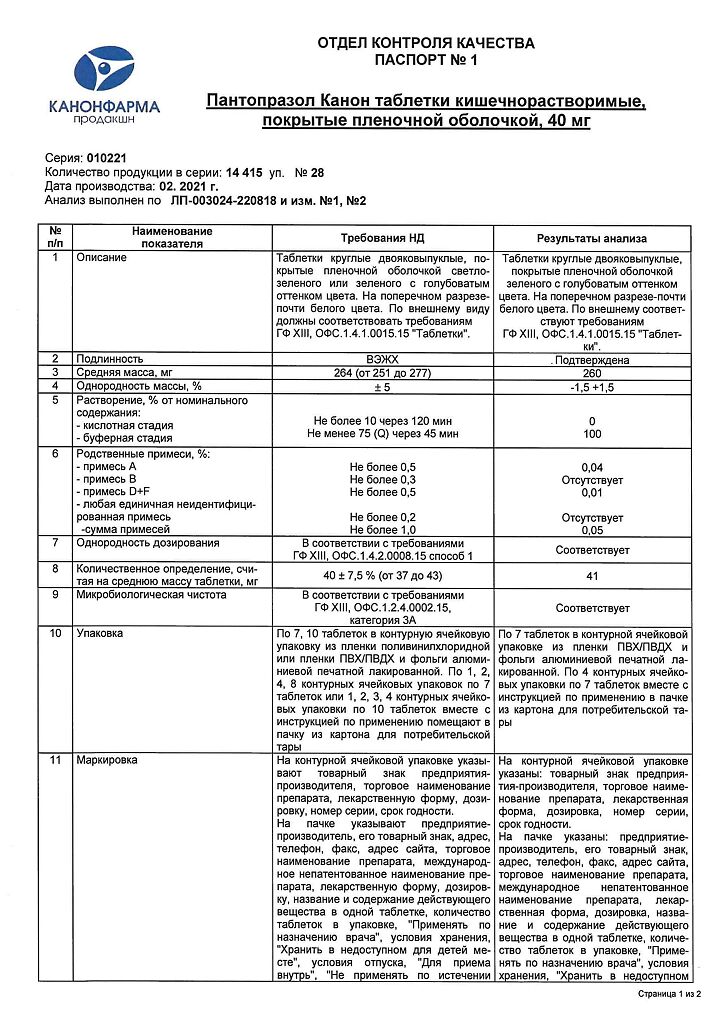
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | In a dry, light-protected place at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Store out of the reach of children. |
| Manufacturer | Kanonfarma Production ZAO, Russia |
| Medication form | enteric soluble tablets |
| Brand | Kanonfarma Production ZAO |
Other forms…
Related products
Buy Pantoprazole Canon, 40 mg 28 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.