No products in the cart.
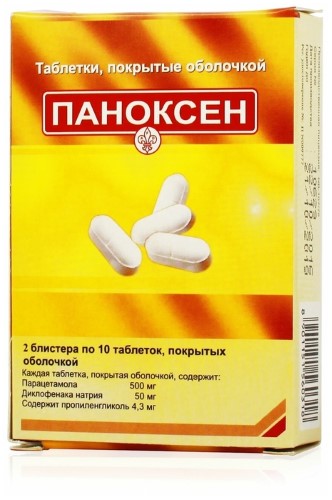
Panoxen, 50 mg+500 mg 20 pcs
€9.93 €8.27
Description
Panoxen is a combined analgesic drug, the effect of which is due to its constituent components.
Diclofenac is a derivative of phenylacetic acid, has anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antipyretic, antiaggregant effect. By inhibiting COX-1 and COX-2 it disrupts arachidonic acid metabolism, decreases quantity of prostaglandins both in inflammation focus and healthy tissues, inhibits exudative and proliferative phases of inflammation.
Paracetamol is aniline derivative, it inhibits COX mainly in CNS, has little effect on water-salt metabolism and gastrointestinal mucosa. In inflamed tissues peroxidases neutralize the effect of paracetamol on COX-1 and COX-2, which explains the almost complete lack of anti-inflammatory effect
Pharmacokinetics
Diclofenac
Absorption
Absorption is rapid and complete; food slows the rate of absorption. After oral administration of 50 mg, Cmax in plasma is 1.5 mcg/ml, Tmax in plasma is 2-3 hours. Plasma concentrations are linearly related to the dose. Bioavailability is 50%. AUC is 2 times less after oral administration than after parenteral administration in the same dose.
Distribution
The binding to plasma proteins is more than 99% (most is bound to albumin).
It penetrates synovial fluid; Cmax in synovial fluid is reached 2-4 h later than in plasma. T1/2 from synovial fluid is 3-6 h (diclofenac concentrations in synovial fluid are higher in 4-6 h after dosing than in plasma and remain high for 12 h).
There is no change in pharmacokinetics of diclofenac on repeated use. It does not cumulate if the recommended interval between meals is observed.
It penetrates into the breast milk.
Metabolism
About 50% of diclofenac is metabolized during “first passage” through the liver. Metabolism occurs as a result of multiple or single hydroxylation and subsequent conjugation with glucuronic acid. The CYP2C9 isoenzyme is also involved in the metabolism of diclofenac. The pharmacological activity of the metabolites is less than that of diclofenac.
The systemic clearance is 260 ml/min. T1/2 from plasma is 1-2 hours. 60% of the administered dose is excreted as metabolites by the kidneys; less than 1% is excreted unchanged, the rest of the dose is excreted as metabolites in the bile.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical cases
In patients with severe renal failure (CKR less than 10 ml/min) excretion of metabolites in bile is increased, while there is no increase of their concentration in blood.
In patients with chronic hepatitis or compensated liver cirrhosis pharmacokinetic parameters do not change.
Paracetamol
Intake and distribution
Absorption is high. Cmax in blood plasma is 5-20 mcg/ml, Tmax is 0.5-2 hours.
The binding to plasma proteins is 15%.
It penetrates through the GEB.
Less than 1% of the dose of paracetamol taken by a nursing mother will penetrate into breast milk.
Metabolism
It is metabolized in the liver by three main pathways: conjugation with glucuronides, conjugation with sulfates, and oxidation by hepatic microsomal enzymes. In the latter case toxic intermediate metabolites are formed, which subsequently conjugate with glutathione and then with cysteine and mercapturic acid. The main cytochrome P450 isoenzymes for this metabolic pathway are CYP2E1 (predominantly), CYP1A2 and CYP3A4 (secondary role). When deficient in glutathione, these metabolites can cause damage and necrosis of hepatocytes.
Additional metabolic pathways are hydroxylation to 3-hydroxyparacetamol and methoxylation to 3-methoxyparacetamol, which are subsequently conjugated to glucuronides or sulfates. In adults, glucuronidation predominates; in newborns (including premature infants) and young children, sulfation predominates. Conjugated metabolites of paracetamol (glucuronides, sulfates and conjugates with glutathione) have low pharmacological (including toxic) activity.
The T1/2 is 1-4 hours. It is excreted by the kidneys as metabolites, mainly conjugates, only 3% unchanged.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical cases
In elderly patients, paracetamol clearance is decreased and T1/2 is increased.
Indications
Indications
to reduce pain and inflammation at the time of use in inflammatory diseases of the musculoskeletal system (rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic, juvenile and chronic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, acute gouty arthritis);
degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system (deforming osteoarthritis, osteochondrosis);
lumbago, sciatica, neuralgia, myalgia;
diseases of periarticular tissues (tenosynovitis, bursitis);
post-traumatic pain syndromes accompanied by inflammation;
toothache.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Panoxen is a combined analgesic drug, the effect of which is determined by the components included in its composition.
Diclofenac is a phenylacetic acid derivative that has anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antipyretic, and antiplatelet effects. By inhibiting COX-1 and COX-2, it disrupts the metabolism of arachidonic acid, reduces the amount of prostaglandins both at the site of inflammation and in healthy tissues, and suppresses the exudative and proliferative phases of inflammation.
Paracetamol is an aniline derivative that inhibits COX mainly in the central nervous system and has little effect on water-salt metabolism and the gastrointestinal mucosa. In inflamed tissues, peroxidases neutralize the effect of paracetamol on COX-1 and COX-2, which explains the almost complete absence of anti-inflammatory effect
Pharmacokinetics
Diclofenac
Suction
Absorption is rapid and complete; food slows down the rate of absorption. After oral administration of 50 mg, Cmax in plasma is 1.5 mcg/ml, Tmax in plasma is 2-3 hours. Plasma concentration is linearly dependent on dose. Bioavailability is 50%. AUC is 2 times less after oral administration than after parenteral administration at the same dose.
Distribution
Plasma protein binding is more than 99% (most of it is bound to albumin).
Penetrates synovial fluid; Cmax in synovial fluid is reached 2-4 hours later than in plasma. T1/2 from synovial fluid is 3-6 hours (concentrations of diclofenac in synovial fluid 4-6 hours after its administration are higher than in plasma, and remain higher for another 12 hours).
There are no changes in the pharmacokinetics of diclofenac due to repeated use. Does not accumulate if the recommended interval between meals is observed.
Passes into breast milk.
Metabolism
About 50% of diclofenac is metabolized during the first pass through the liver. Metabolism occurs as a result of multiple or single hydroxylation and subsequent conjugation with glucuronic acid. The CYP2C9 isoenzyme is also involved in the metabolism of diclofenac. The pharmacological activity of the metabolites is less than that of diclofenac.
Removal
Systemic clearance is 260 ml/min. T1/2 from plasma – 1-2 hours. 60% of the dose taken is excreted in the form of metabolites by the kidneys; less than 1% is excreted unchanged, the rest of the dose is excreted as metabolites in the bile.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical situations
In patients with severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 10 ml/min), the excretion of metabolites in bile increases, but no increase in their concentration in the blood is observed.
In patients with chronic hepatitis or compensated liver cirrhosis, pharmacokinetic parameters do not change.
Paracetamol
Suction and distribution
Absorption is high. Cmax in blood plasma is 5-20 mcg/ml, Tmax is 0.5-2 hours.
Plasma protein binding – 15%.
Penetrates through the BBB.
Less than 1% of the dose of paracetamol taken by a nursing mother passes into breast milk.
Metabolism
Metabolized in the liver in three main ways: conjugation with glucuronides, conjugation with sulfates, oxidation by microsomal liver enzymes. In the latter case, toxic intermediate metabolites are formed, which are subsequently conjugated with glutathione, and then with cysteine and mercapturic acid. The main cytochrome P450 isoenzymes for this metabolic pathway are the CYP2E1 isoenzyme (mainly), CYP1A2 and CYP3A4 (minor role). With glutathione deficiency, these metabolites can cause damage and necrosis of hepatocytes.
Additional metabolic pathways include hydroxylation to 3-hydroxyparacetamol and methoxylation to 3-methoxyparacetamol, which are subsequently conjugated to glucuronides or sulfates. In adults, glucuronidation predominates, in newborns (including premature babies) and young children – sulfation. Conjugated metabolites of paracetamol (glucuronides, sulfates and conjugates with glutathione) have low pharmacological (including toxic) activity.
Removal
T1/2 is 1-4 hours. It is excreted by the kidneys in the form of metabolites, mainly conjugates, only 3% unchanged.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical situations
In elderly patients, paracetamol clearance decreases and T1/2 increases.
Special instructions
Special instructions
To reduce the risk of developing adverse events from the gastrointestinal tract, the drug should be used in the minimum effective dose for the shortest possible short course.
Because of the important role of prostaglandins in maintaining renal blood flow, special caution should be exercised when prescribing to patients with heart or renal failure, as well as when treating elderly patients receiving diuretics, and patients who, for any reason, have a decrease in blood volume (for example, after major surgery). When prescribing Panoxen in such cases, it is recommended to monitor renal function as a precaution.
In order to quickly achieve the desired therapeutic effect, the drug is taken 30 minutes before meals. In other cases, take before, during or after meals, unchewed, with a sufficient amount of water.
In patients with liver failure (chronic hepatitis, compensated cirrhosis of the liver), the kinetics and metabolism do not differ from similar processes in patients with normal liver function.
The use of the drug distorts the results of laboratory tests when quantitatively determining the content of glucose and uric acid in plasma.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
Care must be taken when driving vehicles and other activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Diclofenac, Paracetamol
Composition
Composition
Active ingredients:
paracetamol 500 mg,
diclofenac sodium 50 mg;
Excipients:
corn starch – 290 mg,
cellacephate (cellulose acetylphthalyl) – 15 mg,
diethyl phthalate – 2.5 mg,
talc – 10 mg,
magnesium stearate – 10 mg,
titanium dioxide – 13 mg,
microcrystalline cellulose – 70 mg,
povidone K-30 – 18 mg,
methylparaben (methyl parahydroxybenzoate) – 17.5 mg,
propylparaben (propyl parahydroxybenzoate) – 4 mg.
Shell composition:
tablet coating TS 1005 (white) – 28.5 mg (hypromellose – 5.5 mg, propylene glycol – 4.3 mg, talc – 10.8 mg, titanium dioxide – 7.98 mg).
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
Contraindicated for children under 12 years of age.
The safety of the drug during pregnancy and breastfeeding has not been established, therefore the use of this drug is contraindicated in this category of patients.
Contraindications
Contraindications
complete or incomplete combination of bronchial asthma, recurrent polyposis of the nose and paranasal sinuses and intolerance to acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs (including a history);
erosive and ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract (including the duodenum);
active gastrointestinal bleeding;
inflammatory bowel diseases;
severe liver failure;
severe heart failure;
period after coronary artery bypass surgery;
severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min);
progressive kidney disease;
active liver disease;
hyperkalemia;
pregnancy;
lactation period (breastfeeding);
childhood;
hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
hypersensitivity to other derivatives of phenylacetic acid or aniline.
With caution: peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum (in remission or in history), ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease, history of liver disease, hepatic porphyria, benign hyperbilirubinemia (including Gilbert’s syndrome), viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver damage, mild or moderate chronic heart failure, arterial hypertension, significant decrease in blood volume (including after extensive surgical intervention), bronchial asthma, coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular diseases, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, peripheral arterial diseases, smoking, chronic renal failure (creatinine clearance 30-60 ml/min), Helicobacter pylori infection, long-term use of NSAIDs, alcoholism, severe somatic diseases, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, simultaneous use of corticosteroids, anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, elderly patients.
Side Effects
Side Effects
From the digestive system: epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dyspepsia, flatulence, anorexia, increased activity of hepatic aminotransferases, gastritis, proctitis, bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract (vomiting with blood, melena, diarrhea mixed with blood), ulceration of the gastrointestinal mucosa (with or without bleeding or perforation), hepatitis, jaundice, impaired liver function, stomatitis, glossitis, esophagitis, hemorrhagic colitis, exacerbation of ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease, constipation, pancreatitis, fulminant hepatitis.
From the nervous system: headache, dizziness; drowsiness, sensory disturbances (including paresthesia), memory disorders, tremor, convulsions, anxiety, cerebrovascular disorders, aseptic meningitis, disorientation, depression, insomnia, nightmares, irritability, mental disorders.
From the senses: vertigo, visual impairment (blurred visual perception, diplopia), hearing impairment, tinnitus, impaired taste.
From the urinary system: acute renal failure, hematuria, proteinuria, interstitial nephritis, nephrotic syndrome, papillary necrosis of the kidneys.
From the hematopoietic system: thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, anemia, incl. hemolytic or aplastic, agranulocytosis, methemoglobinemia.
Allergic reactions: urticaria, anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions (including a marked decrease in blood pressure and shock), angioedema (including the face).
From the cardiovascular system: palpitations, chest pain, increased blood pressure, vasculitis, heart failure, myocardial infarction, allergic purpura.
From the respiratory system: bronchial asthma (including shortness of breath), pneumonitis.
From the skin: skin rash (including bullous), erythema, incl. multiforme and Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Lyell’s syndrome, exfoliative dermatitis, itching, hair loss, photosensitivity, purpura.
Other: swelling.
Interaction
Interaction
Diclofenac
Increases the plasma concentration of digoxin, lithium preparations, reduces the effect of diuretics, and against the background of potassium-sparing diuretics, the risk of developing hyperkalemia increases; against the background of anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents and thrombolytics (alteplase, streptokinase, urokinase), the risk of bleeding increases (usually from the gastrointestinal tract).
Reduces the effects of antihypertensive and hypnotic drugs.
Increases the likelihood of side effects of other NSAIDs and corticosteroids (bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract), the toxicity of methotrexate and the nephrotoxicity of cyclosporine (by increasing their concentration in plasma).
Acetylsalicylic acid reduces the concentration of diclofenac in the blood.
Reduces the effect of hypoglycemic drugs.
Paracetamol increases the risk of developing nephrotoxic effects of diclofenac.
Cefamandole, cefoperazone, cefotetan, valproic acid and plicamycin increase the incidence of hypoprothrombinemia.
Cyclosporine and gold preparations increase the effect of diclofenac on the synthesis of prostaglandins in the kidneys, which is manifested by increased nephrotoxicity.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Simultaneous use with ethanol, colchicine, corticotropin and St. John’s wort preparations increases the risk of bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract.
Drugs that cause photosensitivity increase the sensitizing effect of diclofenac to UV radiation.
Agents that block tubular secretion increase the plasma concentration of diclofenac, thereby increasing its effectiveness and toxicity.
Antibacterial agents from the quinolone group increase the risk of developing seizures.
Paracetamol
Reduces the effectiveness of uricosuric drugs.
The simultaneous use of paracetamol in high doses increases the effect of anticoagulants (decreased synthesis of blood coagulation factors in the liver).
Inducers of microsomal liver enzymes (phenytoin, barbiturates, rifampicin, phenylbutazone, tricyclic antidepressants), ethanol and hepatotoxic drugs increase the production of hydroxylated active metabolites, which makes it possible to develop severe intoxications even with a small overdose.
Long-term use of barbiturates reduces the effectiveness of paracetamol.
When taken simultaneously, ethanol promotes the development of acute pancreatitis.
Inhibitors of microsomal liver enzymes (including cimetidine) reduce the risk of hepatotoxicity.
Long-term simultaneous use of paracetamol and NSAIDs increases the risk of developing “analgesic” nephropathy and papillary necrosis of the kidneys, and the onset of terminal renal failure.
Long-term simultaneous use of paracetamol in high doses and salicylates increases the risk of developing kidney or bladder cancer.
Diflunisal increases the plasma concentration of paracetamol by 50%, which increases the risk of hepatotoxicity.
Myelotoxic drugs enhance the hematotoxicity of paracetamol.
Overdose
Overdose
Diclofenac
Symptoms: vomiting, bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract, epigastric pain, diarrhea, dizziness, tinnitus, lethargy, convulsions; rarely – increased blood pressure, acute renal failure, hepatotoxic effect, respiratory depression, coma.
Treatment: gastric lavage, activated charcoal, symptomatic therapy aimed at eliminating increased blood pressure, renal dysfunction, convulsions, gastrointestinal irritation, respiratory depression. Forced diuresis and hemodialysis are ineffective (due to the high degree of binding to plasma proteins and intensive metabolism).
Paracetamol
Symptoms: during the first 24 hours after administration – pallor of the skin, nausea, vomiting, anorexia, abdominal pain; impaired glucose metabolism, metabolic acidosis. Symptoms of liver dysfunction may appear 12-48 hours after an overdose. In case of severe overdose – liver failure with progressive encephalopathy, coma, death; acute renal failure with tubular necrosis (including in the absence of severe liver damage); arrhythmia, pancreatitis. The hepatotoxic effect in adults occurs when taking 4 g or more.
Treatment: administration of SH-group donors and the precursor of glutathione synthesis – methionine within 8-9 hours after an overdose and acetylcysteine - within 8 hours. The need for additional therapeutic measures (further administration of methionine, intravenous administration of acetylcysteine) is determined depending on the concentration of paracetamol in the blood, as well as the time elapsed after its administration.
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C.
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Oxford Laboratories Pvt. Ltd., India
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. |
| Manufacturer | Oxford Laboratories Pvt. Ltd. |
| Medication form | pills |
| Brand | #Н/Д |
Related products
Buy Panoxen, 50 mg+500 mg 20 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.