No products in the cart.
Omez DCP, 30 mg+20 mg 30 pcs
€14.75 €12.29
EAN: 8901148239470
SKU: 294136
Categories: Medicine, Stomach, intestines, liver, Ulcer and gastritis
Description
Sour belching, Bloating, Nausea, Heartburn, Reflux-esophagitis
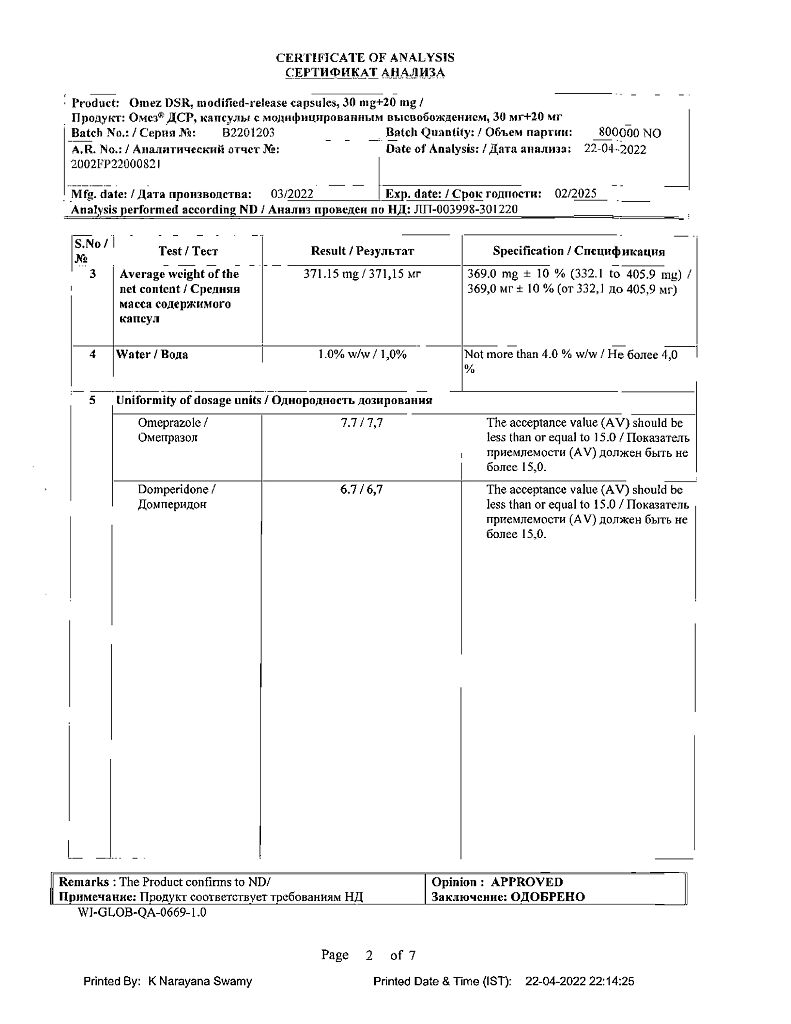
- Dyspepsia, accompanied by delayed gastric emptying, gastroesophageal reflux, esophagitis (feeling of overflow in epigastrium, feeling of bloating, pain in upper abdomen; belching, flatulence; nausea, vomiting; Heartburn with or without gastric contents in the mouth
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- Nausea, vomiting, nauseanausea, vomiting, heartburn associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcer, including after eradication therapy.
.
Indications
Indications
Dyspepsia, accompanied by delayed gastric emptying, gastroesophageal reflux, esophagitis (a feeling of fullness in the epigastrium, a feeling of bloating, pain in the upper abdomen; belching, flatulence; nausea, vomiting; heartburn with or without reflux of gastric contents into the oral cavity);
gastroesophageal reflux disease;
nausea, vomiting, heartburn associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastritis, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, including after eradication therapy.
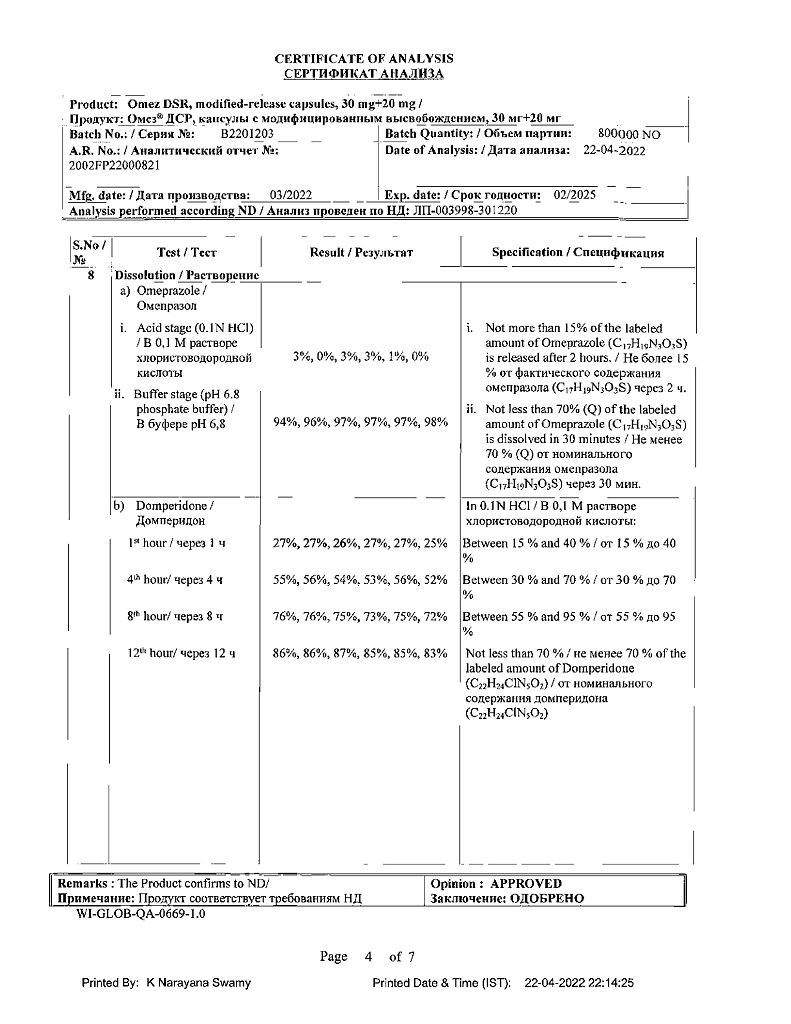
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacological effect
Pharmacodynamics
Special instructions
Special instructions
Lactose
Omeprazole granules contain lactose, so you should not use Omez® DSR in patients with lactose intolerance, galactosemia and impaired absorption of glucose and galactose.
Cardiovascular system
It has been shown that the use of domperidone may be associated with an increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias or sudden coronary death, which is more likely in patients over 60 years of age with a daily dose of domperidone greater than 30 mg. The use of domperidone and other drugs that prolong the QT interval requires caution in patients with existing conduction disturbances due to QT prolongation, severe electrolyte imbalance, or congestive heart failure).
Osteoporosis
Patients at risk of developing osteoporosis or osteoporotic fractures should be under appropriate clinical supervision, although a causal relationship between the use of omeprazole and osteoporotic fractures has not been established.
Hypomagnesemia
There are reports of the occurrence of severe hypomagnesemia in patients receiving therapy with proton pump inhibitors, including omeprazole, for more than one year. Patients receiving omeprazole therapy for a long time, especially in combination with digoxin or other drugs that reduce the level of magnesium in the blood plasma (diuretics), require regular monitoring of magnesium levels.
Active ingredient
Active ingredient
Domperidone, Omeprazole
Composition
Composition
Each capsule contains:
active ingredients:
Pregnancy
Pregnancy
The use of Omez® DSR during pregnancy and breastfeeding is contraindicated.
Contraindications
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to omeprazole, substituted benzimidazoles or other components of the drug.
Sucrase/isomaltase deficiency, fructose intolerance, glucose-galactose malabsorption (due to the presence of sucrose in the drug).
Concomitant use with erlotinib, posaconazole, nelfinavir and atazanavir.
The use of omeprazole in children is contraindicated, except as indicated: gastroesophageal reflux disease for children over 2 years of age and duodenal ulcer caused by Helicobacter pylori for children over 4 years of age (see section “Dosage and Administration”).
Before using the drug, you should consult your doctor in the following cases:
in the presence of previously diagnosed gastric ulcer; severe liver disease accompanied by liver failure; renal failure; jaundice; previous surgical intervention on the gastrointestinal tract;
in the presence of “alarming” symptoms: significant spontaneous loss of body weight, repeated vomiting, vomiting with blood, change in the color of stool (tarry stools – melena), difficulty swallowing;
when new symptoms appear or changes in existing symptoms from the gastrointestinal tract;
when used simultaneously with one or more of the following drugs: clopidogrel, digoxin, ketoconazole, itraconazole, warfarin, cilostazol, diazepam, phenytoin, saquinavir, tacrolimus, clarithromycin, voriconazole, rifampicin, St. John’s wort preparations (see section “Interaction with other drugs”).
Osteoporosis. Although the cause-and-effect relationship of omeprazole use with osteoporotic fractures has not been established, patients at risk of developing osteoporosis or osteoporotic fractures should be under appropriate clinical supervision.
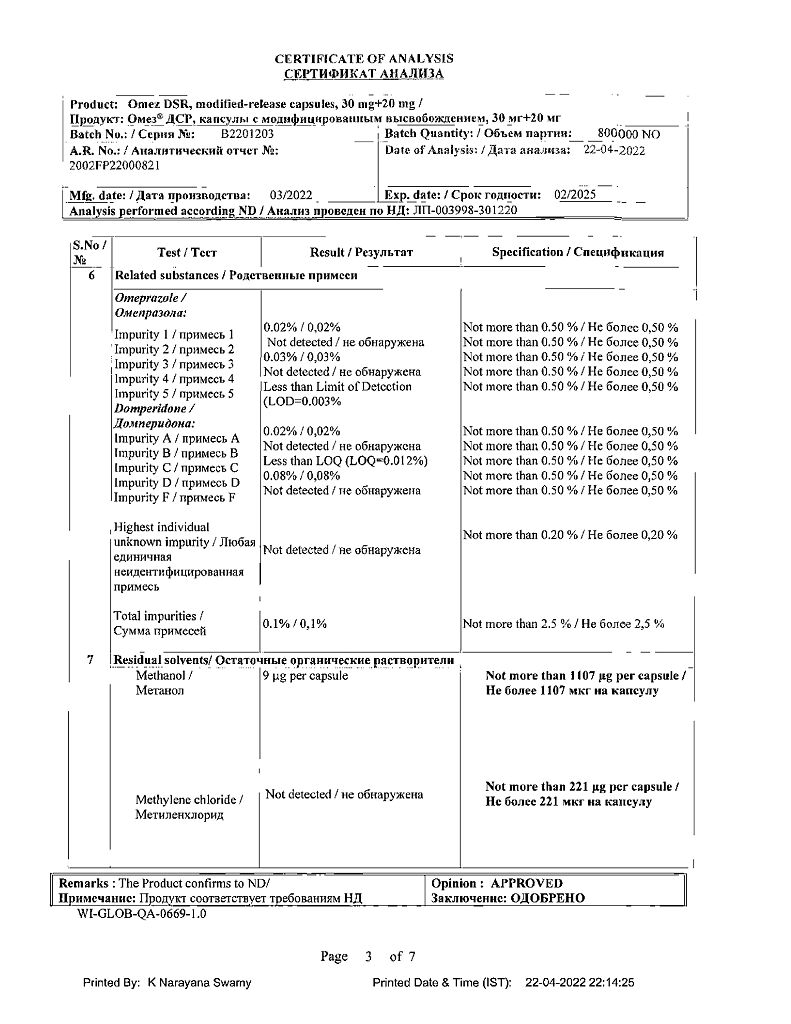
Side Effects
Side Effects
Possible side effects are listed below by body system and frequency of occurrence for omeprazole and domperidone: very common (>1/10); often (≥1/100, <1/10); uncommon (≥1/1000, <1/100); rare (≥1/10000, <1/1000); very rare (<1/10000, including isolated cases and frequency unknown).Blood and lymphatic system disorders
Omeprazole – rarely: leukopenia, thrombocytopenia; very rare: agranulocytosis, pancytopenia, eosinophilia.
Immune system disorders
Omeprazole – rare: hypersensitivity reactions: fever, angioedema, anaphylactic reaction / anaphylactic shock. Domperidone – very rare: anaphylactic reaction/anaphylactic shock, angioedema.
Metabolic and nutritional disorders
Omeprazole – rare: hyponatremia; frequency unknown: hypomagnesemia, which in severe cases can lead to hypocalcemia, hypokalemia.
Mental disorders
Omeprazole – uncommon: insomnia; rarely: increased excitability, depression, reversible confusion; very rarely: aggression, hallucinations. Domperidone – very rarely: agitation, nervousness, increased excitability and irritability.
Nervous system disorders
Omeprazole – often: headache; uncommon: dizziness, paresthesia, drowsiness; rarely: taste disturbance. Domperidone – very rarely: extrapyramidal effects, convulsions, drowsiness, headache.
Visual disorders
Omeprazole – uncommon: visual disturbances, including decreased visual fields, decreased sharpness and clarity of visual perception (usually resolve after cessation of therapy).
Hearing and labyrinth disorders
Omeprazole – uncommon: disturbances in auditory perception, including “ringing in the ears” (usually disappears after stopping therapy), vertigo (a feeling of spinning of one’s own body or surrounding objects).
Cardiovascular system disorders:
Domperidone – very rare: QT prolongation, torsade de pointes (TdP), sudden coronary death (more likely in patients over 60 years of age taking more than 30 mg per day).
Disorders of the respiratory system, chest and mediastinal organs:
Omeprazole – rare: bronchospasm.
Gastrointestinal disorders
Omeprazole – often: abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, flatulence, nausea, vomiting; rarely: dryness of the oral mucosa, stomatitis, gastrointestinal candidiasis, microscopic colitis, discoloration of the tongue to brown-black and the appearance of benign cysts of the salivary glands when used simultaneously with clarithromycin (the phenomena are reversible after cessation of therapy); isolated cases: the formation of gastric glandular cysts during long-term treatment with simultaneous use with clarithromycin (a consequence of inhibition of hydrochloric acid secretion, is benign, reversible).
Disorders of the liver and biliary tract
Omeprazole – uncommon: increased activity of liver enzymes and alkaline phosphatase (reversible); rare: hepatitis (with or without jaundice), liver failure, encephalopathy in patients with pre-existing severe liver disease.
Disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissues
Omeprazole – uncommon: dermatitis, skin itching, skin rash, urticaria; rarely: alopecia, photosensitivity reactions in the form of redness of the skin after ultraviolet irradiation, exudative erythema multiforme, toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome (severe erythema, characterized by the appearance of spots and blisters on the skin and mucous membranes against a background of high fever and joint pain).
Domperidone – very rarely: Quincke’s edema, urticaria.
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Omeprazole – uncommon: fractures of the vertebrae, wrist bones, femoral head associated with osteoporosis; rarely: arthralgia, myalgia, muscle weakness.
Renal and urinary tract disorders
Omeprazole – rare: interstitial nephritis. Domperidone – very rare: urinary retention.
Disorders of the genital organs and breast
Omeprazole – rare: gynecomastia.
General disorders
Omeprazole – uncommon: malaise; rarely: increased sweating, peripheral edema.
Laboratory and instrumental data
Domperidone – very rarely: changes in liver function tests, increased blood prolactin levels.
If side effects occur that are not listed in this instruction, you must immediately inform your doctor.
Interaction
Interaction
Omeprazole: • The possibility of interaction of omeprazole with other drugs is sharply limited. However, since omeprazole slows down the microsomal metabolism of drugs carried out by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system of the liver, the elimination of other drugs requiring the participation of this enzyme system, or high activity of the excretory function of the liver, may be reduced when omeprazole is taken simultaneously.
Overdose
Overdose
Symptoms:
An overdose of domperidone may result in drowsiness, disorientation, and possible extrapyramidal disorders. There is not sufficient information on intentional overdose of omeprazole. Studies using intravenous doses of up to 270 mg per day and up to 650 mg for three days showed that there were no adverse reactions associated with taking the drug.
Treatment:
Storage conditions
Storage conditions
At a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. Keep out of the reach of children!
Shelf life
Shelf life
2 years.
Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Dr. Reddy’s Laboratories Ltd, India
Additional information
| Shelf life | 2 years. |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | At a temperature not exceeding 25 ° C. Keep out of reach of children! |
| Manufacturer | Dr. Reddy's, India |
| Medication form | modified-release capsules |
| Brand | Dr. Reddy's |
Related products
Buy Omez DCP, 30 mg+20 mg 30 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.