Subtotal: €22.15
Nivalin, 1 mg/ml 1 ml 10 pcs
€30.52 €26.45
Out of stock
(E-mail when Stock is available)
Pharmgroup:
Cholinesterase inhibitor.
Pharmic action:
Nivaline is a reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Facilitates the conduction of nerve impulses in the area of neuromuscular synapses, enhances excitation processes in the reflex areas of the spinal cord and brain, penetrates well through the BBB.
It increases tone and stimulates contraction of smooth and skeletal muscles, secretion of digestive and sweat glands, restores neuromuscular conduction blocked by curare-like myorelaxants of non-depolarizing type.
It causes miosis and accommodation spasm, reduces intraocular pressure in closed-angle glaucoma.
Pharmacokinetics:
Intake
After oral administration, it is quickly and completely absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. Absolute bioavailability is high – up to 90%. Therapeutic concentration is reached 30 min after drug administration. Cmax after 10 mg dose is reached by 2 hours and is 1.2 mg/ml.
Distribution
Css of galantamine is established after multiple doses. It is slightly bound to blood proteins. Easily passes through the HEB.
Metabolism
To a negligible extent (about 10%) is metabolized in the liver by demethylation.
Elimination
T1/2 – 5 hours. It is excreted (unchanged and as metabolites) mainly in the urine (up to 74%). Renal clearance is approximately 100 ml/min.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical cases
In patients with Alzheimer’s disease an increase in plasma concentrations of galantamine is possible. In moderate to severe hepatic and renal dysfunction, plasma concentrations of galantamine are increased.
Indications
In neurology:
traumatic damage to the nervous system;
cerebral palsy;
diseases of the spinal cord (myelitis, poliomyelitis, poliomyelitis form of tick-borne encephalitis);
mononeuritis;
polyneuritis;
polyneuropathy;
polyradiculoneuritis;
Guillain-Barre syndrome;
idiopathic facial nerve paresis;
myopathy;
bed-wetting.
In anesthesiology and surgery:
as an antagonist of non-depolarizing muscle relaxants and for the treatment of postoperative atony of the intestine and bladder.
In physiotherapy:
in the form of iontophoresis for diseases of the peripheral nervous system.
In toxicology:
intoxication with anticholinergic drugs, morphine and its analogues.
In radiology:
to improve the quality of functional diagnostics of the digestive system, incl. and gallbladder.
Pharmacological effect
Pharmaceutical group:
cholinesterase inhibitor.
Pharmaceutical action:
Nivalin is a reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. Facilitates the conduction of nerve impulses in the area of neuromuscular synapses, enhances excitation processes in the reflex zones of the spinal cord and brain, and penetrates well through the BBB.
Increases tone and stimulates contraction of smooth and skeletal muscles, secretion of digestive and sweat glands, restores neuromuscular conduction blocked by curare-like muscle relaxants of a non-depolarizing type.
Causes miosis, spasm of accommodation, reduces intraocular pressure in closed-angle glaucoma.
Pharmacokinetics:
Suction
After oral administration, it is quickly and completely absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract. Absolute bioavailability is high – up to 90%. Therapeutic concentration is achieved 30 minutes after taking the drug. Cmax after taking the drug at a dose of 10 mg is reached within 2 hours and is 1.2 mg/ml.
Distribution
After repeated administration, the Css of galantamine is established. Slightly binds to blood proteins. Easily passes through the BBB.
Metabolism
To a small extent (about 10%) is metabolized in the liver by demethylation.
Removal
T1/2 – 5 hours. Excreted (unchanged and in the form of metabolites) mainly in the urine (up to 74%). Renal clearance is approximately 100 ml/min.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical situations
In patients with Alzheimer’s disease, the concentration of galantamine in the blood plasma may be increased. With moderate and severe dysfunction of the liver and kidneys, the concentration of galantamine in the blood plasma increases.
Special instructions
During the treatment period, you must refrain from driving a car or working with complex mechanisms, because the drug may cause blurred vision, dizziness and drowsiness.
Active ingredient
Galantamine
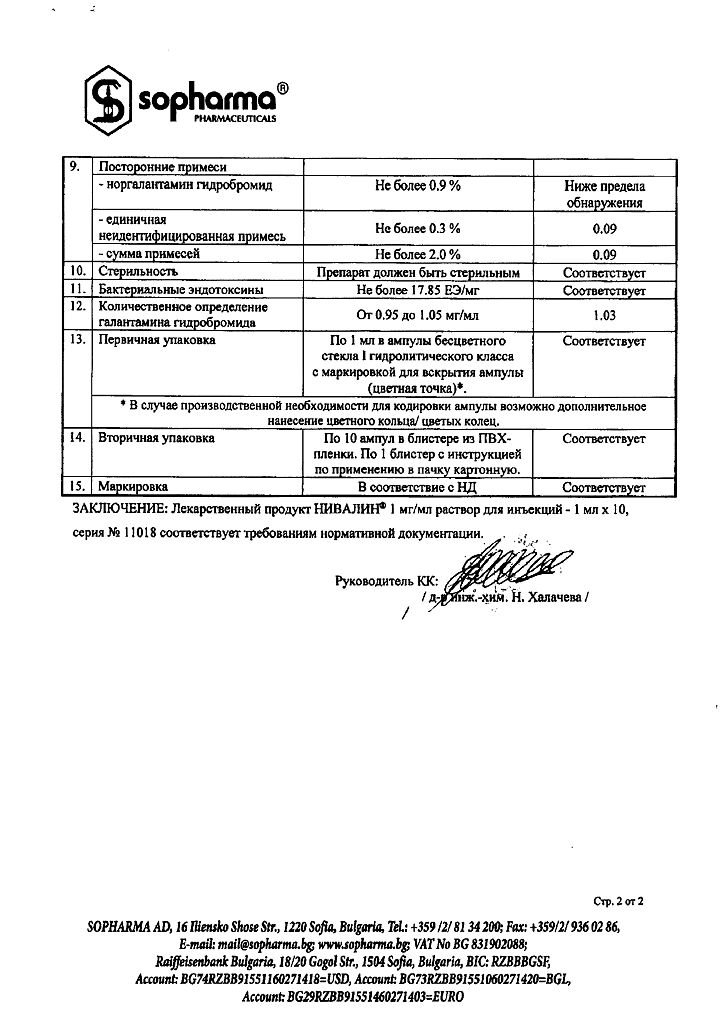
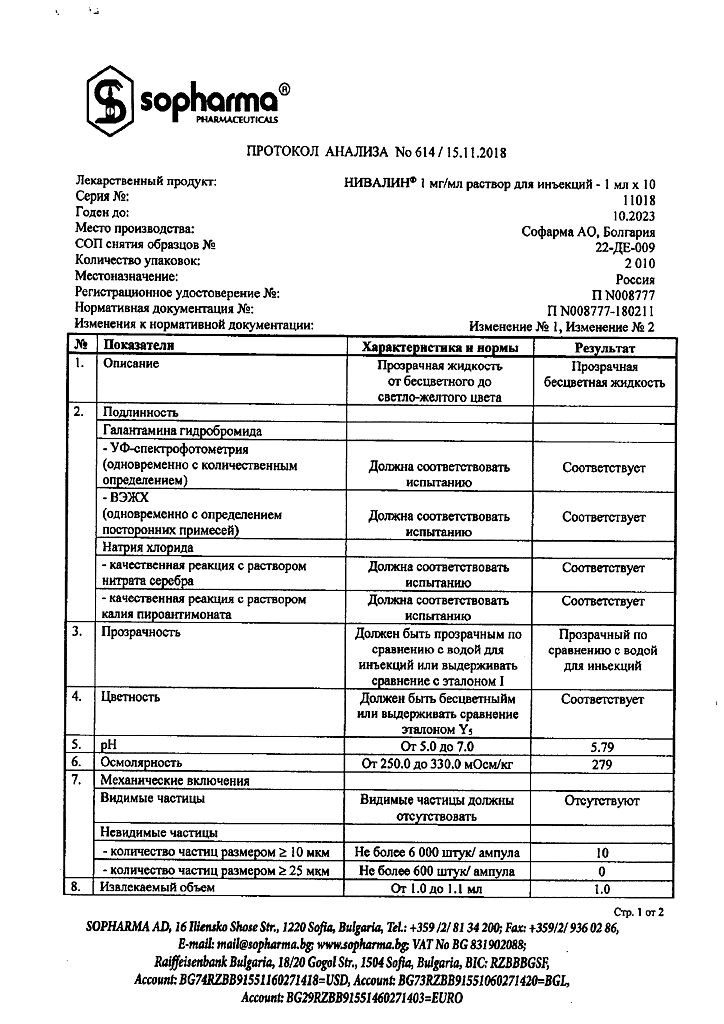
Composition
1 ml of solution contains:
active substance:
galantamine hydrobromide 1 mg
excipients:
sodium chloride;
water for injections
Contraindications
— bronchial asthma;
— bradycardia;
— AV blockade;
– angina pectoris;
— chronic heart failure in the stage of decompensation;
— epilepsy;
– hyperkinesis;
— mechanical intestinal obstruction;
— mechanical disorders of the urinary tract;
– severe liver failure;
– severe renal failure;
– children under 1 year of age;
— pregnancy;
– lactation period;
– hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
The drug is prescribed with caution in case of renal failure, urinary disorders, recent surgery on the prostate gland, or during surgery using general anesthesia.
To improve the quality of X-ray examinations, the drug is not used in children.
Side Effects
From the digestive system: often – nausea, vomiting, cramping abdominal pain, diarrhea, increased salivation, anorexia; rarely – intestinal colic.
From the side of the central nervous system: often – fatigue, dizziness, headache, drowsiness; rarely – insomnia, visual impairment (spasm of accommodation).
Other: increased sweating; rarely – rhinitis, bradycardia, urinary tract infection, bronchospasm, renal colic.
Interaction
Nivalin, when used simultaneously, reduces the inhibitory effect of morphine and its analogues on the respiratory center.
With simultaneous use of Nivalin with m-anticholinergic blockers (atropine), ganglion blockers (hexamethonium, azamethonium bromide, pachycarpine), non-depolarizing muscle relaxants (tubocurarine), quinine and novocainamide, a mutual decrease in effect occurs.
Aminoglycoside antibiotics (gentamicin, amikacin) may reduce the therapeutic effect of Nivalin.
When used simultaneously, it enhances the effect of depolarizing muscle relaxants.
When used concomitantly, cimetidine may increase the bioavailability of galantamine.
CYP2D6 and CYP3D4 are enzymes involved in the metabolism of galantamine. Quinidine, paroxetine, fluoxetine are inhibitors of the CYP2D6 isoenzyme, and the drugs ketoconazole, zidovudine, erythromycin are inhibitors of the CYP3D4 isoenzyme, so they can affect the metabolism of galantamine, which can lead to an increase in its concentration in the blood serum.
Overdose
Symptoms: nausea, vomiting, cramps, diarrhea, decreased blood pressure, bradycardia, bronchospasm; in severe cases – convulsions, coma.
Treatment: carry out symptomatic therapy, monitoring the function of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems. As an antidote – intravenous administration of atropine at a dose of 0.5-1 mg intravenously; the dose can be repeated depending on the clinical picture.
Storage conditions
The drug should be stored in a dry place, protected from light, at a temperature not exceeding 25°C.
Shelf life
5 years
Manufacturer
Sopharma JSC, Bulgaria
| Shelf life | 5 years |
|---|---|
| Conditions of storage | The drug should be stored in a dry place protected from light at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. |
| Manufacturer | Sofarma JSC, Bulgaria |
| Medication form | solution for injection |
| Brand | Sofarma JSC |
Related products
Buy Nivalin, 1 mg/ml 1 ml 10 pcs with delivery to USA, UK, Europe and over 120 other countries.